Tensorflow生成自己的图片数据集TFrecords(支持多标签label)
Tensorflow生成自己的图片数据集TFrecords
尊重原创,转载请注明出处:https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/80857228
使用TensorFlow进行网络训练时,为了提高读取数据的效率,一般建议将训练数据转换为TFrecords格式。为了方面调用,本博客提供一个可通用,已经封装好的create_tf_record.py模块,方便以后调用。
博客Github源码:https://github.com/PanJinquan/tensorflow-learning-tutorials ->tf_record_demo文件夹(觉得可以,还请给个“Star”哦
目录
Tensorflow生成自己的图片数据集TFrecords
1.项目结构
2.生成自己的图片数据集TFrecords
2.1 生成单个record文件 (单label)
2.2 生成单个record文件 (多label)
2.3 生成分割多个record文件
3. 直接文件读取方式
4.数据输入管道:Pipeline机制
map
prefetch
repeat
完整代码
5.参考资料:
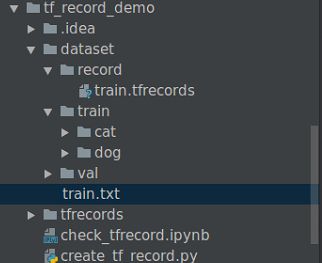
1.项目结构
项目目录结构如下所示:
其中train.txt保存图片的路径和标签信息
dog/1.jpg 0
dog/2.jpg 0
dog/3.jpg 0
dog/4.jpg 0
cat/1.jpg 1
cat/2.jpg 1
cat/3.jpg 1
cat/4.jpg 12.生成自己的图片数据集TFrecords
使用下面create_tf_record.py可以生成自己的图片数据集TFrecords,完整代码和解析如下:
2.1 生成单个record文件 (单label)
下面是封装好的py文件,可以直接生成单个record文件 ,当然这里假设只有一个label情况
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: create_tfrecord
@File : create_tfrecord.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2018-07-27 17:19:54
@desc : 将图片数据保存为单个tfrecord文件
"""
##########################################################################
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
from PIL import Image
##########################################################################
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
# 生成字符串型的属性
def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
# 生成实数型的属性
def float_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value))
def get_example_nums(tf_records_filenames):
'''
统计tf_records图像的个数(example)个数
:param tf_records_filenames: tf_records文件路径
:return:
'''
nums= 0
for record in tf.python_io.tf_record_iterator(tf_records_filenames):
nums += 1
return nums
def show_image(title,image):
'''
显示图片
:param title: 图像标题
:param image: 图像的数据
:return:
'''
# plt.figure("show_image")
# print(image.dtype)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title(title) # 图像题目
plt.show()
def load_labels_file(filename,labels_num=1,shuffle=False):
'''
载图txt文件,文件中每行为一个图片信息,且以空格隔开:图像路径 标签1 标签2,如:test_image/1.jpg 0 2
:param filename:
:param labels_num :labels个数
:param shuffle :是否打乱顺序
:return:images type->list
:return:labels type->list
'''
images=[]
labels=[]
with open(filename) as f:
lines_list=f.readlines()
if shuffle:
random.shuffle(lines_list)
for lines in lines_list:
line=lines.rstrip().split(' ')
label=[]
for i in range(labels_num):
label.append(int(line[i+1]))
images.append(line[0])
labels.append(label)
return images,labels
def read_image(filename, resize_height, resize_width,normalization=False):
'''
读取图片数据,默认返回的是uint8,[0,255]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param normalization:是否归一化到[0.,1.0]
:return: 返回的图片数据
'''
bgr_image = cv2.imread(filename)
if len(bgr_image.shape)==2:#若是灰度图则转为三通道
print("Warning:gray image",filename)
bgr_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)#将BGR转为RGB
# show_image(filename,rgb_image)
# rgb_image=Image.open(filename)
if resize_height>0 and resize_width>0:
rgb_image=cv2.resize(rgb_image,(resize_width,resize_height))
rgb_image=np.asanyarray(rgb_image)
if normalization:
# 不能写成:rgb_image=rgb_image/255
rgb_image=rgb_image/255.0
# show_image("src resize image",image)
return rgb_image
def get_batch_images(images,labels,batch_size,labels_nums,one_hot=False,shuffle=False,num_threads=1):
'''
:param images:图像
:param labels:标签
:param batch_size:
:param labels_nums:标签个数
:param one_hot:是否将labels转为one_hot的形式
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序,一般train时shuffle=True,验证时shuffle=False
:return:返回batch的images和labels
'''
min_after_dequeue = 200
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size # 保证capacity必须大于min_after_dequeue参数值
if shuffle:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([images,labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue,
num_threads=num_threads)
else:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.batch([images,labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
num_threads=num_threads)
if one_hot:
labels_batch = tf.one_hot(labels_batch, labels_nums, 1, 0)
return images_batch,labels_batch
def read_records(filename,resize_height, resize_width,type=None):
'''
解析record文件:源文件的图像数据是RGB,uint8,[0,255],一般作为训练数据时,需要归一化到[0,1]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param type:选择图像数据的返回类型
