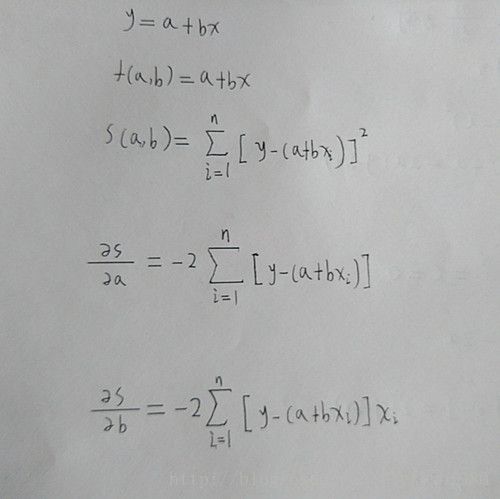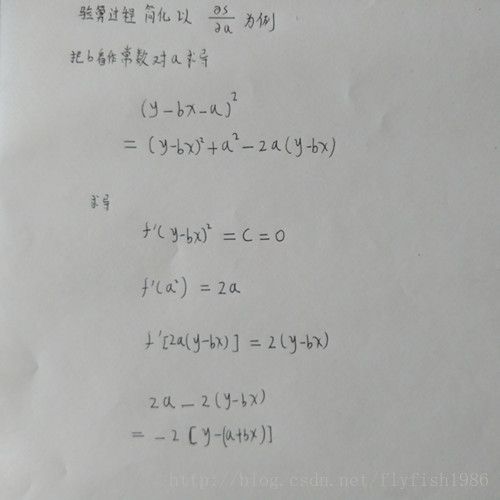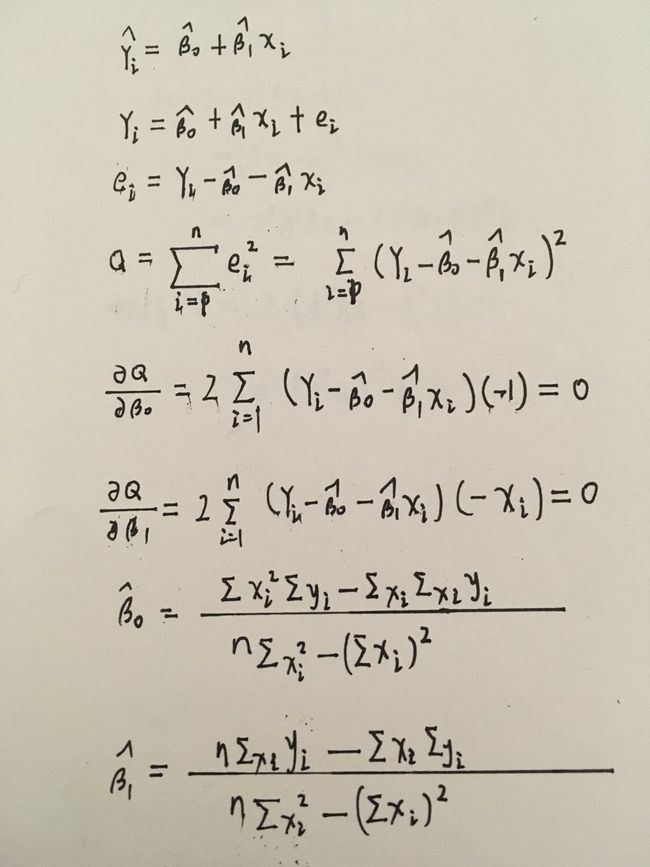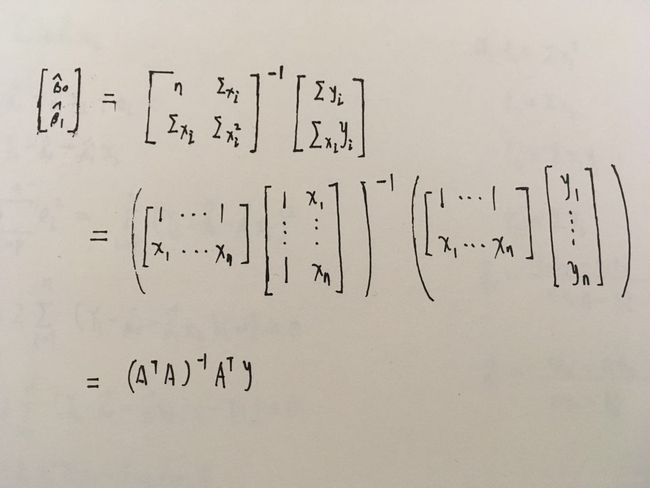TensorFlow - 最小二乘法
TensorFlow - 最小二乘法
flyfish

假设有如下,x和y的值,选取最合适的a, b,让该等式”尽量成立”, 从而找出最优解
y = ax+b 中
x,y的值是
(1,6)
(2,5)
(3,7)
(4,10)
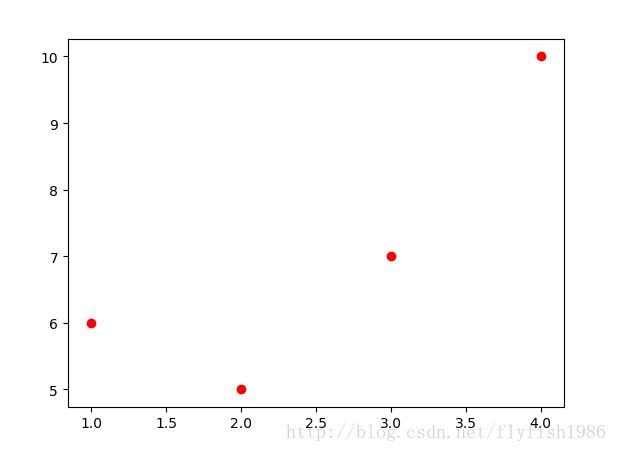
a+1b=6
a+2b=5
a+3b=7
a+4b=10
S(a,b)=[6−(a+1b)]2+[5−(a+2b)]2+[7−(a+3b)]2+[10−(a+4b)]2=4a2+30b2+20ab−56a−154b+210.
∂S∂a=0=8a+20b−56
∂S∂b=0=20a+60b−154.
解得
a = 3.5
b = 1.4
矩阵方式
Ax+By=C
A1x+B1y=C1,
A2x+B2y=C2,
矩阵表示
(A1B1A2B2)(xy)=(C1C2).
Ax=b
minx∈Rn∥Ax−b∥2
解释
∥x∥=|x| x的绝对值
∥x∥2:=x21+⋯+x2n−−−−−−−−−−√.
minx∈Rn∥Ax−b∥22
∥Ax−b∥22=(Ax−b)T∗(Ax−b)
T的含义 矩阵转置
⎡⎣⎢1,23,45,6⎤⎦⎥T=[1,3,52,4,6]
#include "stdafx.h"
#includeTensorFlow的一个例子
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#start stop number
x1 = np.linspace(1,100) #从1到100之间默认产生50个数
x2 = np.linspace(1,10,10)#从1到10之间产生10个数
x3 = np.random.randn(3, 4) #正态分布中返回3列数据,
#print(x1)
#print(x2)
#print(x3)
num_examples = 50
X = np.array([np.linspace(-2, 4, num_examples), np.linspace(-6, 6, num_examples)])
#2行50列数据
X += np.random.randn(2, num_examples)
x, y = X
#print(X.shape);#(2,50)
#print(x);#第一行数据 x是-2, 4之间产生50个数
#print(y);#第二行数据 y是-6, 6之间产生50个数
#print(np.transpose([y]));
#构建 50行,2列的数组,第一列都是1
x_with_bias = np.array([(1., a) for a in x]).astype(np.float32)
#print(x_with_bias.shape)# (50,2) 行数和列数
losses = []
training_steps = 50
learning_rate = 0.002
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Set up all the tensors, variables, and operations.
