sonar安装使用及项目分析
一、Centos7环境安装SonarQube
SonarQube简SonarQube简介
Sonar 是一个用于代码质量管理的开放平台。通过插件机制,Sonar 可以集成不同的测试工具,代码分析工具,以及持续集成工具。比如pmd-cpd、checkstyle、findbugs、Jenkins。通过不同的插件对这些结果进行再加工处理,通过量化的方式度量代码质量的变化,从而可以方便地对不同规模和种类的工程进行代码质量管理。同时 Sonar 还对大量的持续集成工具提供了接口支持,可以很方便地在持续集成中使用 Sonar。
此外,Sonar 的插件还可以对 Java 以外的其他编程语言(支持的语言包括:Java、PHP、C#、C、Cobol、PL/SQL、Flex等)提供支持,对国际化以及报告文档化也有良好的支持。可以说Sonar是目前最强大的代码质量管理工具之一。
SonarQube为静态代码检查工具,采用B/S架构,帮助检查代码缺陷,改善代码质量,提高开发速度,通过插件形式,可以支持Java、C、C++、JavaScripe等等二十几种编程语言的代码质量管理与检测。
通过客户端插件分析源代码,sonar客户端可以采用IDE插件、Sonar-Scanner插件、Ant插件和Maven插件方式,并通过各种不同的分析机制对项目源代码进行分析和扫描,并把分析扫描后的结果上传到sonar的数据库,通过sonar web界面对分析结果进行管理
1.安装环境
系统环境:CentOS7
前置条件:jdk1.8.0_161 , mysql-5.7.21
软件安装目录:/home/sonar/sonarqube-7.7
软件版本:sonarqube-7.7
下载地址:http://www.sonarqube.org/downloads/
2.解压 sonarqube-7.7 jdk1.8.0_161 , mysql-5.7.21 安装这里不做介绍了
3.配置sonar.properties 的mysql相关信息
# Property values can:
# - reference an environment variable, for example sonar.jdbc.url= ${env:SONAR_JDBC_URL}
# - be encrypted. See https://redirect.sonarsource.com/doc/settings-encryption.html
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DATABASE
#
# IMPORTANT:
# - The embedded H2 database is used by default. It is recommended for tests but not for
# production use. Supported databases are MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL and Microsoft SQLServer.
# - Changes to database connection URL (sonar.jdbc.url) can affect SonarSource licensed products.
# User credentials.
# Permissions to create tables, indices and triggers must be granted to JDBC user.
# The schema must be created first.
sonar.jdbc.username=root
sonar.jdbc.password=123456
#----- Embedded Database (default)
# H2 embedded database server listening port, defaults to 9092
#sonar.embeddedDatabase.port=9092
#----- DEPRECATED
#----- MySQL >=5.6 && <8.0
# Support of MySQL is dropped in Data Center Editions and deprecated in all other editions
# Only InnoDB storage engine is supported (not myISAM).
# Only the bundled driver is supported. It can not be changed.
sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://10.128.1.19:3306/sonar?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&useConfigs=maxPerformance&useSSL=false
#----- Oracle 11g/12c
# The Oracle JDBC driver must be copied into the directory extensions/jdbc-driver/oracle/.
# Only the thin client is supported, and only the versions 11.2.x or 12.2.x must be used. See
# https://jira.sonarsource.com/browse/SONAR-9758 for more details.
# If you need to set the schema, please refer to http://jira.sonarsource.com/browse/SONAR-5000
#sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521/XE
#----- PostgreSQL 9.3 or greater
# By default the schema named "public" is used. It can be overridden with the parameter "currentSchema".
#sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost/sonarqube?currentSchema=my_schema
#----- Microsoft SQLServer 2014/2016/2017 and SQL Azure
# A database named sonar must exist and its collation must be case-sensitive (CS) and accent-sensitive (AS)
# Use the following connection string if you want to use integrated security with Microsoft Sql Server
# Do not set sonar.jdbc.username or sonar.jdbc.password property if you are using Integrated Security
# For Integrated Security to work, you have to download the Microsoft SQL JDBC driver package from
# https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=55539
# and copy sqljdbc_auth.dll to your path. You have to copy the 32 bit or 64 bit version of the dll
# depending upon the architecture of your server machine.
#sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=sonar;integratedSecurity=true
