Android深入理解RemoteViews
1 前言
RemoteViews可以理解为一种远程的View,其实他和远程的Service是一样的,RemoteViews表示的是一种View的结构,他可以在其他的进程中显示,最常用的就是通知栏和桌面小组件。
2 RemoteViews应用
2.1 在通知栏上的应用
2.1.1 什么是通知
通知是在常规UI界面之外向用户展示消息的工具,当系统发出通知时,它会以图表的形式显示在状态栏中。
2.1.2 如何发送一个通知
(1)获取NotificationManager通知管理类;
(2)使用Notification.Builder构建器构建Notification对象,必要属性有三项:①小图标,通过setSmallIcon()方法设置;
②标题,通过setContentTitle()方法设置;③内容,通过setContentText()方法设置;
(3)调用manager.notify()发出通知。
2.1.3 基本的Builder方法
(1)方法介绍
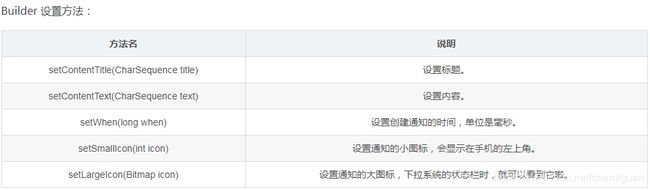
(2)必要属性有三项
①小图标,通过setSmallIcon()方法设置
②标题,通过setContentTitle()方法设置
③内容,通过setContentText()方法设置
(3) 让通知常驻通知栏
//让通知常驻通知栏
builder.setOngoing(true);
Notification n = builder.build();
n.flags = Notification.FLAG_NO_CLEAR;
2.1.5 解决Android 8.0不能弹出通知
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "001";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "my_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
// 是否在桌面icon右上角展示小红点
channel.enableLights(true);
// 小红点颜色
channel.setLightColor(Color.GREEN);
// 是否在久按桌面图标时显示此渠道的通知
channel.setShowBadge(true);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
// Notification.Builder需要多设置一个
builder.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification Android8.0中无法发送通知,提示:No Channel found for pkg
2.1.5 发送默认通知
private void sendDefaultNotification() {
// 1、获取NotificationManager通知管理类
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
// 2、使用Notification.Builder构建器构建Notification对象
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(this);
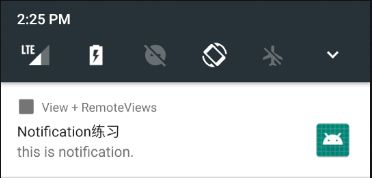
builder.setContentTitle("Notification练习");
builder.setContentText("this is notification.");
builder.setTicker("滚动消息......");
builder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
builder.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.ic_launcher));
builder.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis());
builder.setOngoing(true);
// // 设置通知可以自动取消:builder.setAutoCancel(true)
// notification.flags = Notification.FLAG_AUTO_CANCEL;
// // 让通知常驻通知栏:builder.setOngoing(true)
// notification.flags = Notification.FLAG_NO_CLEAR;
// 设置点击通知执行意图
Intent intent = new Intent(this, DemoActivity_2.class);
// PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT);
builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
// Android 8.0不能弹出通知解决方法
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "001";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "my_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
// 是否在桌面icon右上角展示小红点
channel.enableLights(true);
// 小红点颜色
channel.setLightColor(Color.GREEN);
// 是否在久按桌面图标时显示此渠道的通知
channel.setShowBadge(true);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
// Notification.Builder需要多设置一个
builder.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification notification = builder.build();
// 3、调用manager.notify()发出通知
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_DEFAULT_ID, notification);
}
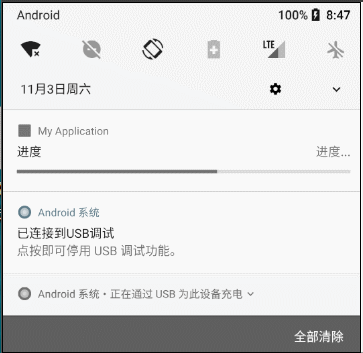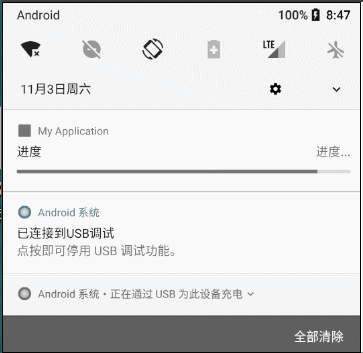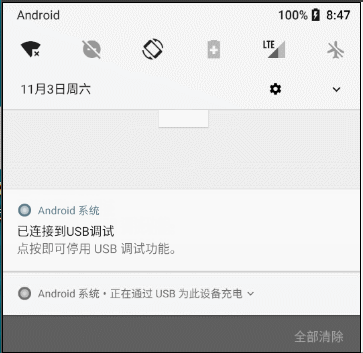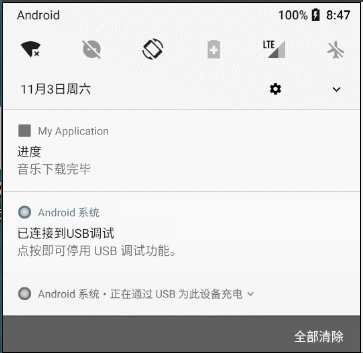
2.1.6 更新通知界面内容
(1)原理:使用相同的Id再次发送一个内容不同的通知即可。
(2)效果
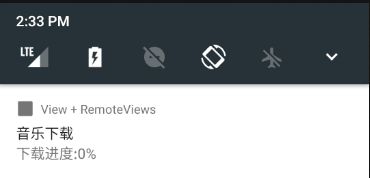
(3)例子
private int mProgress = 0;
private void updateDefaultNotification() {
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(this);
builder.setContentTitle("音乐下载")
.setContentText("下载进度:" + mProgress + "%")
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "002";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "download_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
builder.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification notification = builder.build();
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_DEFAULT_ID, notification);
mProgress += 10;
}
2.1.7 点击通知执行意图
Intent intent = new Intent(this,Main2Activity.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this,0,intent,PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
// 给通知添加点击意图
builder.setContentIntent(pi);
2.1.8 实现进度条的通知
(1)方法
setProgress(100, 10, false); // 带有进度条
setProgress(0, 0, false); // 取消进度条
setProgress(100, 10, true); // 不确定性进度条
private void sendProgressNotification() {
final NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
final Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(this);
builder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setContentTitle("进度")
.setContentText("进度...")
