BlockingQueue
[转自: https://www.cnblogs.com/techyc/p/3782079.html]
BlockingQueue是多线程里面一个非常重要的数据结构。在面试的时候,也常会被问到怎么实现BlockingQueue。本篇根据Java7里ArrayBlockingQueue的源码,简单介绍一下如何实现一个BlockingQueue。
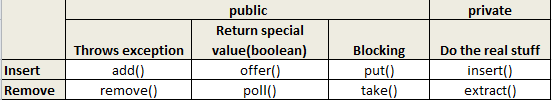
要实现BlockingQueue,首先得了解最主要的方法:
add()和remove()是最原始的方法,也是最不常用的。原因是,当队列满了或者空了的时候,会抛出IllegalStateException("Queue full")/NoSuchElementException(),并不符合我们对阻塞队列的要求;因此,ArrayBlockingQueue里,这两个方法的实现,直接继承自java.util.AbstractQueue:
1 public boolean add(E e) {
2 if (offer(e))
3 return true;
4 else
5 throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
6 }
7
8 public E remove() {
9 E x = poll();
10 if (x != null)
11 return x;
12 else
13 throw new NoSuchElementException();
14 }有上述源码可知,add()和remove()实现的关键,是来自java.util.Queue接口的offer()和poll()方法。
offer():在队列尾插入一个元素。若成功便返回true,若队列已满则返回false。(This method is generally preferable to method add(java.lang.Object)
poll():同理,取出并删除队列头的一个元素。若成功便返回true,若队列为空则返回false。
这里使用的是ReentrantLock,在插入或者取出前,都必须获得队列的锁,以保证同步。
1 public boolean offer(E e) {
2 checkNotNull(e);
3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
4 lock.lock();
5 try {
6 if (count == items.length)
7 return false;
8 else {
9 insert(e);
10 return true;
11 }
12 } finally {
13 lock.unlock();
14 }
15 }
16
17 public E poll() {
18 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
19 lock.lock();
20 try {
21 return (count == 0) ? null : extract();
22 } finally {
23 lock.unlock();
24 }
25 }由于offer()/poll()是非阻塞方法,一旦队列已满或者已空,均会马上返回结果,也不能达到阻塞队列的目的。因此有了put()/take()这两个阻塞方法:
1 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
2 checkNotNull(e);
3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
4 lock.lockInterruptibly();
5 try {
6 while (count == items.length)
7 notFull.await();
8 insert(e);
9 } finally {
10 lock.unlock();
11 }
12 }
13
14 public E take() throws InterruptedException {
15 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
16 lock.lockInterruptibly();
17 try {
18 while (count == 0)
19 notEmpty.await();
20 return extract();
21 } finally {
22 lock.unlock();
23 }
24 }put()/take()的实现,比起offer()/poll()复杂了一些,尤其有两个地方值得注意:
1. 取得锁以后,循环判断队列是否已满或者已空,并加上Condition的await()方法将当前正在调用put()的线程挂起,直至notFull.signal()唤起。
2. 这里使用的是lock.lockInterruptibly()而不是lock.lock()。原因在这里。lockInterruptibly()这个方法,优先考虑响应中断,而不是响应普通获得锁或重入获得锁。简单来说就是,由于put()/take()是阻塞方法,一旦有interruption发生,必须马上做出反应,否则可能会一直阻塞。
最后,无论是offer()/poll()还是put()/take(),都要靠insert()/extract()这个私有方法去完成真正的工作:
1 private void insert(E x) {
2 items[putIndex] = x;
3 putIndex = inc(putIndex);
4 ++count;
5 notEmpty.signal();
6 }
7
8 final int inc(int i) {
9 return (++i == items.length) ? 0 : i;
10 }
11
12 private E extract() {
13 final Object[] items = this.items;
14 E x = this.cast(items[takeIndex]);
15 items[takeIndex] = null;
16 takeIndex = inc(takeIndex);
17 --count;
18 notFull.signal();
19 return x;
20 }
21
22 final int dec(int i) {
23 return ((i == 0) ? items.length : i) - 1;
24 } insert()/extract(),是真正将元素放进数组或者将元素从数组取出并删除的方法。由于ArrayBlockingQueue是有界限的队列(Bounded Queue),因此inc()/dec()方法保证元素不超出队列的界限。另外,每当insert()后,要使用notEmpty.signal()唤起因队列空而等待取出的线程;每当extract()后,同理要使用notFull.signal()唤起因队列满而等待插入的线程。
到此,便将ArrayBlockingQueue的主要的方法粗略介绍了一遍。假设面试时,需要我们自己实现BlockingQueue时,可参考以上的做法,重点放在put()/take()和insert()/extract()方法上,也可将其结合在一起:
1 class BoundedBuffer {
2 final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
3 final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
4 final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
5
6 final Object[] items = new Object[100];
7 int putptr, takeptr, count;
8
9 public void put(Object x) throws InterruptedException {
10 lock.lock();
11 try {
12 while (count == items.length)
13 notFull.await();
14 items[putptr] = x;
15 if (++putptr == items.length) putptr = 0;
16 ++count;
17 notEmpty.signal();
18 } finally {
19 lock.unlock();
20 }
21 }
22
23 public Object take() throws InterruptedException {
24 lock.lock();
25 try {
26 while (count == 0)
27 notEmpty.await();
28 Object x = items[takeptr];
29 if (++takeptr == items.length) takeptr = 0;
30 --count;
31 notFull.signal();
32 return x;
33 } finally {
34 lock.unlock();
35 }
36 }
37 }最后,由于此文的启示,列举一些使用队列时的错误做法:
1. 忽略offer()的返回值。offer()作为有返回值的方法,可以在判断的时候十分有作用(例如add()的实现)。因此,千万不要忽略offer()方法的返回值。
2. 在循环里使用isEmpty()和阻塞方法:
1 while(!queue.isEmpty())
2 {
3 T element = queue.take();
4
5 //Process element.
6 }take()是阻塞方法,无需做isEmpty()的判断,直接使用即可。而这种情况很有可能导致死锁,因为由于不断循环,锁会一直被isEmpty()取得(因为size()方法会取得锁),而生产者无法获得锁。
3. 频繁使用size()方法去记录。size()方法是要取得锁的,意味着这不是一个廉价的方法。可以使用原子变量代替。
本文完