并发编程之ReentrantLock,Condition阻塞队列,尝试锁,获取锁时限时等待,可响应中断,公平锁,同步锁
并发编程的核心简单表述就是一下三点:
1.原子性
所谓原子性是指在一次的操作或者多次的操作中,要么所有的操作全部都得到了执行并且不会受到任何因素的干扰而中断,要么所有的操作都不执行。i++不能保证原子性。synchronized关键字保证
多个原子性操作合在一起就不是原子性操作了
简单的读取和赋值操作是原子性的,将一个变量赋值给另外一个变量的操作不是原子性的
由于synchronized是一种排他机制,因此被他修饰的同步代码是无法被中途打断的,因此其能够保证代码的原子性。
2.可见性
可见性是指当一个线程对共享变量进行了修改,那么另外的线程可以立即看到修改后的最新值
synchronized和Lock保证可见性,他们会在(monitor exit)锁释放之前,会将对变量(共享资源)的修改刷新到主内存中
3.有序性
有序性是指程序代码在执行过程中的先后顺序,由于Java在编译器以及运行期的优化,导致了代码的执行顺序未必就是开发者编写代码时的顺序。
ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock和synchronized在功能上ReentrantLock要更为丰富更加灵活。性能上ReentrantLock也要略微由于synchronized
//ReentrantLock 简单实现同步锁
public class ReentrantLockTest extends Thread {
public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static int i = 0;
public ReentrantLockTest(String name) {
super.setName(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 300000; j++) {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(this.getName() + " " + i);
i++;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest test1 = new ReentrantLockTest("thread1");
ReentrantLockTest test2 = new ReentrantLockTest("thread2");
test1.start();
test2.start();
test1.join();
test2.join();
//最后的结果是 600000;如果去掉锁,那么输出结果是一个小于600000的不确定的数
System.out.println(i);
}
}
公平锁
ReentrantLock的有参构造可简单实现公平锁,采用的策略是等待时长越长的优先执行
/**
* 公平锁
*/
public class ReentrantLockTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SysTest s = new SysTest();
// UnSysTest s = new UnSysTest();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(s);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(s);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class SysTest extends Thread{
public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i<5 ;i++){
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get lock ");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
class UnSysTest extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i<5 ;i++){
synchronized (this){
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get lock ");
}
}
}
}

可响应中断
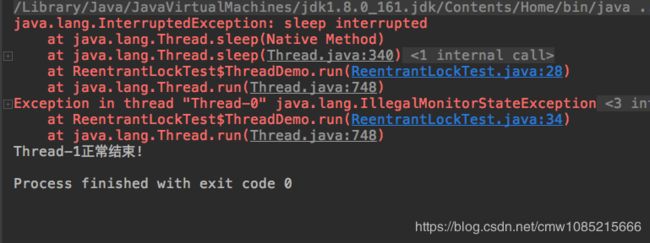
当使用synchronized实现锁时,阻塞在锁上的线程除非获得锁否则将一直等待下去,也就是说这种无限等待获取锁的行为无法被中断。而ReentrantLock给我们提供了一个可以响应中断的获取锁的方法lockInterruptibly()。该方法可以用来解决死锁问题。
public class ReentrantLockTest {
static Lock lock1 = new ReentrantLock();
static Lock lock2 = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadDemo(lock1, lock2));//该线程先获取锁1,再获取锁2
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadDemo(lock2, lock1));//该线程先获取锁2,再获取锁1
thread.start();
thread1.start();
thread.interrupt();//是第一个线程中断
}
static class ThreadDemo implements Runnable {
Lock firstLock;
Lock secondLock;
public ThreadDemo(Lock firstLock, Lock secondLock) {
this.firstLock = firstLock;
this.secondLock = secondLock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
firstLock.lockInterruptibly();
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);//更好的触发死锁
secondLock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
firstLock.unlock();
secondLock.unlock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正常结束!");
}
}
}
}
尝试锁,获取锁时限时等待
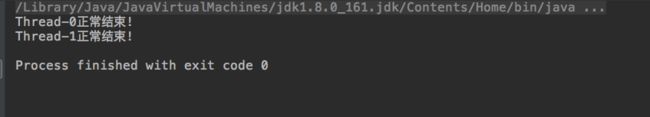
ReentrantLock还给我们提供了获取锁限时等待的方法tryLock(),可以选择传入时间参数,表示等待指定的时间,无参则表示立即返回锁申请的结果:true表示获取锁成功,false表示获取锁失败。我们可以使用该方法配合失败重试机制来更好的解决死锁问题。
public class ReentrantLockTest {
static Lock lock1 = new ReentrantLock();
static Lock lock2 = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadDemo(lock1, lock2));//该线程先获取锁1,再获取锁2
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadDemo(lock2, lock1));//该线程先获取锁2,再获取锁1
thread.start();
thread1.start();
}
static class ThreadDemo implements Runnable {
Lock firstLock;
Lock secondLock;
public ThreadDemo(Lock firstLock, Lock secondLock) {
this.firstLock = firstLock;
this.secondLock = secondLock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(!firstLock.tryLock()){
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
}
while(!secondLock.tryLock()){
lock1.unlock();
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
firstLock.unlock();
secondLock.unlock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正常结束!");
}
}
}
}
Condition
Condition由ReentrantLock对象创建,并且可以同时创建多个
static Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
static Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
Condition接口在使用前必须先调用ReentrantLock的lock()方法获得锁。之后调用Condition接口的await()将释放锁,并且在该Condition上等待,直到有其他线程调用Condition的signal()方法唤醒线程(signalAll()唤醒所有)。使用方式和wait,notify类似。
阻塞队列是一种特殊的先进先出队列,它有以下几个特点
1.入队和出队线程安全
2.当队列满时,入队线程会被阻塞;当队列为空时,出队线程会被阻塞。
public class TestContainer {
private final LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
private final int MAX =10;
private int count;
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition producer = lock.newCondition();
private Condition constumer =lock.newCondition();
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
public void put(E e){
lock.lock();
try {
while (list.size() == MAX){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 等待,,,");
//借助条件生产者进入等待队列,释放锁
producer.await();
}
count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put,,,");
list.add(e);
//借助条件唤醒所有消费者
constumer.signalAll();
}catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E get(){
E e = null;
lock.lock();
try {
while (list.size() == 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 等待,,,");
//借助条件消费者进入等待队列,释放锁
constumer.await();
}
count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get,,,");
e = list.remove();
//借助条件唤醒所有生产者
producer.signalAll();
}catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return e;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestContainer c = new TestContainer<>();
for (int i= 0 ; i <3 ; i++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0;j < 3;j++ ){
System.out.println(c.get());
}
}
},"constumer"+i).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i= 0 ; i < 2 ; i++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 1;j <= 5;j++ ){
c.put("Container value "+j);
}
}
},"producer"+1).start();
}
}
}
打印结果:
constumer0 等待,,,
constumer1 等待,,,
constumer2 等待,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
constumer0 get,,,
Container value 1
constumer1 get,,,
Container value 2
constumer2 等待,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
producer1 put,,,
constumer0 get,,,
Container value 1
constumer1 get,,,
Container value 2
constumer2 get,,,
Container value 3
constumer0 get,,,
Container value 4
constumer1 get,,,
Container value 5
constumer2 get,,,
Container value 3
constumer2 get,,,
Container value 4
ReentrantLock是可重入的独占锁。比起synchronized功能更加丰富,支持公平锁实现,支持中断响应以及限时等待等等。可以配合一个或多个Condition条件方便的实现等待通知机制。
ReentrantLock还有很多丰富的api,比如可以获取一些线程队列信息owner和monitor 。