.setProgress(100, 10, true);
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "003";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "download_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
builder.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification notification = builder.build();
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_PROGRESS_ID, notification);
// 每隔1秒更新进度条进度,启动工作线程
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 发通知:带有进度条
builder.setProgress(100, i * 10, false);
Notification n = builder.build();
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_PROGRESS_ID, n);
}
// 更新通知内容
manager.cancel(NOTIFICATION_PROGRESS_ID); // 清除通知
builder.setProgress(0, 0, false); // 取消进度条
builder.setContentText("音乐下载完毕");
Notification n = builder.build();
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_PROGRESS_ID, n);
}
}, 2000);
}
}.start();
}
2.1.9 自定义通知的UI界面
private void sendCustomNotification() {
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(this);
builder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
builder.setTicker("hello world");
builder.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis());
builder.setOngoing(true);
// 设置整个通知栏点击通知执行意图
Intent intent = new Intent(this, DemoActivity_1.class);
intent.putExtra("sid", "" + NOTIFICATION_CUSTOM_ID);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
System.out.println(pendingIntent);
builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
// 给RemoteViews中的TextView设置文本内容
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), R.layout.layout_notification);
remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.msg, "自定义通知: " + NOTIFICATION_CUSTOM_ID);
remoteViews.setImageViewResource(R.id.icon, R.drawable.icon1);
// 给RemoteViews中的TextView添加点击事件,TextView添加点击意图
PendingIntent openActivity2PendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, new Intent(this, DemoActivity_2.class), PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.open_activity2, openActivity2PendingIntent);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
builder.setCustomContentView(remoteViews);
} else {
builder.setContent(remoteViews);
}
// Android 8.0不能弹出通知解决方法
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "005";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "download_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
builder.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification notification = builder.build();
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_CUSTOM_ID, notification);
}
2.1.10 学习链接
Android中的Notification
2.2 RemoteViews在桌面小部件的应用
Android桌面小部件是我们经常看到的,比如时钟、天气、音乐播放器等等。 它可以让 App 的某些功能直接展示在桌面上,极大的增加了用户的关注度。 误区:当App的小部件被放到了桌面之后,并不代表我们的App就可以一直在手机后台运行了;虽然它还是能被杀掉,但是用户能看的见它了啊,用户可以点击就打开我们的 APP。
2.2.1 Android桌面小部件可以做什么?
(1)展示:每隔N秒/分钟,刷新一次数据;
(2)交互:点击操作App的数据;
(3)打开App:打开主页或指定页面。
2.2.2 实现桌面小部件需要什么?
(1)先声明Widget的一些属性。 在res新建xml文件夹,创建appwidget-provider标签的 xml 文件;
(2)创建桌面要显示的布局。在layout创建app_widget.xml;
(3)然后来管理Widget状态。实现一个继承 AppWidgetProvider 的类;
(4)最后在AndroidManifest.xml里,将AppWidgetProvider类和xml属性注册到一块;
(5)通常我们会加一个Service来控制Widget的更新时间,后面再讲为什么。
2.2.3 声明 Widget 的属性
(1)在res/xml中定义一个appwidget_provider_info.xml
(2)属性说明
(3)重点
①桌面其实是按照“格子”排列的。 看 Google 给的图。上面我们代码定义 110dp 也就是说,它占了2*2的空间:
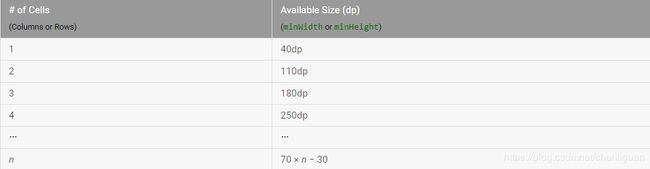
②updatePeriodMillis属性,更新widget的时间间隔(ms)。
官方给提供了小部件的自动更新时间,但是却给了限制,你更新的时间必须大于30分钟,如果小于30分钟,那默认就是30分钟。
可以我们就是要5分钟更新啊,怎么办呢?所以就不能使用这个默认更新,我们要自己来通过发送广播控制更新时间,也就是一开始总步骤里面第4步,加一个 Service 来控制 Widget 的更新时间,这个在最后一步添加。
2.2.4 创建布局文件 widget.xml
2.2.5 实现一个继承AppWidgetProvide 的类管理Widget状态
(1)Widget声明周期

(2)同一个小部件是可以添加多次的,所以更新控件的时候,要把所有的都更新。
(3)onReceive() 用来接收广播,它并不在生命周期里。但是,其实 onReceive() 是掌控生命周期的。 如下是onReceive()父类的源码,右边是每个广播对应的方法。 上面生命周期的图,也比较清楚。
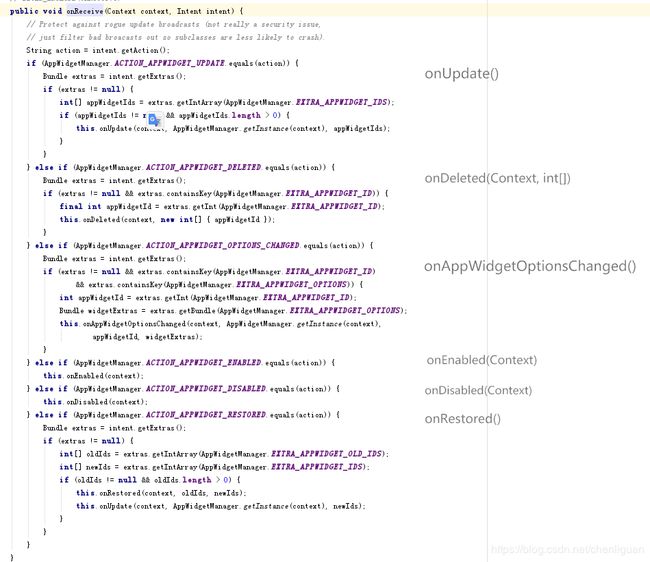
(4)例子
public class MyAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider {
public static final String TAG = "MyAppWidgetProvider";
public static final String CLICK_ACTION = "com.seniorlibs.view.remoteviews.action.CLICK";
public MyAppWidgetProvider() {
super();
}
/**
* 接收窗口小部件点击时发送的广播
*/
@Override
public void onReceive(final Context context, Intent intent) {
super.onReceive(context, intent);
Log.i(TAG, "onReceive : action = " + intent.getAction());
final String action = intent.getAction();
// 这里判断是action
if (CLICK_ACTION.equals(action)) {
clickAction(context);
}
}
/**
* 被点击了要干啥,这里是做一个动画效果
*
* @param context
*/
private void clickAction(final Context context) {