None:默认将uint8-[0,255]转为float32-[0,255]
normalization:归一化float32-[0,1]
standardization:标准化float32-[0,1],再减均值中心化
:return:
'''
# 创建文件队列,不限读取的数量
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([filename])
# create a reader from file queue
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
# reader从文件队列中读入一个序列化的样本
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# get feature from serialized example
# 解析符号化的样本
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'height': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'width': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'depth': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)
}
)
tf_image = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)#获得图像原始的数据
tf_height = features['height']
tf_width = features['width']
tf_depth = features['depth']
tf_label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
# PS:恢复原始图像数据,reshape的大小必须与保存之前的图像shape一致,否则出错
# tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [-1]) # 转换为行向量
tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [resize_height, resize_width, 3]) # 设置图像的维度
# 恢复数据后,才可以对图像进行resize_images:输入uint->输出float32
# tf_image=tf.image.resize_images(tf_image,[224, 224])
# [3]数据类型处理
# 存储的图像类型为uint8,tensorflow训练时数据必须是tf.float32
if type is None:
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32)
elif type == 'normalization': # [1]若需要归一化请使用:
# 仅当输入数据是uint8,才会归一化[0,255]
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, dtype=tf.uint8)
# tf_image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(tf_image, tf.float32)
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255.0) # 归一化
elif type == 'standardization': # 标准化
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, dtype=tf.uint8)
# tf_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(tf_image) # 标准化(减均值除方差)
# 若需要归一化,且中心化,假设均值为0.5,请使用:
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) - 0.5 # 中心化
# 这里仅仅返回图像和标签
# return tf_image, tf_height,tf_width,tf_depth,tf_label
return tf_image,tf_label
def create_records(image_dir,file, output_record_dir, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log=5):
'''
实现将图像原始数据,label,长,宽等信息保存为record文件
注意:读取的图像数据默认是uint8,再转为tf的字符串型BytesList保存,解析请需要根据需要转换类型
:param image_dir:原始图像的目录
:param file:输入保存图片信息的txt文件(image_dir+file构成图片的路径)
:param output_record_dir:保存record文件的路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
PS:当resize_height或者resize_width=0是,不执行resize
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序
:param log:log信息打印间隔
'''
# 加载文件,仅获取一个label
images_list, labels_list=load_labels_file(file,1,shuffle)
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_record_dir)
for i, [image_name, labels] in enumerate(zip(images_list, labels_list)):
image_path=os.path.join(image_dir,images_list[i])
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print('Err:no image',image_path)
continue
image = read_image(image_path, resize_height, resize_width)
image_raw = image.tostring()
if i%log==0 or i==len(images_list)-1:
print('------------processing:%d-th------------' % (i))
print('current image_path=%s' % (image_path),'shape:{}'.format(image.shape),'labels:{}'.format(labels))
# 这里仅保存一个label,多label适当增加"'label': _int64_feature(label)"项
label=labels[0]
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw),
'height': _int64_feature(image.shape[0]),
'width': _int64_feature(image.shape[1]),
'depth': _int64_feature(image.shape[2]),
'label': _int64_feature(label)
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
def disp_records(record_file,resize_height, resize_width,show_nums=4):
'''
解析record文件,并显示show_nums张图片,主要用于验证生成record文件是否成功
:param tfrecord_file: record文件路径
:return:
'''
# 读取record函数
tf_image, tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height,resize_width,type='normalization')
# 显示前4个图片
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(show_nums):
image,label = sess.run([tf_image,tf_label]) # 在会话中取出image和label
# image = tf_image.eval()
# 直接从record解析的image是一个向量,需要reshape显示
# image = image.reshape([height,width,depth])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(image.shape,image.dtype,label))
# pilimg = Image.fromarray(np.asarray(image_eval_reshape))
# pilimg.show()
show_image("image:%d"%(label),image)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