input = tf.constant(x_with_bias)
#矩阵转置 一行50列,变成50行1列
target = tf.constant(np.transpose([y]).astype(np.float32))
# an interface that takes a tuple as the first argument
#2行1列
#tf.random_normal(shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32, seed=None, name=None)
weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1], 0, 0.1))
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
'''
#tf.matmul(a, b, transpose_a=False, transpose_b=False, a_is_sparse=False, b_is_sparse=False, name=None)
# 2-D tensor `a`
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], shape=[2, 3])
# [[1. 2. 3.]
# [4. 5. 6.]]
# 2-D tensor `b`
b = tf.constant([7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12], shape=[3, 2])
# [[7. 8.]
# [9. 10.]
# [11. 12.]]
c = tf.matmul(a, b)
# [[58 64]
# [139 154]]
'''
yhat = tf.matmul(input, weights)
#减法 tf.subtract(10, 4) # 6
yerror = tf.subtract(yhat, target)
'''
tf.nn.l2_loss(t, name=None)
L2 Loss.
Computes half the L2 norm of a tensor without the sqrt:
output = sum(t ** 2) / 2
Args:
t: A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: float32, float64, int64, int32, uint8, int16, int8, complex64, qint8, quint8, qint32. Typically 2-D, but may have any dimensions.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A Tensor. Has the same type as t. 0-D.
'''
loss = tf.nn.l2_loss(yerror)
#梯度下降法 梯度下降法是求解最小二乘问题的一种迭代法
update_weights = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
for _ in range(training_steps):
# Repeatedly run the operations, updating the TensorFlow variable.
update_weights.run()
losses.append(loss.eval())
# Training is done, get the final values for the graphs
betas = weights.eval()
yhat = yhat.eval()
#print(weights.shape);
#print(weights.eval());
# Show the fit and the loss over time.
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=.3)
fig.set_size_inches(10, 4)
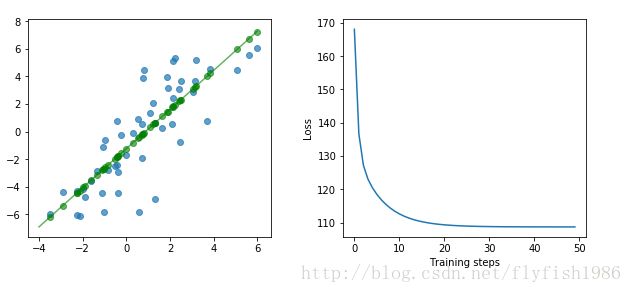
ax1.scatter(x, y, alpha=.7)
ax1.scatter(x, np.transpose(yhat)[0], c="g", alpha=.6)
line_x_range = (-4, 6)
ax1.plot(line_x_range, [betas[0] + a * betas[1] for a in line_x_range], "g", alpha=0.6)
ax2.plot(range(0, training_steps), losses)
ax2.set_ylabel("Loss")
ax2.set_xlabel("Training steps")
plt.show()使用Eigen库 矩阵计算
#include <iostream>
#include "Dense"
int main()
{
Eigen::MatrixXd x(4, 2);
x(0, 0) = 1;
x(1, 0) = 2;
x(2, 0) = 3;
x(3, 0) = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
x(i, 1) = 1;
Eigen::MatrixXd xt = x.transpose();
Eigen::MatrixXd y(4, 1);
y(0, 0) = 6;
y(1, 0) = 5;
y(2, 0) = 7;
y(3, 0) = 10;
Eigen::MatrixXd result(2, 1);
result = (xt * x).inverse() * xt * y;
std::cout << "y = " << result(0, 0) << "x + " << result(1, 0) << "\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}重新再整理一下