python基础 01
python 环境搭建
安装python
进入python官网下载自己电脑对应版本;安装时勾上path、pip、tcl/tk、test suite;并且安装在全英文路径下。
了解python之禅
Beautiful is better than ugly.
# 优美胜于丑陋(Python以编写优美的代码为目标)
Explicit is better than implicit.
# 明了胜于晦涩(优美的代码应当是明了的,命名规范,风格相似)
Simple is better than complex.
# 简洁胜于复杂(优美的代码应当是简洁的,不要有复杂的内部实现)
Complex is better than complicated.
# 复杂胜于凌乱(如果复杂不可避免,那代码间也不能有难懂的关系,要保持接口简洁)
Flat is better than nested.
# 扁平胜于嵌套(优美的代码应当是扁平的,不能有太多的嵌套)
Sparse is better than dense.
# 间隔胜于紧凑(优美的代码有适当的间隔,不要奢望一行代码解决问题)
Readability counts.
# 可读性很重要(优美的代码是可读的)
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
Although practicality beats purity.
# 即便假借特例的实用性之名,也不可违背这些规则(这些规则至高无上)
Errors should never pass silently.
Unless explicitly silenced.
# 不要包容所有错误,除非你确定需要这样做(精准地捕获异常,不写except:pass风格的代码)
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
# 当存在多种可能,不要尝试去猜测
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
# 而是尽量找一种,最好是唯一一种明显的解决方案(如果不确定,就用穷举法)
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
# 虽然这并不容易,因为你不是 Python 之父(这里的Dutch是指Guido)
Now is better than never.
Although never is often better than *right* now.
# 做也许好过不做,但不假思索就动手还不如不做(动手之前要细思量)
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
# 如果你无法向人描述你的方案,那肯定不是一个好方案;反之亦然(方案测评标准)
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
# 命名空间是一种绝妙的理念,我们应当多加利用(倡导与号召)
安装jupyter
安装好python后进去cmd输入python -m pip install ipython jupyter 或者 pip install ipython jupyter
进入jupyter
在cmd中输入 jupyter notebook
退出快捷键
- python ctrl + z
- jupyter ctrl + c
安装sublime Text
下载并安装好程序,并且安装好插件管理工具,在管理工具中安装以下推荐插件:
1. SublimeCodeIntel
2. Emmet
3. Git
4. Python PEP8 Autoformat
5. ConvertToUTF8
安装pycharm
安装前需要有Java运行环境
安装后激活码在百度搜 lanuy 找到激活码,并修改计算机C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件。
turtle
turtel 是python 自带的一个模块,引用前直接导入
turtle 指令集
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| turtle.pendown() | 将笔向下拿—–移动的时候绘制 |
| turtle.penup() | 将笔向上拿—–移动的时候布绘制 |
| turtle.pensize(宽度) | 将线的宽度设置为制定宽度 |
| turtle.forward(d) | 将turtle朝着指向方向向前移动制定距离 |
| turtle.backward(d) | 将turtle朝着指向的反方向向后移动制定距离,turtle的方向不改变 |
| turtle.right(angle) | 将turtle向右转动制定角度 |
| turtle.left(angle) | 将turtle向左转动制定角 |
| turtle.goto(x, y) | 将turtle移动到一个绝对位置 |
| turtle.setx(x) | 将turtle的x坐标移动到指定位置 |
| turtle.setx(y) | 将turtle的y坐标移动到指定位置 |
| turtle.setheading(angle) | 将turtle的方向设定为制定角度。0–东、90–北、180–西、270–南 |
| turtle.home() | 将turtle移动到起点(0, 0)和向东 |
| turtle. circle(r, ext, step) | 绘制一个制定半径,范围和阶数的圆 |
| turtle.dot(diameter, color) | 绘制一个制定半径和颜色的圆 |
