Nginx的安装及配置、安全认证
Nginx的安装及配置
目录
1.下载nginx的linux班安装包... 1
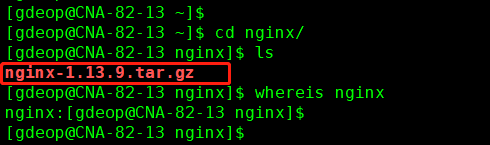
2.上传nginx-1.13.9.tar.gz到服务器上... 2
3.解压tar -zxvf nginx-1.13.9.tar.gz 包... 2
4.进入 cd nginx-1.13.9解压的目录... 3
4.1.查看nginx的安装路径 whereis nginx. 3
5.编译安装,执行以下命令... 3
6.make && make install 4
7.安装中问题解决... 5
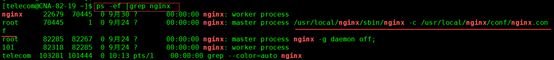
8.查看nginx进程 ps –ef |grep nginx. 6
9.验证nginx配置文件是否正确... 7
9.1 方法一:进入nginx安装目录sbin下,输入命令... 7
9.2 设置nginx开机自启动... 7
9.3 重新加载配置文件... 8
9.4 停止服务... 8
9.5 查看nginx版本... 9
10 错误解决... 9
10.1 方法一:... 10
10.2方法二:... 10
10.3 安装好后,浏览器访问,出现:... 11
11 编辑配置nginx.conf配置文件... 13
11.1.执行命令... 20
11.2 nginx.conf配置图... 21
12.配置集群案例:... 24
13.限制IP访问频率... 26
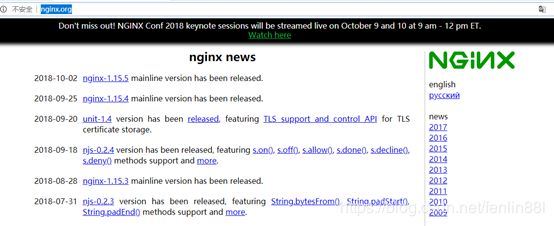
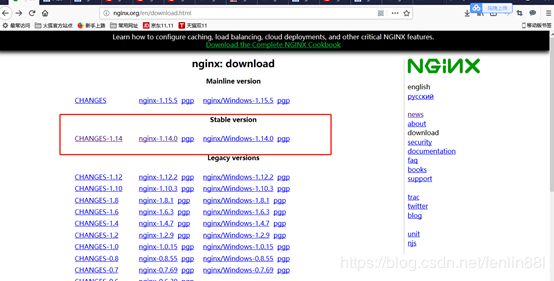
1.下载nginx的linux班安装包
即官网 http://nginx.org/
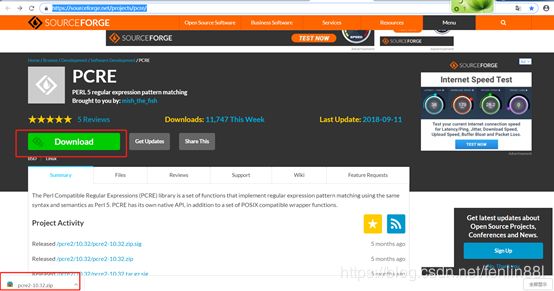
下载https://sourceforge.net/projects/pcre/
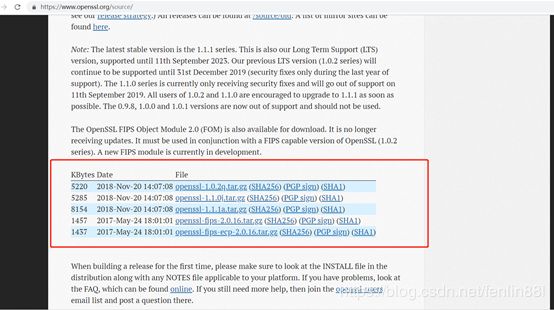
下载openssl安装包
http://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.1.0e.tar.gz
下载zlib包
http://www.zlib.net/
2.上传nginx-1.13.9.tar.gz到服务器上
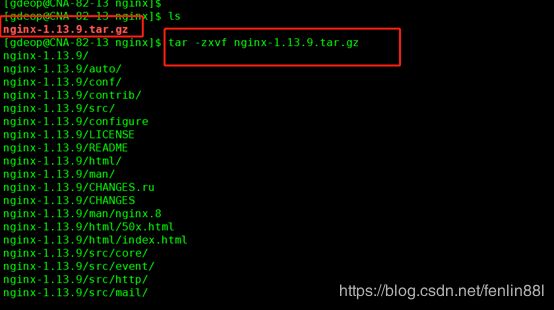
3.解压tar -zxvf nginx-1.13.9.tar.gz 包
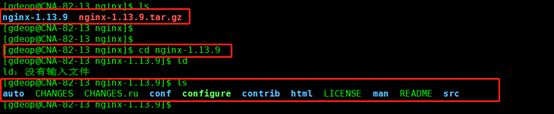
4.进入 cd nginx-1.13.9解压的目录
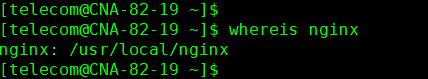
4.1.查看nginx的安装路径 whereis nginx
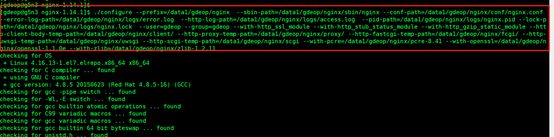
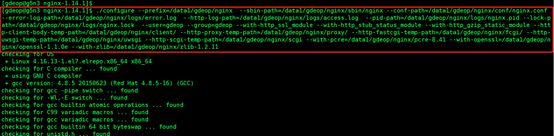
5.编译安装,执行以下命令
./configure --prefix=/data/gdeop/nginx --sbin-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/conf/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/logs/error.log --http-log-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/logs/access.log --pid-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/logs/nginx.pid --lock-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/logs/nginx.lock --user=gdeop --group=gdeop --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/client/ --http-proxy-temp-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/proxy/ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/fcgi/ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/data/gdeop/nginx/scgi --with-pcre= /data/gdeop/nginx/pcre-8.41 --with-openssl=/data/gdeop/nginx/openssl-1.1.0e --with-zlib= /data1/gdeop/nginx/zlib-1.2.11
注:
pcre-8.41 该插件解压目录
openssl-1.1.0e该插件解压目录
zlib-1.2.11该插件解压目录
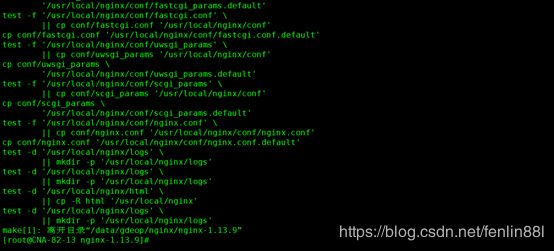
6.make && make install
7.安装中问题解决
如果报一下错:
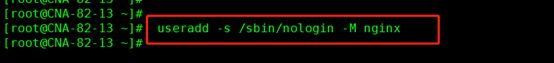
nginx: [emerg] getpwnam("nginx") failed (没有安装nginx用户导致的无法启动)
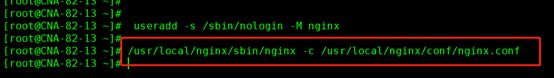
执行如下命令:# useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx
重新 启动nginx #./nginx
报如下错误:nginx: [emerg] mkdir() "/usr/local/nginx/client/ " failed (2: No such file or directory)
由于目录没有创建,手动创建该目录# mkdir sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/client/
重新执行启动nginx命令# ./nginx恭喜 启动成功
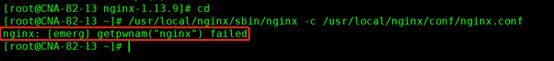
在执行/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 命令就错
8.查看nginx进程 ps –ef |grep nginx
如果nginx的log中没有nginx.pid就用:-c 指定映射 ,执行命令:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
注:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx是nginx安装启动路径
/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 是nginx安装配置文件路径
启动代码格式:nginx安装目录地址 -c nginx配置文件地址
例如:
[root@LinuxServer sbin]#
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
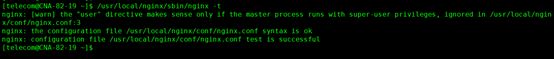
9.验证nginx配置文件是否正确
9.1 方法一:进入nginx安装目录sbin下,输入命令
./nginx –t 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx –t 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
9.2 设置nginx开机自启动
echo "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf" >> /etc/rc.local
相关资料:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhj5551/p/7589078.html
看到如下显示nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx.conf test is successful
说明配置文件正确!