Toast.makeText(context, "clicked it", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Bitmap srcbBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(), R.drawable.icon1);
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
for (int i = 0; i < 37; i++) {
float degree = (i * 10) % 360;
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget);
remoteViews.setImageViewBitmap(R.id.imageView1, rotateBitmap(context, srcbBitmap, degree));
Intent intentClick = new Intent();
intentClick.setAction(CLICK_ACTION);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intentClick, 0);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.imageView1, pendingIntent);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(new ComponentName(context, MyAppWidgetProvider.class),remoteViews);
SystemClock.sleep(30);
}
}
}).start();
}
/**
* 每次窗口小部件被点击更新都调用一次该方法
*/
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) {
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
Log.i(TAG, "onUpdate");
final int counter = appWidgetIds.length;
Log.i(TAG, "counter = " + counter);
for (int appWidgetId : appWidgetIds) {
onWidgetUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId);
}
}
/**
* 窗口小部件更新,在onUpdate()中调用
*
* @param context
* @param appWidgeManger
* @param appWidgetId
*/
private void onWidgetUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgeManger, int appWidgetId) {
Log.i(TAG, "appWidgetId = " + appWidgetId);
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget);
// "窗口小部件"点击事件发送的Intent广播
Intent intentClick = new Intent();
intentClick.setAction(CLICK_ACTION);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intentClick, 0);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.imageView1, pendingIntent);
appWidgeManger.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, remoteViews);
}
/**
* 每删除一次窗口小部件就调用一次
*/
@Override
public void onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds) {
super.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
}
/**
* 当最后一个该窗口小部件删除时调用该方法
*/
@Override
public void onDisabled(Context context) {
super.onDisabled(context);
}
/**
* 当该窗口小部件第一次添加到桌面时调用该方法
*/
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
super.onEnabled(context);
}
/**
* 当小部件大小改变时
*/
@Override
public void onAppWidgetOptionsChanged(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int appWidgetId, Bundle newOptions) {
super.onAppWidgetOptionsChanged(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId, newOptions);
}
/**
* 当小部件从备份恢复时调用该方法
*/
@Override
public void onRestored(Context context, int[] oldWidgetIds, int[] newWidgetIds) {
super.onRestored(context, oldWidgetIds, newWidgetIds);
}
private Bitmap rotateBitmap(Context context, Bitmap srcbBitmap, float degree) {
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.reset();
matrix.setRotate(degree);
return Bitmap.createBitmap(srcbBitmap, 0, 0, srcbBitmap.getWidth(), srcbBitmap.getHeight(), matrix, true);
}
}
2.2.6 在AndroidManifest.xml里,将AppWidgetProvider类和xml属性注册到一块
// 下面的代码有两个Action,其中第一个是识别小部件的动作,第二个就是他的标识,必须存在,这是系统的规范
2.2.7 通常会加一个Service来控制Widget的更新时间
当每隔 N 秒/分钟,就发送一次这个广播。 那到底在哪发呢?也就是我们刚开始说的,用 Service 来控制时间。
参考把你的程序放到桌面——Android桌面部件Widget的第4点。
2.2 8 学习链接
把你的程序放到桌面——Android桌面部件Widget
3 PendingIntent概述
3.1 概述
PendingIntent表示处于一种等待的意图,即特定,等待的意思,就是说你要在某种条件下才会触发,所以我们很容易的就联想到RemoteViews了。
3.2 PendingIntent有三种待定的意图,就是Activity、Service,广播
3.3 PendingIntent的匹配规则
(1)如果两个PendingIntent内部的Intent相同并且requstCode也相同的话,那么PendingIntent就是相同的;
(2)Intent的匹配规则是:如果两个Intent的ComponentName的匹配过程,只要Intent之间的ComponentName和intent-filter相同,那么这两个intent就相同,需要注意的是Extras不参与匹配过程,只要intent之间的name和intent-filter相同就行。
// 包名 包名 + 类名
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.example.otherapp", "com.example.otherapp.MainActivity2"));
关于ComponentName的使用
3.4 flags的参数含义
3.4.1 FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
设置两个PendingIntent的flags均为FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT,PendingIntent如果已经存在,那么就会被cancel,然后系统创建一个新的PendingIntent。即,此时随着p2的创建,p1里面的Intent内容会失效。因此,点击第一个Notification时候,无效点击。当点击第二个Notification的时候,跳转到下一个Activity,并在下一个Activity的tv中显示BBB。
3.4.2 FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT
设置两个PendingIntent的flags均为FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT,使用该flags时,后创建的PendingIntent在遇到已经存在的相同的PendingIntent时,会去更新原先PendingIntent中封装的intent的extra内容。即,p2会把p1的intent的extra内容更新为自己的extra,都可以点击跳转到下一个Activity,并在下一个Activity的tv中显示BBB。
3.4.3 FLAG_ONE_SHOT
