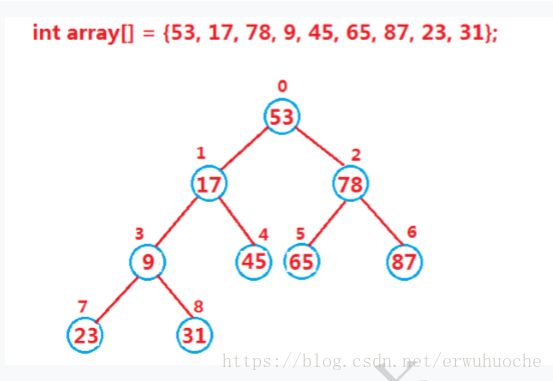
C语言实现堆
堆的概念
如果有一个关键码集合K={K0,K1,…,Kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储在一个数组中,并满足:
Ki <= K2*i + 1且Ki <= K2*i + 2(Ki < K2*i + 1且Ki >= K2*i + 2)i = 0,1,2,…,则称为大堆(或小堆)。
通俗点说,堆就是一个任意节点都小于(或大于)其左右孩子节点的一个二叉树。
堆的性质
堆存储在下标为0开始的数组中,因此它有以下特点:
- 如果i = 0,节点i是根节点,没有双亲节点;否则节点i的双亲节点为节点(i - 1)/ 2。
- 如果2 * i + 1 <= n - 1,则节点i的左孩子为节点2 * i + 1,否则节点i无左孩子。
- 如果2 * i + 2 <= n - 1,则节点i的右孩子为节点 2 * i + 2,否则节点i无右孩子
堆的创建
创建堆就是将数组的数值一次让入到一个二叉树中,然后通过调整使其满足一个堆,其将二叉树调整为一个最小堆的原理就是从最后一个非叶子节点开始整理,一直到根节点为止,将每个节点及其子树调整到满足小堆的性质即可。
具体的调整方法:
- 假设该节点下标为parent
- 找到该节点的左孩子left = parent * 2 + 1;
- 如果parent的右孩子节点存在,则取其左右孩子节点的最小值,和parent比较,若果比parnt小,则和parent值交换,然后就如上图一直调整,直到符合堆的性质为止。
堆的插入
将新元素插入到最小堆的最后面,插入之后,对其进行上浮调整。
上浮思想:
- 将要调整元素的下标定位child,首先需要找到child的父节点,parent = child - 1 / 2
- 比较child和parent的值,如果构建小堆,child的值小于parent的值,就进行交换。
- 然后让child = parent,parent = child - 1 / 2,以此循环
堆的删除
每次删除堆顶元素的时候,先将堆顶的元素和堆的最后一个值进行交换,然后删除最后一个元素,再对第一个元素进行下沉处理。
下沉操作思想:
- 先将下沉元素下标定位parent,找到其子节点child。
- 然后比较child,和child + 1的值,将较小的值和parent的值进行比较,如果建立的是小堆就,当child比parent小的时候就进行交换。
- 最后同上浮操作一样,以此循环。
堆的应用
数组的排序:解决这个问题可以使用两种方法
方法一、创建一个堆,然后每次取堆顶元素,将其放入数组中,然后再删除堆顶元素,以此循环。但这个方法会开辟额外的空间。
方法二、这个方法主要是利用了堆的上浮和下沉操作,不需要创建额外的堆,并且所耗费的时间也相对较少。
实现代码如下:
//heap.h
#pragma once
#include
//对于大堆来说,就是a>b
#define HeapMaxSize 1000
typedef int HeapType;
typedef int (*Compare)(HeapType a, HeapType b);
typedef struct Heap{
HeapType data[HeapMaxSize];
size_t size;
Compare cmp;
}Heap;
//heap.c
#include "heap.h"
//如果a小于b,就返回1,否则返回0
int Less(HeapType a, HeapType b){
return a < b;
}
void HeapInit(Heap* heap, Compare compare){
if(heap == NULL || compare == NULL){
return;//非法输入
}
heap -> size = 0;
heap -> cmp = compare;
return;
}
void Swap(HeapType* a, HeapType* b){
HeapType tmp;
tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b= tmp;
return;
}
void AdjustUp(HeapType data[], size_t size, Compare cmp, size_t index){
if(index >= size){
return;
}
//1.先找到当前节点对应的父节点
size_t child = index;
size_t parent = (child - 1)/2;
while(child > 0){
//2.比较父节点和子节点的大小关系,如果子节点值比父节点小,交换父子节点的值,如果子节点的值比父节点的大,说明调整也完成了
if(cmp( data[child] , data[parent] )){
Swap(&data[child], &data[parent]);
}else{
break;
}
//3.将当前父节点作为新的子节点,再去找子节点的父节点,循环进行比较和交换
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1)/2;
}
//4.子节点下标等于0,循环结束
return;
}
void HeapInsert(Heap* heap, HeapType value){
if(heap == NULL){
return;
}
if(heap -> size >= HeapMaxSize){
return;//堆满了
}
heap -> data[heap -> size++] = value;
AdjustUp(heap -> data, heap -> size, heap -> cmp, heap -> size - 1);
}
int HeapRoot(Heap* heap, HeapType* value){
if(heap == NULL){
return 0;