启动服务
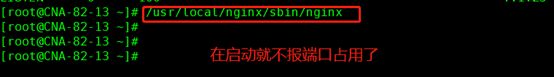
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx启动端口占用在启动用命令停止 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop9.3 重新加载配置文件
(修改后就要执行一次才生效)
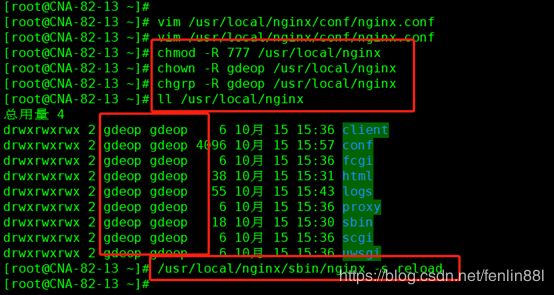
./nginx -s reload 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
9.4 停止服务
./nginx -s stop 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
优雅关闭(不接受新的连接请求,等待旧的连接请求处理完毕再关闭):nginx -s quit 或者 kill -QUIT 主进程号
./nginx -s quit 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx –s quit
重新启动,保存log常用
./nginx -s reopen 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reopen
9.5 查看nginx版本
./nginx –v 或/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx –v
10 错误解决
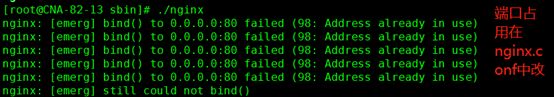
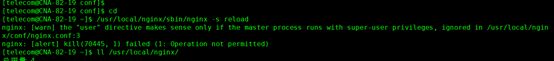
如果修改配置文件后,执行/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload出现以下错误
即解决方法为:
普通用户在restart和reload nginx时,会报错:
nginx: [warn] the "user" directive makes sense only if the master process runs with super-user privileges, ignored in /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:2
不能给开发人员root权限,没办法,只好这么做。
原因是:默认情况下Linux的1024以下端口是只有root用户才有权限占用
10.1 方法一:
所有用户都可以运行(因为是755权限,文件所有者:root,组所有者:root)
chown root.root nginx
chmod 755 nginx
chmod u+s nginx
10.2方法二:
仅 root 用户和 wyq 用户可以运行(因为是750权限,文件所有者:root,组所有者:www)
chown root.www nginx
chmod 750 nginx
chmod u+s nginx
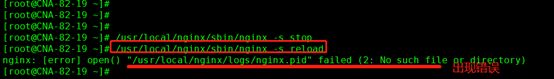
如果停止后重新加载配置文件 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload 出现以下错误
这时用 -c 映射 执行以下命令后:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
在执行/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload 命令
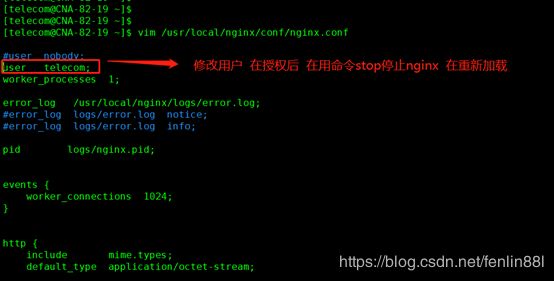
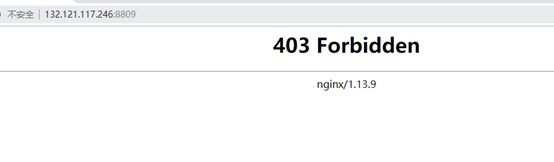
10.3 安装好后,浏览器访问,出现:
解决:
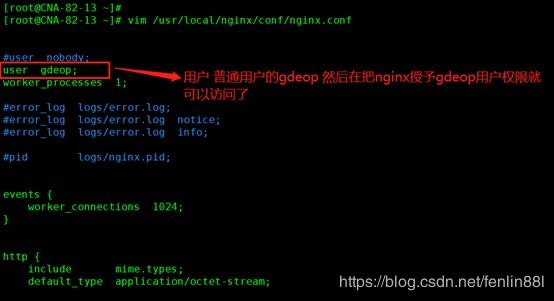
在ngin.conf中更改用户,在授权
授权
[root@CNA-82-13 ~]# chmod -R 777 /usr/local/nginx
[root@CNA-82-13 ~]# chown -R gdeop /usr/local/nginx
[root@CNA-82-13 ~]# chgrp -R gdeop /usr/local/nginx
再在浏览器中访问:
11 编辑配置nginx.conf配置文件
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginx.conf的配置文件(负载均衡 即集群):
#user nobody;
user gdeop;
worker_processes 8;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log notice;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log info;
pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid;
events {
#epoll是多路复用IO(I/O Multiplexing)中的一种方式,但是仅用于linux2.6以上内核,可以大大提高nginx的性能
use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 8m;