def batch_test(record_file,resize_height, resize_width):
'''
:param record_file: record文件路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:return:
:PS:image_batch, label_batch一般作为网络的输入
'''
# 读取record函数
tf_image,tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height,resize_width,type='normalization')
image_batch, label_batch= get_batch_images(tf_image,tf_label,batch_size=4,labels_nums=5,one_hot=False,shuffle=False)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess: # 开始一个会话
sess.run(init)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
for i in range(4):
# 在会话中取出images和labels
images, labels = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch])
# 这里仅显示每个batch里第一张图片
show_image("image", images[0, :, :, :])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(images.shape,images.dtype,labels))
# 停止所有线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 参数设置
resize_height = 224 # 指定存储图片高度
resize_width = 224 # 指定存储图片宽度
shuffle=True
log=5
# 产生train.record文件
image_dir='dataset/train'
train_labels = 'dataset/train.txt' # 图片路径
train_record_output = 'dataset/record/train.tfrecords'
create_records(image_dir,train_labels, train_record_output, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log)
train_nums=get_example_nums(train_record_output)
print("save train example nums={}".format(train_nums))
# 产生val.record文件
image_dir='dataset/val'
val_labels = 'dataset/val.txt' # 图片路径
val_record_output = 'dataset/record/val.tfrecords'
create_records(image_dir,val_labels, val_record_output, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log)
val_nums=get_example_nums(val_record_output)
print("save val example nums={}".format(val_nums))
# 测试显示函数
# disp_records(train_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
batch_test(train_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
2.2 生成单个record文件 (多label)
对于多label的情况,你可以在单label的基础上增加多个“label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)“,但每次label个数不一样时,都需要修改,挺麻烦的。这里提供一个方法:label数据也可以像图像数据那样,转为string类型来保存:labels_raw = np.asanyarray(labels,dtype=np.float32).tostring() ,读取也跟图像数据一样:tf_label = tf.decode_raw(features['labels'],tf.float32) ,这样,不管多少个label,我们都可以保存为record文件了:
多label的TXT文件:
0.jpg 0.33 0.55
1.jpg 0.42 0.73
2.jpg 0.16 0.75
3.jpg 0.78 0.66
4.jpg 0.46 0.59
5.jpg 0.46 0.09
6.jpg 0.89 0.93
7.jpg 0.42 0.82
8.jpg 0.39 0.76
9.jpg 0.46 0.40
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: create_tfrecord
@File : create_tf_record_multi_label.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2018-07-27 17:19:54
@desc : 将图片数据,多label,保存为单个tfrecord文件
"""
##########################################################################
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
from PIL import Image
##########################################################################
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
def _float_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[value]))
# 生成字符串型的属性
def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
# 生成实数型的属性
def float_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value))
def get_example_nums(tf_records_filenames):
'''
统计tf_records图像的个数(example)个数
:param tf_records_filenames: tf_records文件路径
:return:
'''
nums= 0
for record in tf.python_io.tf_record_iterator(tf_records_filenames):
nums += 1
return nums
def show_image(title,image):
'''
显示图片
:param title: 图像标题
:param image: 图像的数据
:return:
'''
# plt.figure("show_image")
# print(image.dtype)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title(title) # 图像题目
plt.show()
def load_labels_file(filename,labels_num=1,shuffle=False):
'''
载图txt文件,文件中每行为一个图片信息,且以空格隔开:图像路径 标签1 标签2,如:test_image/1.jpg 0 2
:param filename:
:param labels_num :labels个数
:param shuffle :是否打乱顺序
:return:images type->list
:return:labels type->list
'''
images=[]
labels=[]
with open(filename) as f:
lines_list=f.readlines()
if shuffle:
random.shuffle(lines_list)
for lines in lines_list:
line=lines.rstrip().split(' ')
label=[]
for i in range(labels_num):
label.append(float(line[i+1]))
images.append(line[0])
labels.append(label)
return images,labels
def read_image(filename, resize_height, resize_width,normalization=False):
'''
读取图片数据,默认返回的是uint8,[0,255]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param normalization:是否归一化到[0.,1.0]
:return: 返回的图片数据
'''