设置两个PendingIntent的flags均为FLAG_ONE_SHOT,后续通知中的PendingIntent会和第一条通知保持完全一致,包括其中的Extras,单击任何一条通知后,剩下的通知均无法再打开,当所有的通知都被清除后,会再次重复这个过程。即,如果先点击通知2,会跳转到下一个Activity,并在下一个Activity的tv中显示AAA;再点击通知1,无效点击。如果先点击通知1,会跳转到下一个Activity,并在下一个Activity的tv中显示AAA,再点击通知2,无效点击。
3.4.4 FLAG_NO_CREAT
当前描述的PendingIntent不会主动去创建,如果当前PendingIntent之前不存在,那么getActivity等方法都会直接返回null,即获取PendingIntent失败,这个标记位很少见,他无法单独使用,因此在日常开发当中,并没有太多的意义,这里就不过多的介绍了。
3.4.5 例子-测试PendingIntent的flags参数
(1)ActivityA
private void testPendingIntentFlags() {
Intent intentA = new Intent(this, ReceivePendingIntentFlagsActivity.class);
intentA.putExtra("name", "AAA");
Intent intentB = new Intent(this, ReceivePendingIntentFlagsActivity.class);
intentB.putExtra("name", "BBB");
PendingIntent p1 = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intentA, PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT);
PendingIntent p2 = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intentB, PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT);
Log.e(TAG, "两个intent是否相等(equals)" + intentA.equals(intentB));//false
Log.e(TAG, "两个PendingIntent是否相等:" + p1.equals(p2)); // true
Log.e(TAG, "两个intent是否相等(filterEquals):" + intentA.filterEquals(intentB)); // true
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification.Builder builder1 = new Notification.Builder(this);
builder1.setContentTitle("title");
builder1.setContentText("Content Text");
builder1.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
builder1.setOngoing(true);
builder1.setContentIntent(p1);
// Android 8.0不能弹出通知解决方法
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "006";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "download_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
builder1.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification notification1 = builder1.build();
manager.notify(1, notification1);
Notification.Builder builder2 = new Notification.Builder(this);
builder2.setContentTitle("title2");
builder2.setContentText("Content Text2");
builder2.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_yellow);
builder2.setOngoing(true);
builder2.setContentIntent(p2);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
String channelId = "007";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(channelId, "download_channel", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
builder2.setChannelId(channelId);
}
Notification notification2 = builder2.build();
manager.notify(2, notification2);
}
(2)ActivityB
public class ReceivePendingIntentFlagsActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_receive_pending_intent_flags);
TextView tvReceive = findViewById(R.id.tv_receive);
tvReceive.setText(getIntent().getStringExtra("name"));
}
}
(3)参考链接
构造PendingIntent时第四个参数flags的设置以及在Notification中的不同作用
4 RemoteViews的内部机制
4.1 RemoteViews基础
RemoteViews的作用在其他进程中显示并且更新View的界面,为了更好的理解他的内部机制,我们来看一下他的主要功能,首先我们看一下他的构造方法。
public RemoteViews(String packageName, int layoutId) {
this(getApplicationInfo(packageName, UserHandle.myUserId()), layoutId);
}
他接受两个参数,第一个表示当前的包名,第二个是加载的布局,这个很好理解,RemoteViews目前并不能支持所有的View类型,我们看下他支持哪些:
Layout
FrameLayout LinearLayout RelativeLayout GridLayout
View
AnalogClock,Button,Chronometer,ImageButton,ImageView,ProgressBar,TextView,ViewFlipper
ListView,GridView,stackView,AdapterViewFlipper,ViewStub
4.2 RemoteViews会通过Binder与SystemService进程中的NotificationManagerService通信原理分析
4.2.1 原理分析
由于RemoteViews主要用于通知栏和通知栏和桌面小部件,分别由NotificationManager和AppWidgetProvider管理,而NotificationManager和AppWidgetProvider通过Binder分别和SystemService进程中的NotificationManagerService和AppWidgetService通信。由此可见,通知栏和小部件的布局文件实际上是在NotificationManagerService和AppWidgetService中被加载的,这就是我们的进程构成了跨进程通信的原理。
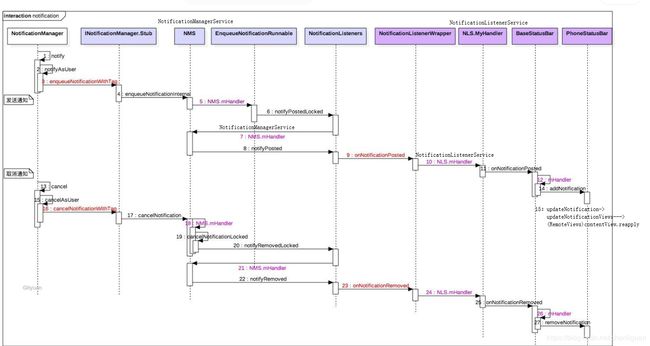
4.2.2 架构图
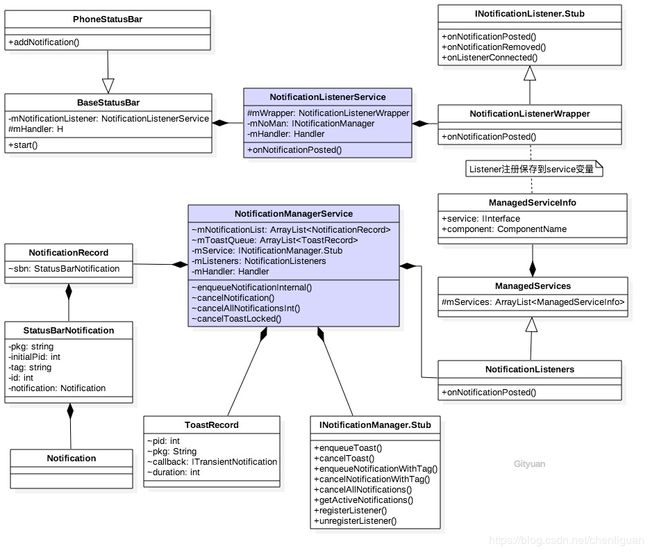
(1)核心类图
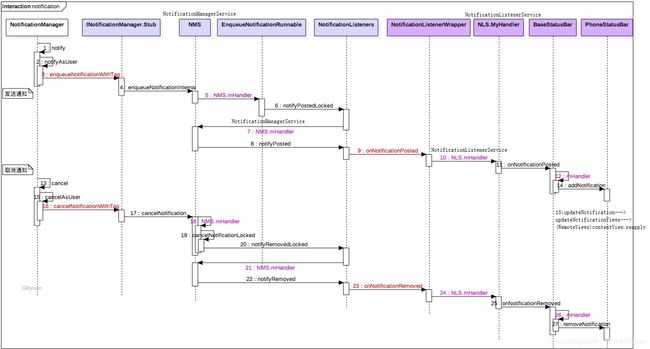
(2)Notification处理UML流程图
4.3 RemoteViews会通过Binder与SystemService进程中的NotificationManagerService通信的源码分析
4.3.1 NotificationManager.notify()
public void notify(int id, Notification notification) {
notify(null, id, notification);
}
public void notify(String tag, int id, Notification notification) {
notifyAsUser(tag, id, notification, new UserHandle(UserHandle.myUserId()));
}
public void notifyAsUser(String tag, int id, Notification notification, UserHandle user) {
int[] idOut = new int[1];
// 获取通知的代理对象
INotificationManager service = getService();
String pkg = mContext.getPackageName();
// 将包名和userId保存到通知的extras
Notification.addFieldsFromContext(mContext, notification);
...
