工厂方法模式与抽象工厂模式
本文是转的
一、引子
话说十年前,有一个暴发户,他家有三辆汽车——Benz奔驰、Bmw宝马、Audi奥迪,还雇了司机为他开车。不过,暴发户坐车时总是怪怪的:上Benz车后跟司机说“开奔驰车!”,坐上Bmw后他说“开宝马车!”,坐上Audi说“开奥迪车!”。你一定说:这人有病!直接说开车不就行了?!
而当把这个暴发户的行为放到我们程序设计中来时,会发现这是一个普遍存在的现象。幸运的是,这种有病的现象在OO(面向对象)语言中可以避免了。下面就以Java语言为基础来引入我们本文的主题:工厂模式。
二、分类
工厂模式主要是为创建对象提供过渡接口,以便将创建对象的具体过程屏蔽隔离起来,达到提高灵活性的目的。
工厂模式在《Java与模式》中分为三类:
1)简单工厂模式(Simple Factory)
2)工厂方法模式(Factory Method)
3)抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory)
这三种模式从上到下逐步抽象,并且更具一般性。
GOF在《设计模式》一书中将工厂模式分为两类:工厂方法模式(Factory Method)与抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory)。将简单工厂模式(Simple Factory)看为工厂方法模式的一种特例,两者归为一类。两者皆可,在本文使用《Java与模式》的分类方法。下面来看看这些工厂模式是怎么来“治病”的。
三、简单工厂模式
简单工厂模式又称静态工厂方法模式。重命名上就可以看出这个模式一定很简单。它存在的目的很简单:定义一个用于创建对象的接口。
先来看看它的组成:
1) 工厂类角色:这是本模式的核心,含有一定的商业逻辑和判断逻辑。在java中它往往由一个具体类实现。
2) 抽象产品角色:它一般是具体产品继承的父类或者实现的接口。在java中由接口或者抽象类来实现。
3) 具体产品角色:工厂类所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由一个具体类实现。
来用类图来清晰的表示下的它们之间的关系(如果对类图不太了解,请参考我关于类图的文章):
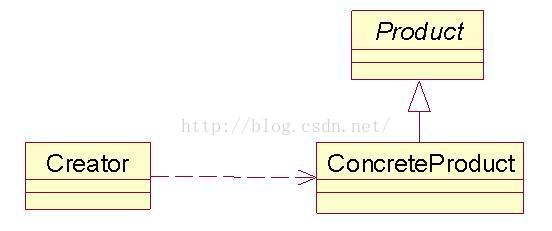
那么简单工厂模式怎么来使用呢?我们就以简单工厂模式来改造暴发户坐车的方式——现在暴发户只需要坐在车里对司机说句:“开车”就可以了。
将本程序空缺的其他信息填充完整后即可运行。如果你将所有的类放在一个文件中,请不要忘记只能有一个类被声明为public。本程序在jdk1.4 下运行通过。
程序中各个类的关系表达如下:

这便是简单工厂模式了。怎么样,使用起来很简单吧?那么它带来了什么好处呢?
首先,使用了简单工厂模式后,我们的程序不在“有病”,更加符合现实中的情况;而且客户端免除了直接创建产品对象的责任,而仅仅负责“消费”产品(正如暴发户所为)。
下面我们从开闭原则(对扩展开放;对修改封闭)上来分析下简单工厂模式。当暴发户增加了一辆车的时候,只要符合抽象产品制定的合同,那么只要通知工厂类知道就可以被客户使用了。所以对产品部分来说,它是符合开闭原则的;但是工厂部分好像不太理想,因为每增加一辆车,都要在工厂类中增加相应的业务逻辑或者判断逻辑,这显然是违背开闭原则的。可想而知对于新产品的加入,工厂类是很被动的。对于这样的工厂类(在我们的例子中是为司机师傅),我们称它为全能类或者上帝类。
我们举的例子是最简单的情况,而在实际应用中,很可能产品是一个多层次的树状结构。由于简单工厂模式中只有一个工厂类来对应这些产品,所以这可能会把我们的上帝累坏了,也累坏了我们这些程序员:(
于是工厂方法模式作为救世主出现了。
四、工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式去掉了简单工厂模式中工厂方法的静态属性,使得它可以被子类继承。这样在简单工厂模式里集中在工厂方法上的压力可以由工厂方法模式里不同的工厂子类来分担。
你应该大致猜出了工厂方法模式的结构,来看下它的组成:
1) 抽象工厂角色: 这是工厂方法模式的核心,它与应用程序无关。是具体工厂角色必须实现的接口或者必须继承的父类。在java中它由抽象类或者接口来实现。
2) 具体工厂角色:它含有和具体业务逻辑有关的代码。由应用程序调用以创建对应的具体产品的对象。
3) 抽象产品角色:它是具体产品继承的父类或者是实现的接口。在java中一般有抽象类或者接口来实现。
4) 具体产品角色:具体工厂角色所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由具体的类来实现。
用类图来清晰的表示下的它们之间的关系:

工厂方法模式使用继承自抽象工厂角色的多个子类来代替简单工厂模式中的“上帝类”。正如上面所说,这样便分担了对象承受的压力;而且这样使得结构变得灵活起来——当有新的产品(即暴发户的汽车)产生时,只要按照抽象产品角色、抽象工厂角色提供的合同来生成,那么就可以被客户使用,而不必去修改任何已有的代码。可以看出工厂角色的结构也是符合开闭原则的!