| turtle.undo() | 取消(反复)最后一个图操作 |
| turtle.speed(s) | 设置turtle的速度为一个在1到10之间的整数,10 最大 |
| turtle.color(c) | 设置笔的颜色 |
| turtle.fillcolor(c) | 设置笔填充颜色 |
| turtle.begin_fill() | 在填充图形前访问这个方法 |
| turtle.end_fill | 在最后调用beain_fill之前填充绘制的图形 |
| turtle.filling() | 返回填充状态:True、False |
| turtle.clear() | 清除窗口,turtle的状态和位置布受影响 |
| turtle.reset() | 清除窗口,turtle的状态和位置将恢复默认值 |
| turtle.screensize(w, h) | 设置画布的宽度和高度 |
| turtle.hideturtle() | 隐藏turtle |
| turtle.showturtle() | 显示turtle |
| turtle.isvisible() | 如果turtle可见返回True |
| turtle.write(s, font = (“Arial”, 8, “normal”)) | 在turtle位置编写字符串s,字体是由字体名、字体大小和字体类型三部分组成 |
例题
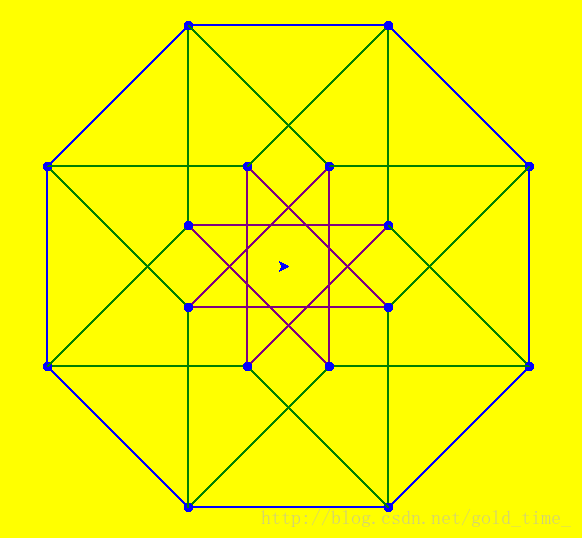
绘制超立方体
循环时需要海归的起始方向为0°(每次循环加固定角度), 或者在循环夹角的一半处(在循环的代码前后加上循环角度的一半)
import turtle
for i in range(0,8):
turtle.penup()
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.forward(41.42)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.pensize(2)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.color('blue')
turtle.dot(10)
turtle.color('purple')
turtle.forward(200)
turtle.color('blue')
turtle.dot(10)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.color('green')
turtle.forward(200)
turtle.color('blue')
turtle.dot(10)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.color('blue')
turtle.forward(200)
turtle.color('blue')
turtle.dot(10)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.color('green')
turtle.forward(200)
turtle.color('blue')
turtle.dot(10)
turtle.penup()
turtle.left(90)
turtle.goto(0,0)
turtle.left(45)
turtle.bgcolor('yellow')
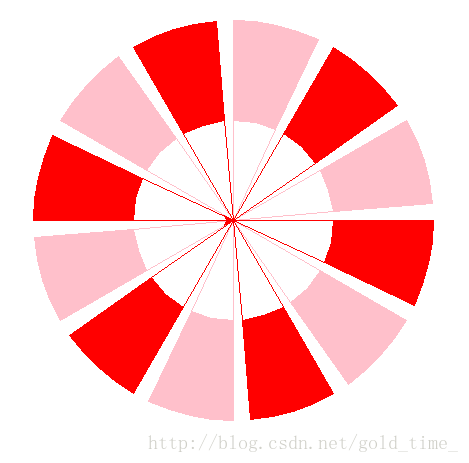
turtle.mainloop()绘制扇形
注意:圆弧的反向绘制和绘制不同角度的圆弧
import turtle
for _ in range(6):
turtle.color('pink')
turtle.left(30)
turtle.penup()
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.left(90)
turtle.begin_fill()
turtle.circle(100, -25)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.circle(200, 25)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.backward(200)
turtle.end_fill()
turtle.right(25)
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.penup()
turtle.backward(100)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.left(25)
turtle.left(30)
for _ in range(6):
turtle.color('red')
turtle.penup()
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.left(90)
turtle.begin_fill()
turtle.circle(100, -25)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.circle(200, 25)
turtle.right(90)
turtle.backward(200)
turtle.end_fill()
turtle.right(25)