fixLegacySmallIcon(notification, pkg);
// 对于Android 5.0之后的版本,smallIcon不可为空
if (mContext.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion > Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP_MR1) {
if (notification.getSmallIcon() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(...);
}
}
final Notification copy = Builder.maybeCloneStrippedForDelivery(notification);
try {
// binder调用,进入system_server进程【4.3.2】
service.enqueueNotificationWithTag(pkg, mContext.getOpPackageName(), tag, id,
copy, idOut, user.getIdentifier());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
在App端调用NotificationManager类的notify()方法,最终通过binder调用INotificationManager.Stub.enqueueNotificationWithTag(),最终会进入system_server进程的 NotificationManagerService,执行enqueueNotificationWithTag()方法。
4.3.2 NotificationManagerService.enqueueNotificationInternal()
public void enqueueNotificationWithTag(String pkg, String opPkg, String tag, int id, Notification notification, int[] idOut, int userId) throws RemoteException {
enqueueNotificationInternal(pkg, opPkg, Binder.getCallingUid(), Binder.getCallingPid(), tag, id, notification, idOut, userId);
}
void enqueueNotificationInternal(final String pkg, final String opPkg, final int callingUid, final int callingPid, final String tag, final int id, final Notification notification, int[] idOut, int incomingUserId) {
// 检查发起者是系统进程或者同一个app,否则抛出异常
checkCallerIsSystemOrSameApp(pkg);
final boolean isSystemNotification = isUidSystem(callingUid) || ("android".equals(pkg));
final boolean isNotificationFromListener = mListeners.isListenerPackage(pkg);
// 除了系统通知和已注册的监听器允许入队列,其他通知都会限制数量上限,默认是一个package上限50个
...
// 将通知信息封装到StatusBarNotification对象
final StatusBarNotification n = new StatusBarNotification(pkg, opPkg, id, tag, callingUid, callingPid, 0, notification, user);
// 创建记录通知实体的对象NotificationRecord
final NotificationRecord r = new NotificationRecord(getContext(), n);
// 将通知异步发送到handler线程-system_server的主线程【4.3.3】
mHandler.post(new EnqueueNotificationRunnable(userId, r));
}
这个过程主要功能:①创建NotificationRecord对象,里面包含了notification相关信息;②采用异步方式,将任务交给mHandler线程来处理,mHandler是WorkerHandler类的实例对象;
接下来看看WorkerHandler到底运行在哪个线程,这需要从NotificationManagerService服务初始化过程来说起:
(1)SystemServer.startOtherServices()
// 该过程运行在system_server进程的主线程
private void startOtherServices() {
//【(2)】
mSystemServiceManager.startService(NotificationManagerService.class);
...
}
(2)SystemServiceManager.startService()
public T startService(Class serviceClass) {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Constructor constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
// 创建NotificationManagerService对象
final T service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
// 注册该服务
mServices.add(service);
// 调用NotificationManagerService的onStart方法,【(3)】
service.onStart();
return service;
}
该过程先创建NotificationManagerService,然后再调用其onStart方法
(3)NotificationManagerService.onStart()
public void onStart() {
...
mHandler = new WorkerHandler(); //运行在system_server的主线程
mRankingThread.start(); //线程名为"ranker"的handler线程
mRankingHandler = new RankingHandlerWorker(mRankingThread.getLooper());
...
//用于记录所有的listeners的MangedServices对象
mListeners = new NotificationListeners();
...
publishBinderService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE, mService);
publishLocalService(NotificationManagerInternal.class, mInternalService);
}
到此,我们可以得知onStart()过程创建的mHandler运行在system_server的主线程。那么上面的执行流便进入了system_server主线程。
4.3.3 NotificationManagerService.EnqueueNotificationRunnable
private class EnqueueNotificationRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run() {
synchronized (mNotificationList) {
// 此处r为NotificationRecord对象
final StatusBarNotification n = r.sbn;
final Notification notification = n.getNotification();
...
// 从通知列表mNotificationList查看是否存在该通知
int index = indexOfNotificationLocked(n.getKey());
if (index < 0) {
mNotificationList.add(r);
mUsageStats.registerPostedByApp(r);
} else {
old = mNotificationList.get(index);
mNotificationList.set(index, r);
mUsageStats.registerUpdatedByApp(r, old);
//确保通知的前台服务属性不会被丢弃
notification.flags |= old.getNotification().flags & Notification.FLAG_FOREGROUND_SERVICE;
r.isUpdate = true;
}
mNotificationsByKey.put(n.getKey(), r);
// 如果是前台服务的通知,则添加不允许被清除和正在运行的标签
if ((notification.flags & Notification.FLAG_FOREGROUND_SERVICE) != 0) {
notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT | Notification.FLAG_NO_CLEAR;
}
applyZenModeLocked(r);
mRankingHelper.sort(mNotificationList);
if (notification.getSmallIcon() != null) {
StatusBarNotification oldSbn = (old != null) ? old.sbn : null;
// 当设置小图标,则通知NotificationListeners处理 【4.3.4】
mListeners.notifyPostedLocked(n, oldSbn);
} else {
if (old != null && !old.isCanceled) {
mListeners.notifyRemovedLocked(n);
}
}
// 处理该通知,主要是是否发声,震动,Led灯
buzzBeepBlinkLocked(r);
}
}
}
这里的mListeners是指NotificationListeners对象
4.3.4 NotificationManagerService.NotificationListeners.notifyPostedLocked()
public class NotificationListeners extends ManagedServices {
public void notifyPostedLocked(StatusBarNotification sbn, StatusBarNotification oldSbn) {
TrimCache trimCache = new TrimCache(sbn);
// 遍历整个ManagedServices中的所有ManagedServiceInfo
for (final ManagedServiceInfo info : mServices) {
boolean sbnVisible = isVisibleToListener(sbn, info);
boolean oldSbnVisible = oldSbn != null ? isVisibleToListener(oldSbn, info) : false;
if (!oldSbnVisible && !sbnVisible) {
continue;
}
final NotificationRankingUpdate update = makeRankingUpdateLocked(info);
// 通知变得不可见,则移除老的通知
if (oldSbnVisible && !sbnVisible) {
final StatusBarNotification oldSbnLightClone = oldSbn.cloneLight();
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
notifyRemoved(info, oldSbnLightClone, update);
}
});
continue;
}
final StatusBarNotification sbnToPost = trimCache.ForListener(info);
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
notifyPosted(info, sbnToPost, update); //【4.3.5】
}
});
}
}
...