# Use the following connection string if you want to use SQL Auth while connecting to MS Sql Server.
# Set the sonar.jdbc.username and sonar.jdbc.password appropriately.
#sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=sonar
#----- Connection pool settings
# The maximum number of active connections that can be allocated
# at the same time, or negative for no limit.
# The recommended value is 1.2 * max sizes of HTTP pools. For example if HTTP ports are
# enabled with default sizes (50, see property sonar.web.http.maxThreads)
# then sonar.jdbc.maxActive should be 1.2 * 50 = 60.
sonar.jdbc.maxActive=60
# The maximum number of connections that can remain idle in the
# pool, without extra ones being released, or negative for no limit.
sonar.jdbc.maxIdle=5
# The minimum number of connections that can remain idle in the pool,
# without extra ones being created, or zero to create none.
sonar.jdbc.minIdle=2
# The maximum number of milliseconds that the pool will wait (when there
# are no available connections) for a connection to be returned before
# throwing an exception, or <= 0 to wait indefinitely.
sonar.jdbc.maxWait=5000
sonar.jdbc.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=600000
sonar.jdbc.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# WEB SERVER
# Web server is executed in a dedicated Java process. By default heap size is 512Mb.
# Use the following property to customize JVM options.
# Recommendations:
#
# The HotSpot Server VM is recommended. The property -server should be added if server mode
# is not enabled by default on your environment:
# http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/vm/server-class.html
#
# Startup can be long if entropy source is short of entropy. Adding
# -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom is an option to resolve the problem.
# See https://wiki.apache.org/tomcat/HowTo/FasterStartUp#Entropy_Source
#
#sonar.web.javaOpts=-Xmx512m -Xms128m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
# Same as previous property, but allows to not repeat all other settings like -Xmx
#sonar.web.javaAdditionalOpts=
# Binding IP address. For servers with more than one IP address, this property specifies which
# address will be used for listening on the specified ports.
# By default, ports will be used on all IP addresses associated with the server.
sonar.web.host=10.128.1.19
# Web context. When set, it must start with forward slash (for example /sonarqube).
# The default value is root context (empty value).
#sonar.web.context=
# TCP port for incoming HTTP connections. Default value is 9000.
sonar.web.port=9000
# The maximum number of connections that the server will accept and process at any given time.
# When this number has been reached, the server will not accept any more connections until
# the number of connections falls below this value. The operating system may still accept connections
# based on the sonar.web.connections.acceptCount property. The default value is 50.
#sonar.web.http.maxThreads=50
# The minimum number of threads always kept running. The default value is 5.
#sonar.web.http.minThreads=5
# The maximum queue length for incoming connection requests when all possible request processing
# threads are in use. Any requests received when the queue is full will be refused.
# The default value is 25.
#sonar.web.http.acceptCount=25
# By default users are logged out and sessions closed when server is restarted.
# If you prefer keeping user sessions open, a secret should be defined. Value is
# HS256 key encoded with base64. It must be unique for each installation of SonarQube.
# Example of command-line:
# echo -n "type_what_you_want" | openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac "key" -binary | base64
#sonar.auth.jwtBase64Hs256Secret=
# The inactivity timeout duration of user sessions, in minutes. After the configured
# period of time, the user is logged out.
# The default value is set to 3 days (4320 minutes)
# and cannot be greater than 3 months. Value must be strictly positive.
#sonar.web.sessionTimeoutInMinutes=4320
# A passcode can be defined to access some web services from monitoring
# tools without having to use the credentials of a system administrator.
# Check the Web API documentation to know which web services are supporting this authentication mode.
# The passcode should be provided in HTTP requests with the header "X-Sonar-Passcode".
# By default feature is disabled.
#sonar.web.systemPasscode=
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# SSO AUTHENTICATION
# Enable authentication using HTTP headers
#sonar.web.sso.enable=false
# Name of the header to get the user login.
# Only alphanumeric, '.' and '@' characters are allowed
#sonar.web.sso.loginHeader=X-Forwarded-Login
# Name of the header to get the user name
#sonar.web.sso.nameHeader=X-Forwarded-Name
# Name of the header to get the user email (optional)
#sonar.web.sso.emailHeader=X-Forwarded-Email
# Name of the header to get the list of user groups, separated by comma (optional).
# If the sonar.sso.groupsHeader is set, the user will belong to those groups if groups exist in SonarQube.
# If none of the provided groups exists in SonarQube, the user will only belong to the default group.
# Note that the default group will always be set.
#sonar.web.sso.groupsHeader=X-Forwarded-Groups
# Interval used to know when to refresh name, email and groups.
# During this interval, if for instance the name of the user is changed in the header, it will only be updated after X minutes.