我们还是老规矩,使用一个完整的例子来看看工厂模式各个角色之间是如何来协调的。话说暴发户生意越做越大,自己的爱车也越来越多。这可苦了那位司机师傅了,什么车它都要记得,维护,都要经过他来使用!于是暴发户同情他说:看你跟我这么多年的份上,以后你不用这么辛苦了,我给你分配几个人手,你只管管好他们就行了!于是,工厂方法模式的管理出现了。代码如下:
五、小结
工厂方法模式仿佛已经很完美的对对象的创建进行了包装,使得客户程序中仅仅处理抽象产品角色提供的接口。那我们是否一定要在代码中遍布工厂呢?大可不必。也许在下面情况下你可以考虑使用工厂方法模式:
1) 当客户程序不需要知道要使用对象的创建过程。
2)客户程序使用的对象存在变动的可能,或者根本就不知道使用哪一个具体的对象。
简单工厂模式与工厂方法模式真正的避免了代码的改动了?没有。在简单工厂模式中,新产品的加入要修改工厂角色中的判断语句;而在工厂方法模式中,要么将判断逻辑留在抽象工厂角色中,要么在客户程序中将具体工厂角色写死(就象上面的例子一样)。而且产品对象创建条件的改变必然会引起工厂角色的修改。
面对这种情况,Java的反射机制与配置文件的巧妙结合突破了限制——这在Spring中完美的体现了出来。
六、抽象工厂模式
先来认识下什么是产品族: 位于不同产品等级结构中,功能相关联的产品组成的家族。还是让我们用一个例子来形象地说明一下吧。

图中的BmwCar和BenzCar就是两个产品树(产品层次结构);而如图所示的BenzSportsCar和BmwSportsCar就是一个产品族。他们都可以放到跑车家族中,因此功能有所关联。同理BmwBussinessCar和BenzSportsCar也是一个产品族。
回到抽象工厂模式的话题上。可以说,抽象工厂模式和工厂方法模式的区别就在于需要创建对象的复杂程度上。而且抽象工厂模式是三个里面最为抽象、最具一般性的。抽象工厂模式的用意为:给客户端提供一个接口,可以创建多个产品族中的产品对象,而且使用抽象工厂模式还要满足一下条件:
1) 系统中有多个产品族,而系统一次只可能消费其中一族产品。
2) 同属于同一个产品族的产品以其使用。
来看看抽象工厂模式的各个角色(和工厂方法的如出一辙):
1) 抽象工厂角色: 这是工厂方法模式的核心,它与应用程序无关。是具体工厂角色必须实现的接口或者必须继承的父类。在java中它由抽象类或者接口来实现。
2) 具体工厂角色:它含有和具体业务逻辑有关的代码。由应用程序调用以创建对应的具体产品的对象。在java中它由具体的类来实现。
3)抽象产品角色:它是具体产品继承的父类或者是实现的接口。在java中一般有抽象类或者接口来实现。
4) 具体产品角色:具体工厂角色所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由具体的类来实现。
类图如下:
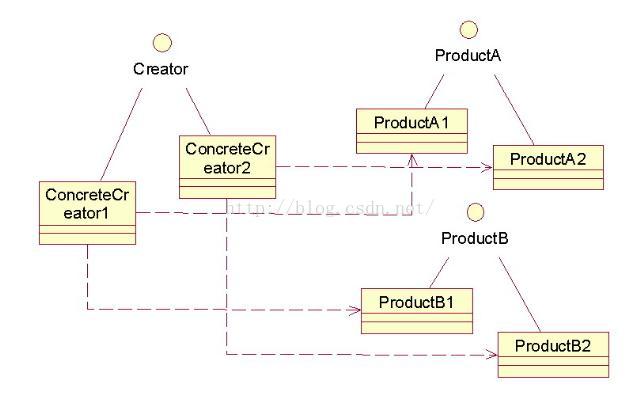
看过了前两个模式,对这个模式各个角色之间的协调情况应该心里有个数了,我就不举具体的例子了。只是一定要注意满足使用抽象工厂模式的条件哦。
抽象工厂示例:
抽象工厂模式与工厂方法模式的区别 :可以这么说,工厂方法模式是一种极端情况的抽象工厂模式,而抽象工厂模式可以看成是工厂方法模式的一种推广。
(1)、其实工厂方法模式是用来创建一个产品的等级结构的,而抽象工厂模式是用来创建多个产品的等级结构的。工厂方法创建一般只有一个方法,创建一种产品。抽象工厂一般有多个方法,创建一系列产品。
(2)、工厂方法模式只有一个抽象产品类,而抽象工厂模式有多个。工厂方法模式的具体工厂类只能创建一个具体产品类的实例,而抽象工厂模式可以创建多个。
简而言之->
每个具体工厂类只能创建一个具体产品类的实例。
每个具体工厂类可以创建多个具体产品类的实例。
一、引子
话说十年前,有一个暴发户,他家有三辆汽车——Benz奔驰、Bmw宝马、Audi奥迪,还雇了司机为他开车。不过,暴发户坐车时总是怪怪的:上Benz车后跟司机说“开奔驰车!”,坐上Bmw后他说“开宝马车!”,坐上Audi说“开奥迪车!”。你一定说:这人有病!直接说开车不就行了?!