tcp_nodelay on;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
#proxy_buffer_size 64k;
#proxy_buffers 32 64k;
#charset utf-8;
#gzip_min_length 1024k;
#gzip_buffers 4 16k;
#gzip_http_version 1.0;
#gzip_comp_level 2;
#gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml;
#gzip_vary on;
upstream mule {
ip_hash;
#设定Nginx与服务器通信的尝试失败的次数。
#在fail_timeout参数定义的时间段内,如果失败的次数达到此值,Nginx就认为服务器不可用。
#在下一个fail_timeout时间段,服务器不会再被尝试。 失败的尝试次数默认是1。
#设为0就会停止统计尝试次数,认为服务器是一直可用的
#server 192.168.1.1:9092; #9092是用于测试
#server 192.168.1.1:8622 weight=2 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=10s;
#server 192.168.1.1:8622 weight=4;
#对name这个负载均衡条目中的所有节点,每个3秒检测一次,请求2次正常则标记 realserver状态为up,
#如果检测 5 次都失败,则标记 realserver的状态为down,超时时间为1秒
#check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=1000 type=http;
}
server {
listen 8808;
server_name _;#_代表任意地址
autoindex on; # 显示目录
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
index index.html;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
#root html;
#index index.html index.htm;
#mule是upstream模块化的名字(自定义) 即 upstream mule,下面代理proxy_pass http://名字要一样/项目访问路径,
#例 proxy_pass http://mule/Presure
proxy_pass http://mule;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
#下句为重定向,配置的话就多转发一次
#proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
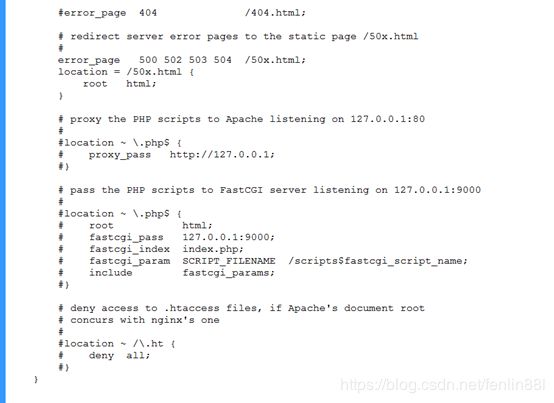
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
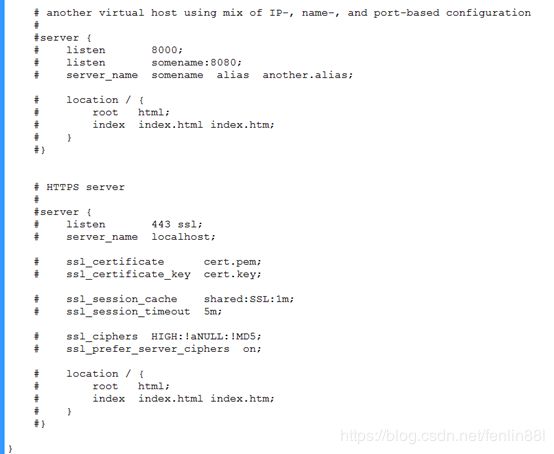
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
}
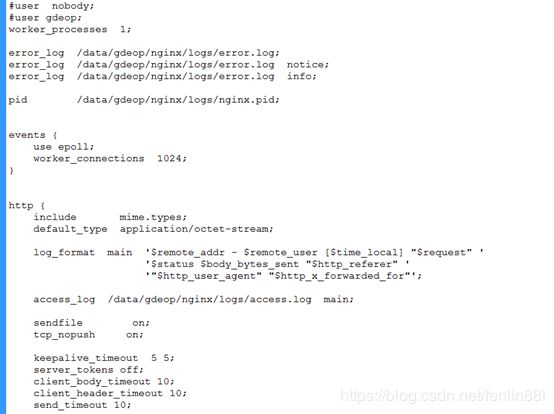
更新后(更完整):
#user nobody;
#user gdeop;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /data/gdeop/nginx/logs/error.log;
error_log /data/gdeop/nginx/logs/error.log notice;
error_log /data/gdeop/nginx/logs/error.log info;
pid /data/gdeop/nginx/logs/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /data/gdeop/nginx/logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 5 5;
server_tokens off;
client_body_timeout 10;
client_header_timeout 10;
send_timeout 10;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 8m;
tcp_nodelay on;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
upstream mule {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.1.1:8622 weight=1;
server 192.168.1.2:8623;
server 192.168.1.3:8624;
server 192.168.1.4:8622 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 9999;
server_name _;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 136.126.117.0/24;