#sonar.web.sso.refreshIntervalInMinutes=5
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# LDAP CONFIGURATION
# Enable the LDAP feature
# sonar.security.realm=LDAP
# Set to true when connecting to a LDAP server using a case-insensitive setup.
# sonar.authenticator.downcase=true
# URL of the LDAP server. Note that if you are using ldaps, then you should install the server certificate into the Java truststore.
# ldap.url=ldap://localhost:10389
# Bind DN is the username of an LDAP user to connect (or bind) with. Leave this blank for anonymous access to the LDAP directory (optional)
# ldap.bindDn=cn=sonar,ou=users,o=mycompany
# Bind Password is the password of the user to connect with. Leave this blank for anonymous access to the LDAP directory (optional)
# ldap.bindPassword=secret
# Possible values: simple | CRAM-MD5 | DIGEST-MD5 | GSSAPI See http://java.sun.com/products/jndi/tutorial/ldap/security/auth.html (default: simple)
# ldap.authentication=simple
# See :
# * http://java.sun.com/products/jndi/tutorial/ldap/security/digest.html
# * http://java.sun.com/products/jndi/tutorial/ldap/security/crammd5.html
# (optional)
# ldap.realm=example.org
# Context factory class (optional)
# ldap.contextFactoryClass=com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory
# Enable usage of StartTLS (default : false)
# ldap.StartTLS=true
# Follow or not referrals. See http://docs.oracle.com/javase/jndi/tutorial/ldap/referral/jndi.html (default: true)
# ldap.followReferrals=false
# USER MAPPING
# Distinguished Name (DN) of the root node in LDAP from which to search for users (mandatory)
# ldap.user.baseDn=cn=users,dc=example,dc=org
# LDAP user request. (default: (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid={login})) )
# ldap.user.request=(&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={login}))
# Attribute in LDAP defining the user’s real name. (default: cn)
# ldap.user.realNameAttribute=name
# Attribute in LDAP defining the user’s email. (default: mail)
# ldap.user.emailAttribute=email
# GROUP MAPPING
# Distinguished Name (DN) of the root node in LDAP from which to search for groups. (optional, default: empty)
# ldap.group.baseDn=cn=groups,dc=example,dc=org
# LDAP group request (default: (&(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)(uniqueMember={dn})) )
# ldap.group.request=(&(objectClass=group)(member={dn}))
# Property used to specifiy the attribute to be used for returning the list of user groups in the compatibility mode. (default: cn)
# ldap.group.idAttribute=sAMAccountName
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# COMPUTE ENGINE
# The Compute Engine is responsible for processing background tasks.
# Compute Engine is executed in a dedicated Java process. Default heap size is 512Mb.
# Use the following property to customize JVM options.
# Recommendations:
#
# The HotSpot Server VM is recommended. The property -server should be added if server mode
# is not enabled by default on your environment:
# http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/vm/server-class.html
#
#sonar.ce.javaOpts=-Xmx512m -Xms128m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
# Same as previous property, but allows to not repeat all other settings like -Xmx
#sonar.ce.javaAdditionalOpts=
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ELASTICSEARCH
# Elasticsearch is used to facilitate fast and accurate information retrieval.
# It is executed in a dedicated Java process. Default heap size is 512Mb.
#
# --------------------------------------------------
# Word of caution for Linux users on 64bits systems
# --------------------------------------------------
# Please ensure Virtual Memory on your system is correctly configured for Elasticsearch to run properly
# (see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.5/vm-max-map-count.html for details).
#
# When SonarQube runs standalone, a warning such as the following may appear in logs/es.log:
# "max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]"
# When SonarQube runs as a cluster, however, Elasticsearch will refuse to start.
#
# JVM options of Elasticsearch process
#sonar.search.javaOpts=-Xms512m -Xmx512m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