而当把这个暴发户的行为放到我们程序设计中来时,会发现这是一个普遍存在的现象。幸运的是,这种有病的现象在OO(面向对象)语言中可以避免了。下面就以Java语言为基础来引入我们本文的主题:工厂模式。
二、分类
工厂模式主要是为创建对象提供过渡接口,以便将创建对象的具体过程屏蔽隔离起来,达到提高灵活性的目的。
工厂模式在《Java与模式》中分为三类:
1)简单工厂模式(Simple Factory)
2)工厂方法模式(Factory Method)
3)抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory)
这三种模式从上到下逐步抽象,并且更具一般性。
GOF在《设计模式》一书中将工厂模式分为两类:工厂方法模式(Factory Method)与抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory)。将简单工厂模式(Simple Factory)看为工厂方法模式的一种特例,两者归为一类。两者皆可,在本文使用《Java与模式》的分类方法。下面来看看这些工厂模式是怎么来“治病”的。
三、简单工厂模式
简单工厂模式又称静态工厂方法模式。重命名上就可以看出这个模式一定很简单。它存在的目的很简单:定义一个用于创建对象的接口。
先来看看它的组成:
1) 工厂类角色:这是本模式的核心,含有一定的商业逻辑和判断逻辑。在java中它往往由一个具体类实现。
2) 抽象产品角色:它一般是具体产品继承的父类或者实现的接口。在java中由接口或者抽象类来实现。
3) 具体产品角色:工厂类所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由一个具体类实现。
来用类图来清晰的表示下的它们之间的关系(如果对类图不太了解,请参考我关于类图的文章):

那么简单工厂模式怎么来使用呢?我们就以简单工厂模式来改造暴发户坐车的方式——现在暴发户只需要坐在车里对司机说句:“开车”就可以了。
//抽象产品角色
public interface Car{
public void drive();
}
//具体产品角色
public class Benz implements Car{
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving Benz ");
}
}
public class Bmw implements Car{
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving Bmw ");
}
}
。。。(奥迪我就不写了:P)
//工厂类角色
public class Driver{
//工厂方法.注意 返回类型为抽象产品角色
public static Car driverCar(String s)throws Exception {
//判断逻辑,返回具体的产品角色给Client
if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("Benz"))
return new Benz();
else if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("Bmw"))
return new Bmw();
......
else throw new Exception();
//欢迎暴发户出场......
public class Magnate{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
//告诉司机我今天坐奔驰
Car car = Driver.driverCar("benz");
//下命令:开车
car.drive();
......