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.penup()
turtle.backward(100)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.left(25)
turtle.left(60)
turtle.done()随意行走
海龟 在格子里随意行走,碰到边缘则停止
import turtle
from random import randint
turtle.speed(10)
turtle.color('gray')
for y in range(-80, 81, 10):
x= -80
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(x, y)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.forward(160)
turtle.left(90)
for x in range(-80, 81, 10):
y = -80
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(x, y)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.forward(160)
turtle.penup()
turtle.home()
turtle.pendown()
turtle.speed(1)
turtle.pensize(3)
turtle.color('red')
x = y = 0
while abs(x) < 80 and abs(y) < 80:
num = randint(1, 4)
if num == 1:
turtle.setheading(0)
turtle.forward(10)
x += 10
elif num == 2:
turtle.setheading(90)
turtle.forward(10)
y += 10
elif num == 3:
turtle.setheading(180)
turtle.forward(10)
x -= 10
else:
turtle.setheading(270)
turtle.forward(10)
y -= 10
turtle.done()运算符
数据类型:整数、浮点数、字符串、复数(complex)、布尔(bool)
赋值运算符、关系运算符、算术运算符、逻辑运算符、
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [][:] | 下标、切片 |
| ** | 指数 |
| ~ + - | 按位取反、正负号 |
| * / % // | 乘、除、模、整除 |
| + - | 加减 |
| >> << | 右移、左移 |
| & | 按位与 |
| ^| | 按位异或、按位或 |
| <= < > >= | 小于等于、小于、大于、大于等于 |
| == != | 等于、不等于 |
| is is not | 身份运算符 |
| in not in | 成员运算符 |
| not or and | 逻辑运算符 |
| = += -= = /= %= //= *= &= |= ^= >>= <<= | (复合)赋值运算符 |
常用命令符
| 命令 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| int() | 将一个数值或字符串转换成整数,可以指定编码。 |
| str() | 将一个字符串转换成浮点数。 |
| chr() | 将整数转换成该编码对应的字符串(一个字符)。 |
| ord() | 将字符串(一个字符)转换成对应的编码(整数) |
格式化输出
price = 6.3232
print('总造价是:¥ %.2f 元' % price) # %0.2f 精度为2位小数的浮点数
print('总造价是:¥ %f 元' % price) # %f 浮点数
print('总造价是:¥ %d 元' % price) # %d 整数
print('总造价是:¥ %s 元' % price) # %s 字符串变量
变量命名规则
硬性规则:
- 变量名由字母、数字和下划线构成,数字不能开头。
- 大小写敏感。
- 不要与关键字、保留字冲突。
官方建议:用全小写字母,多个单词用下划线连接,变量名中间不能有空格。见名知意。
PEP8要求:
- 用小写字母拼写,多个单词用下划线连接。
- 受保护的实例属性用单个下划线开头。
- 私有的实例属性用两个下划线开头。
实例
判断是不是闰年
year = eval(input('请输入年份:'))
condition1 = year % 4 == 0
condition2 = year % 100 != 0
condition3 = year % 400 == 0
is_leap = condition1 and condition2 or condition3
print(is_leap)分支结构
if···else···
实例
判断用户名和密码是否对应
import getpass # 输入密文时把input改成getpass.getpass
# 输入密码时没有回显
username = input('请输入用户名:')
password = getpass.getpass('请输入密码:')
if username == 'admin' and password =='123456':
print('欢迎使用本系统!')
print('开始使用App')
else:
print('用户名或密码错误!')