# Same as previous property, but allows to not repeat all other settings like -Xmx
#sonar.search.javaAdditionalOpts=
# Elasticsearch port. Default is 9001. Use 0 to get a free port.
# As a security precaution, should be blocked by a firewall and not exposed to the Internet.
#sonar.search.port=9001
# Elasticsearch host. The search server will bind this address and the search client will connect to it.
# Default is loopback address.
# As a security precaution, should NOT be set to a publicly available address.
#sonar.search.host=
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# UPDATE CENTER
# Update Center requires an internet connection to request https://update.sonarsource.org
# It is enabled by default.
#sonar.updatecenter.activate=true
# HTTP proxy (default none)
#http.proxyHost=
#http.proxyPort=
# HTTPS proxy (defaults are values of http.proxyHost and http.proxyPort)
#https.proxyHost=
#https.proxyPort=
# NT domain name if NTLM proxy is used
#http.auth.ntlm.domain=
# SOCKS proxy (default none)
#socksProxyHost=
#socksProxyPort=
# Proxy authentication (used for HTTP, HTTPS and SOCKS proxies)
#http.proxyUser=
#http.proxyPassword=
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# LOGGING
# SonarQube produces logs in 4 logs files located in the same directory (see property sonar.path.logs below),
# one per process:
# Main process (aka. App) logs in sonar.log
# Web Server (aka. Web) logs in web.log
# Compute Engine (aka. CE) logs in ce.log
# Elasticsearch (aka. ES) logs in es.log
#
# All 4 files follow the same rolling policy (see sonar.log.rollingPolicy and sonar.log.maxFiles) but it applies
# individually (eg. if sonar.log.maxFiles=4, there can be at most 4 of each files, ie. 16 files in total).
#
# All 4 files have logs in the same format:
# 1 2 3 4 5 6
# |-----------------| |---| |-|--------------------||------------------------------| |------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
# 2016.11.16 16:47:00 INFO ce[AVht0dNXFcyiYejytc3m][o.s.s.c.t.CeWorkerCallableImpl] Executed task | project=org.sonarqube:example-java-maven | type=REPORT | id=AVht0dNXFcyiYejytc3m | submitter=admin | time=1699ms
#
# 1: timestamp. Format is YYYY.MM.DD HH:MM:SS
# YYYY: year on 4 digits
# MM: month on 2 digits
# DD: day on 2 digits
# HH: hour of day on 2 digits in 24 hours format
# MM: minutes on 2 digits
# SS: seconds on 2 digits
# 2: log level.
# Possible values (in order of descending criticality): ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE
# 3: process identifier. Possible values: app (main), web (Web Server), ce (Compute Engine) and es (Elasticsearch)
# 4: SQ thread identifier. Can be empty.
# In the Web Server, if present, it will be the HTTP request ID.
# In the Compute Engine, if present, it will be the task ID.
# 5: logger name. Usually a class canonical name.
# Package names are truncated to keep the whole field to 20 characters max
# 6: log payload. Content of this field does not follow any specific format, can vary in length and include line returns.