}
这里是在system_server进程中第二次采用异步方式来处理。
4.3.5 NotificationManagerService.notifyPosted()
private void notifyPosted(final ManagedServiceInfo info, final StatusBarNotification sbn, NotificationRankingUpdate rankingUpdate) {
final INotificationListener listener = (INotificationListener)info.service;
StatusBarNotificationHolder sbnHolder = new StatusBarNotificationHolder(sbn);
try {
// 【4.3.6】
listener.onNotificationPosted(sbnHolder, rankingUpdate);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
...
}
}
此处的listener来自于ManagedServiceInfo的service成员变量,listener数据类型是NotificationListenerWrapper的代理对象,详见下面的分析,总结在(14)。
此处sbnHolder的数据类型为StatusBarNotificationHolder,继承于IStatusBarNotificationHolder.Stub对象,经过binder调用进入到systemui进程的 便是IStatusBarNotificationHolder.Stub.Proxy对象。
(1)SystemServer.startOtherServices()
private void startOtherServices() {
startSystemUi(context);
...
}
static final void startSystemUi(Context context) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.android.systemui", "com.android.systemui.SystemUIService"));
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
// 启动服务SystemUIService,运行在进程com.android.systemui,接下来进入systemui进程【(2)】
context.startServiceAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM);
}
(2)SystemUIService
public class SystemUIService extends Service {
// 服务启动后,先执行其onCreate()方法
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//【(3)】
((SystemUIApplication) getApplication()).startServicesIfNeeded();
}
...
}
(3)SystemUIApplication.startServicesIfNeeded()
// SERVICES常量值
private final Class[] SERVICES = new Class[] {
com.android.systemui.tuner.TunerService.class,
com.android.systemui.keyguard.KeyguardViewMediator.class,
com.android.systemui.recents.Recents.class,
com.android.systemui.volume.VolumeUI.class,
Divider.class,
com.android.systemui.statusbar.SystemBars.class, // SystemBars【(4)】
com.android.systemui.usb.StorageNotification.class,
com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class,
com.android.systemui.media.RingtonePlayer.class,
com.android.systemui.keyboard.KeyboardUI.class,
com.android.systemui.tv.pip.PipUI.class,
com.android.systemui.shortcut.ShortcutKeyDispatcher.class
};
public void startServicesIfNeeded() {
startServicesIfNeeded(SERVICES); //【(4)】
}
(4)SystemUIApplication.startServicesIfNeeded()
private void startServicesIfNeeded(Class[] services) {
if (mServicesStarted) {
return;
}
if (!mBootCompleted) {
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
mBootCompleted = true;
}
}
final int N = services.length;
for (int i=0; i cl = services[i];
try {
// 初始化对象
Object newService = SystemUIFactory.getInstance().createInstance(cl);
mServices[i] = (SystemUI) ((newService == null) ? cl.newInstance() : newService);
} catch (Exception ex) {
...
}
mServices[i].mContext = this;
mServices[i].mComponents = mComponents;
// 此处以SystemBars为例来展开【(5)】
mServices[i].start();
if (mBootCompleted) {
mServices[i].onBootCompleted();
}
}
mServicesStarted = true;
}
(5)SystemBars.start()
public void start() {
mServiceMonitor = new ServiceMonitor(TAG, DEBUG, mContext, Settings.Secure.BAR_SERVICE_COMPONENT, this);
mServiceMonitor.start(); // 当远程服务不存在,则执行下面的onNoService
}
public void onNoService() {
//【6】
createStatusBarFromConfig();
}
(6)SystemBars.createStatusBarFromConfig()
private void createStatusBarFromConfig() {
//config_statusBarComponent是指PhoneStatusBar
final String clsName = mContext.getString(R.string.config_statusBarComponent);
Class cls = null;
try {
cls = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(clsName);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
try {
mStatusBar = (BaseStatusBar) cls.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
mStatusBar.mContext = mContext;
mStatusBar.mComponents = mComponents;
// config_statusBarComponent的定义位于文件config.xml中,其值为PhoneStatusBar。【(7)】
mStatusBar.start();
}
(7)PhoneStatusBar.start()
public void start() {
...
super.start(); //此处调用BaseStatusBar【(8)】
}
(8)BaseStatusBar.start()
NotificationListenerService mNotificationListener = new NotificationListenerService() {
public void onNotificationPosted(final StatusBarNotification sbn, final RankingMap rankingMap) {
}
}
public void start() {
...
// 安装通知的初始化状态【(9)】
mNotificationListener.registerAsSystemService(mContext,
new ComponentName(mContext.getPackageName(), getClass().getCanonicalName()), UserHandle.USER_ALL);
...
createAndAddWindows(); // 添加状态栏
...