print('今天天气真好!') # 不受if或else控制if···elif···else···
实例
9*9乘法表
for row in range(1, 10):
for col in range(1, row + 1):
print('%d * %d = %d' % (row, col, row * col), end = '\t')
print()摇色子
from random import randint,random
face = randint(1,6)
if face == 1:
print('脱衣服')
elif face == 2:
print('唱歌')
elif face == 3:
print('喝酒')
elif face == 4:
print('真心话')
elif face == 5:
print('磕头')
else:
print('学狗叫')循环结构
for循环
实例
求能被3和5整除的数的和
my_sum = 0
for num in range(0,101):
if num % 3 == 0 or num % 5 == 0:
my_sum += num
print(my_sum) while循环
实例
和电脑玩石头剪刀布的游戏
from random import randint
'''
1 剪刀
2 石头
3 布
'''
my_money = ma_money = int(input('请输入开始金额'))
c = int(input('请输入赌注'))
while my_money > 0 and ma_money > 0:
x = input('请出拳:')
if x =='剪刀':
my = 1
elif x =='石头':
my = 2
else:
my = 3
ma = randint(1,3)
if my == 1:
if ma == 1:
print('电脑:剪刀 平局\n')
elif ma == 2:
my_money -= c
ma_money += c
print('电脑:石头,你:剪刀。\n电脑赢,扣你%d大洋 。\n电脑:¥%d ,你:¥%d\n'% (c, ma_money, my_money))
else:
my_money += c
ma_money -= c
print('电脑:布,你:剪刀。\n你赢,扣电脑%d大洋 。\n电脑:¥%d ,你:¥%d\n'% (c, ma_money, my_money))
elif my == 2:
if ma == 1:
my_money += c
ma_money -= c
print('电脑:剪刀,你:石头。\n你赢,扣电脑%d大洋 。\n电脑:¥%d ,你:¥%d\n'% (c, ma_money, my_money))
elif ma == 2:
print('电脑:石头 平局\n')
else:
my_money -= c
ma_money += c
print('电脑:布,你:石头。\n电脑赢,扣你%d大洋 。\n电脑:¥%d ,你:¥%d\n'% (c, ma_money, my_money))
else:
if ma == 1:
my_money -= c
ma_money += c
print('电脑:剪刀,你:布。\n电脑赢,扣你%d大洋 。\n电脑:¥%d ,你:¥%d\n'% (c, ma_money, my_money)
elif ma == 2:
my_money += c
ma_money -= c
print('电脑:石头,你:布。\n你赢,扣电脑%d大洋 。\n电脑:¥%d ,你:¥%d\n'% (c, ma_money, my_money))
else:
print('电脑:布 平局\n')
if my_money<=0:
print('很遗憾,你失败了')
if ma_money<=0:
print('恭喜,你赢了')人出数字电脑猜
要求电脑根据产生的值的大小和我的值比较后调整下一次产生值的范围
需要有两个变量储每次变化范围的值
from random import randint
my = int(input('计算机要猜的数(1-100):'))
game_over = False
if my < 1 or my > 100:
game_over = True
print('重新输入:')
nextmax = 0
my_max = 100
my_max = randint(nextmax+1 , my_max )
data = 101
while not game_over:
if my_max > my:
data= my_max
my_max = randint(nextmax+1 , data-1 )
print(my_max)
elif my_max < my:
nextmax = my_max
my_max = randint(nextmax+1 , data-1 )
print(my_max)
else:
print('哈哈,就这么简单')
game_over = True穷举法
捕鱼
a b c d e 五人半晚钓鱼后都睡觉了,早上a起床后把掉的鱼分成5份 拿走自己的一份 并扔掉多的一条1条,b、c、d、e依次这样做,问,最少捕了多少条鱼
fish = 1
while True:
total = fish
oo = True
for _ in range(5):
if (total - 1) % 5 == 0:
total = (total - 1) // 5 * 4
else:
oo = False
break
if oo:
print(fish)
break
fish += 1买鸡
'''
公鸡五元一只,母鸡三元一只,小鸡一元三只
用100元买100只鸡 问公鸡母鸡和小鸡各多少只
'''
'''
for x in range(21): # 执行了 21*34*34 次
for y in range(34):
for z in range (0, 100, 3):
if 5 * x + 3 * y + z // 3 == 100 and x + y + z == 100:
print(x, y, z)
'''
for x in range(21): # 执行了 21*34 次
for y in range(34):
if 5 * x + 3 * y + (100 - x - y) // 3 == 100 and x + y + (100 - x - y) == 100 and (100 - x - y) % 3 == 0:
z = 100 - x - y
print(x, y, z)计算机浮点数运算的 坑
浮点数运算例子
# 由于计算机浮点数存储方式
# 千万不要做浮点数的 == 和 != 运算
# 否则,计算结果将完全出乎意料
print(0.1 + 0.2 + 0.3) # 0.6000000000000001
print(0.3 + 0.2 + 0.1) # 0.6代码优化
完美数原代码
完美数 = 自身所有因子的和
such :6 = 1 + 2 + 3 :28 = 1+2+7+4+14
求1-10000的所有完美数
import time
start = time.time()
for num in range(1, 10000):
my = 0
q = num / 2 + 1
for i in range(1, int(q)):
if num % i == 0:
my += i
# print(my)
if num == my:
print(num)
end = time.time()
print(end - start,'s')完美数优化代码
优化后代码运行时间大幅缩短
import time
from math import sqrt
start = time.time()