# Some logs, however, will follow the convention to provide data in payload in the format " | key=value"
# Especially, log of profiled pieces of code will end with " | time=XXXXms".
# Global level of logs (applies to all 4 processes).
# Supported values are INFO (default), DEBUG and TRACE
#sonar.log.level=INFO
# Level of logs of each process can be controlled individually with their respective properties.
# When specified, they overwrite the level defined at global level.
# Supported values are INFO, DEBUG and TRACE
#sonar.log.level.app=INFO
#sonar.log.level.web=INFO
#sonar.log.level.ce=INFO
#sonar.log.level.es=INFO
# Path to log files. Can be absolute or relative to installation directory.
# Default is /logs
#sonar.path.logs=logs
# Rolling policy of log files
# - based on time if value starts with "time:", for example by day ("time:yyyy-MM-dd")
# or by month ("time:yyyy-MM")
# - based on size if value starts with "size:", for example "size:10MB"
# - disabled if value is "none". That needs logs to be managed by an external system like logrotate.
#sonar.log.rollingPolicy=time:yyyy-MM-dd
# Maximum number of files to keep if a rolling policy is enabled.
# - maximum value is 20 on size rolling policy
# - unlimited on time rolling policy. Set to zero to disable old file purging.
#sonar.log.maxFiles=7
# Access log is the list of all the HTTP requests received by server. If enabled, it is stored
# in the file {sonar.path.logs}/access.log. This file follows the same rolling policy as other log file
# (see sonar.log.rollingPolicy and sonar.log.maxFiles).
#sonar.web.accessLogs.enable=true
# Format of access log. It is ignored if sonar.web.accessLogs.enable=false. Possible values are:
# - "common" is the Common Log Format, shortcut to: %h %l %u %user %date "%r" %s %b
# - "combined" is another format widely recognized, shortcut to: %h %l %u [%t] "%r" %s %b "%i{Referer}" "%i{User-Agent}"
# - else a custom pattern. See http://logback.qos.ch/manual/layouts.html#AccessPatternLayout.
# The login of authenticated user is not implemented with "%u" but with "%reqAttribute{LOGIN}" (since version 6.1).
# The value displayed for anonymous users is "-".
# The SonarQube's HTTP request ID can be added to the pattern with "%reqAttribute{ID}" (since version 6.2).
# If SonarQube is behind a reverse proxy, then the following value allows to display the correct remote IP address:
#sonar.web.accessLogs.pattern=%i{X-Forwarded-For} %l %u [%t] "%r" %s %b "%i{Referer}" "%i{User-Agent}" "%reqAttribute{ID}"
# Default value (which was "combined" before version 6.2) is equivalent to "combined + SQ HTTP request ID":
#sonar.web.accessLogs.pattern=%h %l %u [%t] "%r" %s %b "%i{Referer}" "%i{User-Agent}" "%reqAttribute{ID}"
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OTHERS
# Delay in seconds between processing of notification queue. Default is 60 seconds.
#sonar.notifications.delay=60
# Paths to persistent data files (embedded database and search index) and temporary files.
# Can be absolute or relative to installation directory.
# Defaults are respectively /data and /temp
#sonar.path.data=data
#sonar.path.temp=temp
# Telemetry - Share anonymous SonarQube statistics
# By sharing anonymous SonarQube statistics, you help us understand how SonarQube is used so we can improve the product to work even better for you.
# We don't collect source code or IP addresses. And we don't share the data with anyone else.
# To see an example of the data shared: login as a global administrator, call the WS api/system/info and check the Statistics field.
#sonar.telemetry.enable=true
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEVELOPMENT - only for developers
# The following properties MUST NOT be used in production environments.
# Elasticsearch HTTP connector
#sonar.search.httpPort=-1
4启动sonarqube
注意:不要用root账号启动,因为sonar有elasticsearch
先创建一个sonar用户
useradd sonar
su sonar /home/sonar/sonarqube-7.7/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh
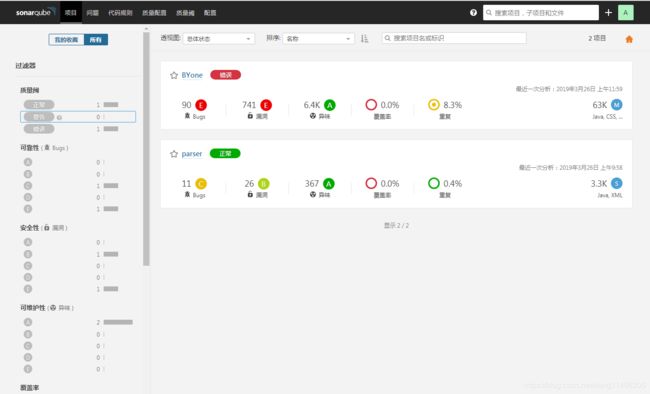
二、怎么分析项目
我用的是 idea+maven项目
1.在maven 的setting.xml文件中配置如下内容
sonar
true
http://10.128.1.19:9000
admin
admin
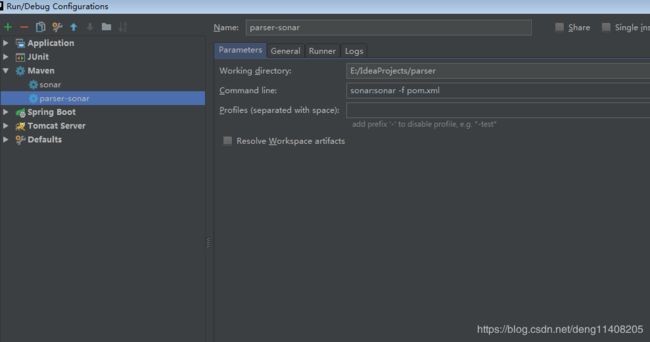
2.在idea中配置如下信息然后执行就能分析项目了
sonar:sonar -f pom.xml