将本程序空缺的其他信息填充完整后即可运行。如果你将所有的类放在一个文件中,请不要忘记只能有一个类被声明为public。本程序在jdk1.4 下运行通过。
程序中各个类的关系表达如下:

这便是简单工厂模式了。怎么样,使用起来很简单吧?那么它带来了什么好处呢?
首先,使用了简单工厂模式后,我们的程序不在“有病”,更加符合现实中的情况;而且客户端免除了直接创建产品对象的责任,而仅仅负责“消费”产品(正如暴发户所为)。
下面我们从开闭原则(对扩展开放;对修改封闭)上来分析下简单工厂模式。当暴发户增加了一辆车的时候,只要符合抽象产品制定的合同,那么只要通知工厂类知道就可以被客户使用了。所以对产品部分来说,它是符合开闭原则的;但是工厂部分好像不太理想,因为每增加一辆车,都要在工厂类中增加相应的业务逻辑或者判断逻辑,这显然是违背开闭原则的。可想而知对于新产品的加入,工厂类是很被动的。对于这样的工厂类(在我们的例子中是为司机师傅),我们称它为全能类或者上帝类。
我们举的例子是最简单的情况,而在实际应用中,很可能产品是一个多层次的树状结构。由于简单工厂模式中只有一个工厂类来对应这些产品,所以这可能会把我们的上帝累坏了,也累坏了我们这些程序员:(
于是工厂方法模式作为救世主出现了。
四、工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式去掉了简单工厂模式中工厂方法的静态属性,使得它可以被子类继承。这样在简单工厂模式里集中在工厂方法上的压力可以由工厂方法模式里不同的工厂子类来分担。
你应该大致猜出了工厂方法模式的结构,来看下它的组成:
1) 抽象工厂角色: 这是工厂方法模式的核心,它与应用程序无关。是具体工厂角色必须实现的接口或者必须继承的父类。在java中它由抽象类或者接口来实现。
2) 具体工厂角色:它含有和具体业务逻辑有关的代码。由应用程序调用以创建对应的具体产品的对象。
3) 抽象产品角色:它是具体产品继承的父类或者是实现的接口。在java中一般有抽象类或者接口来实现。
4) 具体产品角色:具体工厂角色所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由具体的类来实现。
用类图来清晰的表示下的它们之间的关系:

工厂方法模式使用继承自抽象工厂角色的多个子类来代替简单工厂模式中的“上帝类”。正如上面所说,这样便分担了对象承受的压力;而且这样使得结构变得灵活起来——当有新的产品(即暴发户的汽车)产生时,只要按照抽象产品角色、抽象工厂角色提供的合同来生成,那么就可以被客户使用,而不必去修改任何已有的代码。可以看出工厂角色的结构也是符合开闭原则的!
我们还是老规矩,使用一个完整的例子来看看工厂模式各个角色之间是如何来协调的。话说暴发户生意越做越大,自己的爱车也越来越多。这可苦了那位司机师傅了,什么车它都要记得,维护,都要经过他来使用!于是暴发户同情他说:看你跟我这么多年的份上,以后你不用这么辛苦了,我给你分配几个人手,你只管管好他们就行了!于是,工厂方法模式的管理出现了。代码如下:
//抽象产品角色,具体产品角色与简单工厂模式类似,只是变得复杂了些,这里略。
//抽象工厂角色
public interface Driver{
public Car driverCar();
}
public class BenzDriver implements Driver{
public Car driverCar(){
return new Benz();
}
}
public class BmwDriver implements Driver{
public Car driverCar() {
return new Bmw();
}
}
//应该和具体产品形成对应关系...
