JAVA中的各种引用
JAVA中引用的分类
- 强引用
- 软引用 表示一个有用但是非必须的对象。
- 弱引用 表示希望在下一次垃圾回收时回收的对象
- 虚引用 主要用于监控对象何时被回收
实现
Reference
Reference是软引用,弱引用和虚引用的基类。
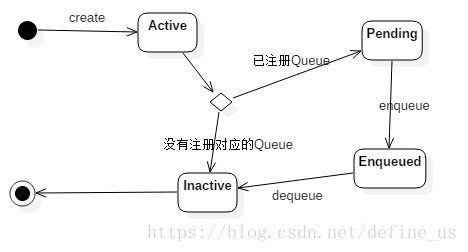
该类在初始化时,会启动一个内部线程
Thread handler = new ReferenceHandler(tg, "Reference Handler");
/* If there were a special system-only priority greater than
* MAX_PRIORITY, it would be used here
*/
handler.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
handler.setDaemon(true);
handler.start();
该线程一直试图重复下面逻辑
transient private Reference discovered;
static boolean tryHandlePending(boolean waitForNotify) {
Reference SoftReference
内部维持了一个clock(由垃圾处理器负责更新)和一个timestamp(由get方法负责更新)。如果clock大于很多timestamp,则表示推荐回收。
public class SoftReference extends Reference {
/**
* Timestamp clock, updated by the garbage collector
*/
static private long clock;
/**
* Timestamp updated by each invocation of the get method. The VM may use
* this field when selecting soft references to be cleared, but it is not
* required to do so.
*/
private long timestamp;
/**
* Creates a new soft reference that refers to the given object. The new
* reference is not registered with any queue.
*
* @param referent object the new soft reference will refer to
*/
public SoftReference(T referent) {
super(referent);
this.timestamp = clock;
}
/**
* Creates a new soft reference that refers to the given object and is
* registered with the given queue.
*
* @param referent object the new soft reference will refer to
* @param q the queue with which the reference is to be registered,
* or null if registration is not required
*
*/
public SoftReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue q) {
super(referent, q);
this.timestamp = clock;
}
/**
* Returns this reference object's referent. If this reference object has
* been cleared, either by the program or by the garbage collector, then
* this method returns null.
*
* @return The object to which this reference refers, or
* null if this reference object has been cleared
*/
public T get() {
T o = super.get();
if (o != null && this.timestamp != clock)
this.timestamp = clock;
return o;
}
}
WeakReference
public class WeakReference extends Reference {
/**
* Creates a new weak reference that refers to the given object. The new
* reference is not registered with any queue.
*
* @param referent object the new weak reference will refer to
*/
public WeakReference(T referent) {
super(referent);
}
/**
* Creates a new weak reference that refers to the given object and is
* registered with the given queue.
*
* @param referent object the new weak reference will refer to
* @param q the queue with which the reference is to be registered,
* or null if registration is not required
*/
public WeakReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue q) {
super(referent, q);
}
}
PhantomReference
PhantomReference的get方法永远返回null。
public class PhantomReference extends Reference {
/**
* Returns this reference object's referent. Because the referent of a
* phantom reference is always inaccessible, this method always returns
* null.
*
* @return null
*/
public T get() {
return null;
}
/**
* Creates a new phantom reference that refers to the given object and
* is registered with the given queue.
*
* It is possible to create a phantom reference with a null
* queue, but such a reference is completely useless: Its get
* method will always return null and, since it does not have a queue, it
* will never be enqueued.
*
* @param referent the object the new phantom reference will refer to
* @param q the queue with which the reference is to be registered,
* or null if registration is not required
*/
public PhantomReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue q) {
super(referent, q);
}
}
ReferenceQueue
标准用法如下
ReferenceQueue queue = new ReferenceQueue();
WeakReference reference = new WeakReference(new Object(), queue);
System.out.println(reference);
System.gc();
Reference reference1 = queue.remove();
System.out.println(reference1);
应用
WeakHashMap
Finalize
Object类中默认给出了finalize方法,也就是什么也不做。
实现了object的finalize的类在创建时会新建一个FinalizerReference,这个对象是强引用类型,封装了override finalize的对象,下面直接叫原对象。原对象没有被其他对象引用时(FinalizeReference除外),执行GC不会马上被清除掉,而是放入一个静态链表中(ReferenceQueue),有一个守护线程专门去维护这个链表,如何维护呢?就是轮到该线程执行时就弹出里面的对象,执行它们的finalize,对应的FinalizerReference对象在下次执行GC时就会被清理掉。
一个堆的FinalizerReference会组成一条双向链表,垃圾回收器应该会持有链表头(链表头在FinalizerReference中为一个静态成员)。
这种机制有些时候会导致内存泄露。
直接原因就是守护线程优先级比较低,运行的时间比较少。如果较短时间内创建较多的原对象,就会因为守护线程来不及弹出原对象而使FinalizerReference和原对象都得不到回收。无论怎样调用GC都没有用的,因为只要原对象没有被守护线程弹出执行其finalize()方法,FinalizerReference对象就不会被GC回收。
多说一句,没事别使用Finalize机制。