}
(9)NotificationListenerService.registerAsSystemService()
public void registerAsSystemService(Context context, ComponentName componentName, int currentUser) throws RemoteException {
if (mWrapper == null) {
mWrapper = new NotificationListenerWrapper();
}
mSystemContext = context;
// 获取NotificationManagerService的接口代理对象
INotificationManager noMan = getNotificationInterface();
// 运行在主线程的handler
mHandler = new MyHandler(context.getMainLooper());
mCurrentUser = currentUser;
// 经过binder调用,向system_server中的NotificationManagerService注册监听器【(10)】
noMan.registerListener(mWrapper, componentName, currentUser);
}
protected class NotificationListenerWrapper extends INotificationListener.Stub {
@Override
public void onNotificationPosted(IStatusBarNotificationHolder sbnHolder, NotificationRankingUpdate update) {
}
}
经过binder调用,向system_server中的NotificationManagerService注册监听器:NotificationListenerService.NotificationListenerWrapper子类。
(10)NotificationManagerService.registerListener()
private final IBinder mService = new INotificationManager.Stub() {
...
public void registerListener(final INotificationListener listener, final ComponentName component, final int userid) {
enforceSystemOrSystemUI("INotificationManager.registerListener");
// 此处的mListeners是NotificationManagerService.NotificationListeners,而NotificationListeners extends ManagedServices
// INotificationListener便是NotificationListenerWrapper代理对象 【(11)】
mListeners.registerService(listener, component, userid);
}
}
此处的mListeners是NotificationManagerService.NotificationListeners,而NotificationListeners extends ManagedServices。
INotificationListener便是NotificationListenerWrapper代理对象。
(11)ManagedServices.registerService()
public void registerService(IInterface service, ComponentName component, int userid) {
// registerServiceImpl【(12)】
ManagedServiceInfo info = registerServiceImpl(service, component, userid);
if (info != null) {
onServiceAdded(info);
}
}
(12)ManagedServices.registerServiceImpl()
private ManagedServiceInfo registerServiceImpl(final IInterface service, final ComponentName component, final int userid) {
// 将NotificationListenerWrapper对象保存到ManagedServiceInfo.service
ManagedServiceInfo info = new ServiceInfo(service, component, userid, true, null, Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP);
//【(13)】
return registerServiceImpl(info);
}
将NotificationListenerWrapper对象保存到ManagedServiceInfo.service。
(13)ManagedServices.registerServiceImpl()
private ManagedServiceInfo registerServiceImpl(ManagedServiceInfo info) {
synchronized (mMutex) {
try {
info.service.asBinder().linkToDeath(info, 0);
mServices.add(info);
return info;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
return null;
}
(14)总结
final INotificationListener listener = (INotificationListener)info.service;
前面4.3.5中通过(INotificationListener)得到的listener便是运行在systemui中的NotificationListenerWrapper的代理对象。
4.3.6 NotificationListenerService.NotificationListenerWrapper.onNotificationPosted()
protected class NotificationListenerWrapper extends INotificationListener.Stub {
public void onNotificationPosted(IStatusBarNotificationHolder sbnHolder, NotificationRankingUpdate update) {
StatusBarNotification sbn;
try {
sbn = sbnHolder.get(); // 向system_server进程来获取sbn对象
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return;
}
synchronized (mLock) {
applyUpdateLocked(update);
if (sbn != null) {
SomeArgs args = SomeArgs.obtain();
args.arg1 = sbn;
args.arg2 = mRankingMap;
//【4.3.7】
mHandler.obtainMessage(MyHandler.MSG_ON_NOTIFICATION_POSTED, args).sendToTarget();
} else {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MyHandler.MSG_ON_NOTIFICATION_RANKING_UPDATE, mRankingMap).sendToTarget();
}
}
}
...
}
此时运行在systemui进程,sbnHolder是IStatusBarNotificationHolder的代理端。 此处mHandler = new MyHandler(getMainLooper()),也就是运行在systemui主线程的handler。
4.3.7 NotificationListenerService.MyHandler.onNotificationPosted()
private final class MyHandler extends Handler {
...
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_ON_NOTIFICATION_POSTED: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
StatusBarNotification sbn = (StatusBarNotification) args.arg1;
RankingMap rankingMap = (RankingMap) args.arg2;
args.recycle();
onNotificationPosted(sbn, rankingMap);
} break;
case ...
}
}
}
public void onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn, RankingMap rankingMap) {
onNotificationPosted(sbn);
}
// 在子类中实现
public void onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
// optional
}
由4.3.5的(8)中,在BaseStatusBar类中通过定义NotificationListenerService mNotificationListener = new NotificationListenerService() { }监听NotificationListenerService的回调。所以,在BaseStatusBar.NotificationListenerService.onNotificationPosted()中实现,如:【4.3.8】。
4.3.8 BaseStatusBar.NotificationListenerService.onNotificationPosted()
private final NotificationListenerService mNotificationListener = new NotificationListenerService() {
public void onNotificationPosted(final StatusBarNotification sbn, final RankingMap rankingMap) {
if (sbn != null) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
...
String key = sbn.getKey();
boolean isUpdate = mNotificationData.get(key) != null;
if (isUpdate) {
// 【4.3.9】
updateNotification(sbn, rankingMap);
} else {
addNotification(sbn, rankingMap, null );
}
}
});
}
}
}
4.3.9 PhoneStatusBar.updateNotification()
public void updateNotification(StatusBarNotification notification, RankingMap ranking) {
Entry entry = mNotificationData.get(key);
...
updateNotificationViews(entry, notification);
...
}
4.3.10 PhoneStatusBar.updateNotificationViews()
private void updateNotificationViews(Entry entry, StatusBarNotification sbn) {
RemoteViews contentView = entry.cachedContentView;
...
// Reapply the RemoteViews
contentView.reapply(mContext, entry.getContentView(), mOnClickHandler);
...
}
接着具体分析:RemoteViews.reapply()如何加载布局
4.4 RemoteViews的apply()/reapply()加载布局
public class RemoteViews implements Parcelable, Filter {
......