//有请暴发户先生
public class Magnate
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
Driver driver = new BenzDriver();
Car car = driver.driverCar();
car.drive();
}
……
}五、小结
工厂方法模式仿佛已经很完美的对对象的创建进行了包装,使得客户程序中仅仅处理抽象产品角色提供的接口。那我们是否一定要在代码中遍布工厂呢?大可不必。也许在下面情况下你可以考虑使用工厂方法模式:
1) 当客户程序不需要知道要使用对象的创建过程。
2)客户程序使用的对象存在变动的可能,或者根本就不知道使用哪一个具体的对象。
简单工厂模式与工厂方法模式真正的避免了代码的改动了?没有。在简单工厂模式中,新产品的加入要修改工厂角色中的判断语句;而在工厂方法模式中,要么将判断逻辑留在抽象工厂角色中,要么在客户程序中将具体工厂角色写死(就象上面的例子一样)。而且产品对象创建条件的改变必然会引起工厂角色的修改。
面对这种情况,Java的反射机制与配置文件的巧妙结合突破了限制——这在Spring中完美的体现了出来。
六、抽象工厂模式
先来认识下什么是产品族: 位于不同产品等级结构中,功能相关联的产品组成的家族。还是让我们用一个例子来形象地说明一下吧。

图中的BmwCar和BenzCar就是两个产品树(产品层次结构);而如图所示的BenzSportsCar和BmwSportsCar就是一个产品族。他们都可以放到跑车家族中,因此功能有所关联。同理BmwBussinessCar和BenzSportsCar也是一个产品族。
回到抽象工厂模式的话题上。可以说,抽象工厂模式和工厂方法模式的区别就在于需要创建对象的复杂程度上。而且抽象工厂模式是三个里面最为抽象、最具一般性的。抽象工厂模式的用意为:给客户端提供一个接口,可以创建多个产品族中的产品对象,而且使用抽象工厂模式还要满足一下条件:
1) 系统中有多个产品族,而系统一次只可能消费其中一族产品。
2) 同属于同一个产品族的产品以其使用。
来看看抽象工厂模式的各个角色(和工厂方法的如出一辙):
1) 抽象工厂角色: 这是工厂方法模式的核心,它与应用程序无关。是具体工厂角色必须实现的接口或者必须继承的父类。在java中它由抽象类或者接口来实现。
2) 具体工厂角色:它含有和具体业务逻辑有关的代码。由应用程序调用以创建对应的具体产品的对象。在java中它由具体的类来实现。
3)抽象产品角色:它是具体产品继承的父类或者是实现的接口。在java中一般有抽象类或者接口来实现。
4) 具体产品角色:具体工厂角色所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由具体的类来实现。
类图如下:

看过了前两个模式,对这个模式各个角色之间的协调情况应该心里有个数了,我就不举具体的例子了。只是一定要注意满足使用抽象工厂模式的条件哦。
抽象工厂示例:
Java代码 收藏代码
// 产品 Plant接口
public interface Plant { }//标志接口
//具体产品PlantA,PlantB
public class PlantA implements Plant {
public PlantA () {
System.out.println("create PlantA !");
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println(" PlantA do something ...");
}
}
public class PlantB implements Plant {
public PlantB () {
System.out.println("create PlantB !");
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println(" PlantB do something ...");
}
}
// 产品 Fruit接口
public interface Fruit { }
//具体产品FruitA,FruitB
public class FruitA implements Fruit {
public FruitA() {
System.out.println("create FruitA !");
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println(" FruitA do something ...");
}
}
public class FruitB implements Fruit {
public FruitB() {
System.out.println("create FruitB !");
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println(" FruitB do something ...");
}
}
// 抽象工厂方法
public interface AbstractFactory {
public Plant createPlant();
public Fruit createFruit();
}
//具体工厂方法
public class FactoryA implements AbstractFactory {
public Plant createPlant() {
return new PlantA();
}
public Fruit createFruit() {
return new FruitA();
}
}
public class FactoryB implements AbstractFactory {
public Plant createPlant() {
return new PlantB();
}
public Fruit createFruit() {
return new FruitB();
}
}
Java代码 收藏代码
//调用工厂方法
public Client {
public method1() {
AbstractFactory instance = new FactoryA();
instance.createPlant();
}
} 抽象工厂模式与工厂方法模式的区别 :可以这么说,工厂方法模式是一种极端情况的抽象工厂模式,而抽象工厂模式可以看成是工厂方法模式的一种推广。
(1)、其实工厂方法模式是用来创建一个产品的等级结构的,而抽象工厂模式是用来创建多个产品的等级结构的。工厂方法创建一般只有一个方法,创建一种产品。抽象工厂一般有多个方法,创建一系列产品。
(2)、工厂方法模式只有一个抽象产品类,而抽象工厂模式有多个。工厂方法模式的具体工厂类只能创建一个具体产品类的实例,而抽象工厂模式可以创建多个。
简而言之->
(1)工厂方法模式:
一个抽象产品类,可以派生出多个具体产品类。
一个抽象工厂类,可以派生出多个具体工厂类。每个具体工厂类只能创建一个具体产品类的实例。
(2)抽象工厂模式:
多个抽象产品类,每个抽象产品类可以派生出多个具体产品类。
一个抽象工厂类,可以派生出多个具体工厂类。每个具体工厂类可以创建多个具体产品类的实例。