allow 136.126.0.0/16;
allow 136.96.0.0/16;
allow 136.122.213.0/24;
allow 136.122.150.0/24;
deny all;
limit_rate 20k;
proxy_pass http://mule;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$ {
valid_referers none blocked video.artxun.com www.artxun.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite "/[a-zA-Z]\w{1,9}/" /$1/auth/signin last;
rewrite "/[a-zA-Z]\w{1,9}" /$1/auth/signin last;
return 404;
}
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
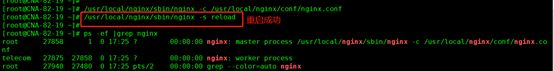
11.1.执行命令
停止:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
Pid用-c指定:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
加载配置文件:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
11.2 nginx.conf配置图
如果是配置nginx.service的话用以下命令开启服务:
添加至服务管理列表,并让其开机自动启动
[root@nginx ~]# chkconfig --add nginx
[root@nginx ~]# chkconfig nginx on
[root@nginx ~]# chkconfig nginx --list
nginx 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
2、nginx启动、停止、无间断服务重启
service nginx start
service nginx stop
Service nginx reload
12.配置集群案例:
13.限制IP访问频率
HttpLimitZoneModule 限制并发连接数实例
limit_zone只能定义在http作用域,limit_conn可以定义在http server location作用域
http {
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=conn:10m; #定义一个名为conn的limit_conn_zone用来存储session,大小是10M内存,1M能存储16000个状态;$binary_remote_addr是限制同一客户端ip地址;$server_name是限制同一server最大并发数;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=allips:10m rate=20r/s; #定义一个名为allips的limit_req_zone用来存储session,大小是10M内存,1M能存储16000个状态,以$binary_remote_addr为key,限制平均每秒的请求为20个,rate的值必须为整数,如果限制两秒钟一个请求,可以设置成30r/m
server{
location {
limit_conn conn 20; #limit_conn为限制并发连接数;
limit_rate 500k; #limit_rate为限制下载速度;
limit_req zone=allips burst=5 nodelay; #限制每ip每秒不超过20个请求,漏桶数burst为5,brust的意思是,如果第1秒、2,3,4秒请求为19个,第5秒的请求为25个是被允许的。但是如果你第1秒就25个请求,第2秒超过20的请求返回503错误。nodelay,如果不设置该选项,严格使用平均速率限制请求数,第1秒25个请求时,5个请求放到第2秒执行,设置nodelay,25个请求将在第1秒执行。
}
}
或
为了限流,我们可以在nginx的server中使用limit_zone设置一个限制域,比如
limit_zone zone1 $binary_remote_addr 10m
zone1为限制域的名称,$binary_remote_addr为客户端ip的二进制形式,这种方式比较节约空间,10m是此限制域的总大小。接着在location中配置limit_conn,限制单个用户最多连接数,比如
limit_conn zone1 10把用户连接限制在zone1,最多连接数为10,每个连接的最大速率为1Mbit(zonesize/limit_conn )。
为了防止用户大并发下载图片或视频等资源导致我们服务器带宽不够用,我们可以使用nginx的limit_rate_after和limit_rate限制下载速度,比如
location ^~ /videos/ {
...
limit_rate_after 1m;
limit_rate 150k;
...
}
limit_rate_after 1m表示用户的某个连接下载到1m后才开始限制,limit_rate表示下载的最大速度。这种情况下还得使用上面的配置来限制连接数,否则如果用户发起100个连接,那么总下载速度是150k*100,单个用户占用的带宽还是很大。
[A1]