public void reapply(Context context, View v, OnClickHandler handler) {
RemoteViews rvToApply = getRemoteViewsToApply(context);
View result;
// 通过LayoutInflater 去加载RemoteViews中的布局文件,RemoteViews中的布局文件可以通过getLayoutId这个方法获得
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
inflater = inflater.cloneInContext(inflationContext);
inflater.setFilter(this);
result = inflater.inflate(rvToApply.getLayoutId(), parent, false);
// 加载完布局之后会通过performApply去执行一些更新操作
RemoteViews rvToApply = getRemoteViewsToApply(context);
rvToApply.performApply(result, parent, handler);
return result;
}
private void performApply(View v, ViewGroup parent, OnClickHandler handler) {
if (mActions != null) {
handler = handler == null ? DEFAULT_ON_CLICK_HANDLER : handler;
final int count = mActions.size();
// 遍历mActions 这个列表并执行每一个Action对象的apply方法
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Action a = mActions.get(i);
a.apply(v, parent, handler);
}
}
}
}
4.5 RemoteViews是如何更新远程View的?
4.5.1 RemoteViews提供的set方法访问远程View
RemoteViews也没有提供findViewById方法,因此无法直接访问里面的View元素,而必须通过RemoteViews所提供的一系列set方法来完成,当然这是因为RemoteViews在远程进程中显示,所以没办法直接findViewById,关于set方法,可以看下这表:
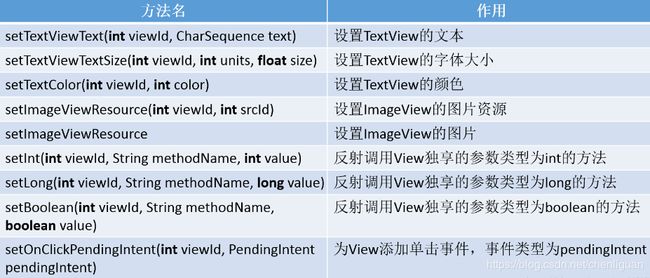
从这张表可以看出,原本可以直接调用View的方法,现在都需要通过set来完成,而从这些方法的声明来看,很像是通过反射来完成的,事实上也是如此。
(1)setTextViewText()
public class RemoteViews implements Parcelable, Filter {
public void setTextViewText(int viewId, CharSequence text) {
setCharSequence(viewId, "setText", text);
}
}
(2)setCharSequence()
// 上述ID中,viewId是被操作的View的id,setText是一个方法名,text是给TextView要设置的文
public void setCharSequence(int viewId, String methodName, CharSequence value) {
addAction(new ReflectionAction(viewId, methodName, ReflectionAction.CHAR_SEQUENCE, value));
}
(3)从setCharSequence的实现来看,他的内部并没有对View进行直接的处理,然是添加了一个ReflectionAction独享,ReflectionAction继承自Action,是用反射调用的:
private final class ReflectionAction extends Action {
ReflectionAction(int viewId, String methodName, int type, Object value) {
this.viewId = viewId;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.type = type;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent, OnClickHandler handler) {
final View view = root.findViewById(viewId);
if (view == null) return;
Class param = getParameterType();
if (param == null) {
throw new ActionException("bad type: " + this.type);
}
try {
getMethod(view, this.methodName, param).invoke(view, wrapArg(this.value));
} catch (ActionException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new ActionException(ex);
}
}
}
(4)再看addAction的实现:
private void addAction(Action a) {
if (mActions == null) {
mActions = new ArrayList();
}
mActions.add(a);
// update the memory usage stats
a.updateMemoryUsageEstimate(mMemoryUsageCounter);
}
从上述代码可以得知RemoteViews内部有一个mActions 成员,他是一个ArrayList,外界每一次调用一个set方法,他都能保存下来并未对view进行实际的操作。
(5)除了ReflectionAction 还有Action,等,这里我们拿TextViewSizeAction来分析,具体实现如下:
private class TextViewSizeAction extends Action {
public TextViewSizeAction(int viewId, int units, float size) {
this.viewId = viewId;
this.units = units;
this.size = size;
}
public TextViewSizeAction(Parcel parcel) {
viewId = parcel.readInt();
units = parcel.readInt();
size = parcel.readFloat();
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeInt(TAG);
dest.writeInt(viewId);
dest.writeInt(units);
dest.writeFloat(size);
}
@Override
public void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent, OnClickHandler handler) {
final TextView target = (TextView) root.findViewById(viewId);
if (target == null) return;
target.setTextSize(units, size);
}
public String getActionName() {
return "TextViewSizeAction";
}
int units;
float size;
public final static int TAG = 13;
}
之所以不用反射来实现,是因为setTextView这个方法有2个参数,因此无法复用ReflectionAction,因为ReflectionAction 的反射调用只需要一个参数,这里就不一一分析了。
(6)关于单击事件,RemoteView中只支持PendingIntent,是不支持其他模式的,我们这里需要注意的就是setOnClickPendingIntent,setPendingIntentTemplate,以及setonClickFillinIntent的区别,首先setOnClickPendingIntent用于给普通view设置单击事件,但是不能给ListView之类的View设置,如果需要,就用后两者。
4.5.2 跨进程通信修改View的原理
首先RemoteViews会通过Binder传递到SystemServer进程,这是因为RemoteViews实现了Parcelable接口,因此它可以跨进程传输,系统会根据RemoteViews中的包名等信息去得到该应用的资源。然后会通过Layoutinflater去加载RemoteViews中的布局文件,在SystemServer进程中加载后的布局文件是一个普通的View,只不过相对于我们的进程他是一个RemoteViews而已。接着系统会对View执行一系列界面更新任务,这些任务就是之前我们通过set方法来提交的。set方法对View所做的更新并不是立刻执行的,在RemoteViews内部会记录所有的更新操作,具体的执行时机要等到RemoteViews被加载以后才能执行,这样RemoteViews就可以在SystemServer进程中显示了。
从理论上来说,系统完全可以通过Binder去支持所有的View和View操作,但是这样做的话代价太大,因为View的方法太多了,另外就是大量的IPC操作会影响效率。为了解决这个问题,系统并没有通过Binder去直接支持View的跨进程访问,而是提供了一个Action,Action代表一个View操作,Action同样实现了Parcelable接口。这个过程可以参看下面的图片,系统首先调用set()将Vew操作封装到Action对象,并调用notify()将这些对象跨进程传输到远程进程,远程进程通过RemoteViews的apply方法来进行View的更新操作,RemoteViews的apply方法内部则会去遍历所有的Action对象并调用它们的apply方法,具体的View更新操作是由Acton对apply方法来完成的。
上述做法的好处:首先不需要定义大量的Binder,其次通过在远程进程中批量执行RemoteViews的修改操作从而避免了大量的IPC视作这就提高了程序的性能。

4.6 学习链接
NotificationManagerService原理分析-基于Android 7.0
完全理解 Android 中的 RemoteViews
5 RemoteViews的意义
6 学习链接
Android开发艺术探索第五章——理解RemoteView