}
*value = heap -> data[0];
return *value;
}
void AdjustDown(HeapType data[], size_t size, Compare cmp, size_t index){
//1.设定parent指向开始的位置,找到对应的子树节点
size_t parent = index;
//2.设定一个child指向parent的左子树
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
//3.判定child和child+1的大小关系,如果child+1的值比child小,就让child = child + 1
while(child < size){
if(child + 1 < size && cmp(data[child + 1], data[child])){
child = child + 1;
}
//4.判定parent和child的值的大小关系,如果parent比child的值打,就进行交换
if(cmp(data[child], data[parent])){
Swap(&data[child], &data[parent]);
}else{
//否则就说明调整已经完成
break;
}
//5.parent赋值为child,child再重新复制成parent的做孩子节点
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
}
void HeapErase(Heap* heap){
if(heap == NULL){
return;//非法输入
}
if(heap -> size == 0){
return;//堆为空
}
Swap(&heap -> data[0], &heap -> data[heap -> size - 1]);
--heap -> size;
AdjustDown(heap -> data, heap -> size, heap -> cmp, 0);
}
//void HeapErase(Heap* heap){
// if(heap == NULL){
// return;
// }
// heap -> data[0] = heap -> data[heap -> size - 1];
// heap -> size--;
// size_t parent = 0 ;
// size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
// while(child < heap -> size){
// if(child < heap -> size && heap -> data[child ] < heap -> data[child - 1]){
// child ++;
// }
// if(Less(heap -> data[child], heap -> data[parent])){
// Swap(&heap -> data[child], &heap -> data[parent]);
// parent = child;
// child = 2 * parent + 1;
// }else{
// break;
// }
//
// }
//}
int HeapEmpty(Heap* heap){
if(heap == NULL){
return 0;
}
return heap -> size == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
size_t HeapSize(Heap* heap){
if(heap == NULL){
return 0;
}
return heap -> size;
}
void HeapDestroy(Heap* heap){
if(heap == NULL){
return;
}
heap -> size = 0;
return;
}
//需要开辟额外的空间
void HeapSort1(HeapType array[], size_t size){
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap, Less);
//1.先将数组里的所有元素插入到一个堆里面
size_t i = 0;
for(; i < size; ++i){
HeapInsert(&heap, array[i]);
}
//2.然后依次进行取堆顶元素,放回原数组,并删除堆顶元素
size_t output_index = 0;
while(HeapEmpty(&heap) != 1){
HeapType root = 0;
HeapRoot(&heap, &root);
array[output_index] = root;
++output_index;
HeapErase(&heap);
}
}
//不需要开辟额外的空间,和浪费额外的时间
void HeapSort2(HeapType array[], size_t size, Compare cmp){
if(size == 0 || size == 1){
return;
}
//1.将数组的所有元素放在一个堆中,循环结束之后,就调整成一个小堆
size_t i = 0;
for(; i < size;){
AdjustUp(array, i, cmp, i);
++i;
}
//2.依次去堆顶元素
while(i > 0){
Swap(&array[0], &array[i - 1]);
--i;
AdjustDown(array, i, cmp, 0);
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////TEST////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#if 1
#include