for num in range(2, 10000):
my = 0
q = int(sqrt(num))
for i in range(1, q+1):
if num % i == 0:
my += i
if i != 1 and i !=num // i:
my += num // i
if num == my:
print(num)
end = time.time()
print(end - start,'s')综合训练
craps 赌博游戏
规则:玩家掷两个骰子,每个骰子点数为1-6,如果第一次点数和为7或11,则玩家胜;如果点数和为2、3或12,则玩家输庄家胜。若和为其他点数,则记录第一次的点数和,玩家继续掷骰子,直至点数和等于第一次掷出的点数和则玩家胜;若掷出的点数和为7则庄家胜。
from random import randint
salary_all1 = eval(input('请输入玩家起始赌金:'))
salary_all2 = eval(input('请输入庄家起始赌金:'))
salary = eval(input('请输入赌注:'))
i = 0
while True:
'''
i += 1
if i != 1:
salary = eval(input('请输入赌注:')) # 是否每把调整赌注
'''
frist1 = randint(1, 6)
frist2 = randint(1, 6)
frist_sum = frist1 + frist2
print(frist_sum)
if frist_sum == 7 or frist_sum == 11:
salary_all1 += salary
salary_all2 -= salary
print('玩家胜,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
if salary_all1 <= 0 :
print('玩家赌金不足')
break
elif salary_all2 <= 0:
print('庄家赌金不足')
break
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'y':
continue
elif frist_sum == 2 or frist_sum == 3 or frist_sum == 12:
salary_all1 -= salary
salary_all2 += salary
print('庄家赢,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
if salary_all1 <= 0 :
print('玩家赌金不足')
break
elif salary_all2 <= 0:
print('庄家赌金不足')
break
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'y':
continue
else:
while True:
# salary = eval(input('请输入赌注:')) # 是否每把调整赌注
next1 = randint(1, 6)
next2 = randint(1, 6)
count = next1 + next2
print(count)
if count == frist_sum:
salary_all1 += salary
salary_all2 -= salary
print('玩家胜,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
if salary_all1 <= 0 :
print('玩家赌金不足')
break
elif salary_all2 <= 0:
print('庄家赌金不足')
break
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'n':
break
elif count == 7:
salary_all1 -= salary
salary_all2 += salary
print('庄家胜,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
if salary_all1 <= 0 :
print('玩家赌金不足')
break
elif salary_all2 <= 0:
print('庄家赌金不足')
break
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'n':
break
print('游戏结束')
break每次重新开始的craps
下面代码表示:若每次分出胜负后,重新开始将重新摇出第一次的点数
from random import randint
salary_all1 = eval(input('请输入玩家起始赌金:'))
salary_all2 = eval(input('请输入庄家起始赌金:'))
salary = eval(input('请输入赌注'))
while True:
restart = True
frist1 = randint(1, 6)
frist2 = randint(1, 6)
frist_sum = frist1 + frist2
print('第一次摇色子',frist_sum)
if frist_sum == 7 or frist_sum == 11:
salary_all1 += salary
salary_all2 -= salary
print('玩家胜,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'y':
print('重新开始')
continue
elif frist_sum == 2 or frist_sum == 3 or frist_sum == 12:
salary_all1 -= salary
salary_all2 += salary
print('庄家赢,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'y':
print('重新开始')
continue
else:
while True:
next1 = randint(1, 6)
next2 = randint(1, 6)
count = next1 + next2
print('非第一次摇色子', count)
if count == frist_sum:
salary_all1 += salary
salary_all2 -= salary
print('玩家胜,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'n':
restart = True
break
else:
restart = False
break
elif count == 7:
salary_all1 -= salary
salary_all2 += salary
print('庄家胜,玩家剩余金额为%d,庄家剩余金额为%d' % (salary_all1,salary_all2))
is_continue = input('赌豪继续吗(y/n)?')
if is_continue == 'n':
restart = True
break
else:
restart = False
break
if salary_all1 <= 0 :
print('玩家赌金不足')
break
elif salary_all2 <= 0:
print('庄家赌金不足')
break
if restart == True:
print('游戏结束')
break
else:
print('重新开始')