bgr_image = cv2.imread(filename)
if len(bgr_image.shape)==2:#若是灰度图则转为三通道
print("Warning:gray image",filename)
bgr_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)#将BGR转为RGB
# show_image(filename,rgb_image)
# rgb_image=Image.open(filename)
if resize_height>0 and resize_width>0:
rgb_image=cv2.resize(rgb_image,(resize_width,resize_height))
rgb_image=np.asanyarray(rgb_image)
if normalization:
# 不能写成:rgb_image=rgb_image/255
rgb_image=rgb_image/255.0
# show_image("src resize image",image)
return rgb_image
def get_batch_images(images,labels,batch_size,labels_nums,one_hot=False,shuffle=False,num_threads=1):
'''
:param images:图像
:param labels:标签
:param batch_size:
:param labels_nums:标签个数
:param one_hot:是否将labels转为one_hot的形式
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序,一般train时shuffle=True,验证时shuffle=False
:return:返回batch的images和labels
'''
min_after_dequeue = 200
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size # 保证capacity必须大于min_after_dequeue参数值
if shuffle:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([images,labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue,
num_threads=num_threads)
else:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.batch([images,labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
num_threads=num_threads)
if one_hot:
labels_batch = tf.one_hot(labels_batch, labels_nums, 1, 0)
return images_batch,labels_batch
def read_records(filename,resize_height, resize_width,type=None):
'''
解析record文件:源文件的图像数据是RGB,uint8,[0,255],一般作为训练数据时,需要归一化到[0,1]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param type:选择图像数据的返回类型
None:默认将uint8-[0,255]转为float32-[0,255]
normalization:归一化float32-[0,1]
standardization:归一化float32-[0,1],再减均值中心化
:return:
'''
# 创建文件队列,不限读取的数量
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([filename])
# create a reader from file queue
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
# reader从文件队列中读入一个序列化的样本
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# get feature from serialized example
# 解析符号化的样本
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'height': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'width': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'depth': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'labels': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
}
)
tf_image = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)#获得图像原始的数据
tf_height = features['height']
tf_width = features['width']
tf_depth = features['depth']
# tf_label = tf.cast(features['labels'], tf.float32)
tf_label = tf.decode_raw(features['labels'],tf.float32)
# PS:恢复原始图像数据,reshape的大小必须与保存之前的图像shape一致,否则出错
# tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [-1]) # 转换为行向量
tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [resize_height, resize_width, 3]) # 设置图像的维度
tf_label=tf.reshape(tf_label, [2]) # 设置图像的维度
# 恢复数据后,才可以对图像进行resize_images:输入uint->输出float32
# tf_image=tf.image.resize_images(tf_image,[224, 224])
# [3]数据类型处理
# 存储的图像类型为uint8,tensorflow训练时数据必须是tf.float32
if type is None:
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32)
elif type == 'normalization': # [1]若需要归一化请使用:
# 仅当输入数据是uint8,才会归一化[0,255]
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, dtype=tf.uint8)
# tf_image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(tf_image, tf.float32)
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255.0) # 归一化
elif type == 'standardization': # 标准化
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, dtype=tf.uint8)
# tf_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(tf_image) # 标准化(减均值除方差)
# 若需要归一化,且中心化,假设均值为0.5,请使用:
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) - 0.5 # 中心化
# 这里仅仅返回图像和标签
# return tf_image, tf_height,tf_width,tf_depth,tf_label
return tf_image,tf_label
def create_records(image_dir,file, output_record_dir, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log=5):
'''
实现将图像原始数据,label,长,宽等信息保存为record文件
注意:读取的图像数据默认是uint8,再转为tf的字符串型BytesList保存,解析请需要根据需要转换类型
:param image_dir:原始图像的目录
:param file:输入保存图片信息的txt文件(image_dir+file构成图片的路径)
:param output_record_dir:保存record文件的路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
PS:当resize_height或者resize_width=0是,不执行resize
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序
:param log:log信息打印间隔
'''
# 加载文件,仅获取一个label
labels_num=2
images_list, labels_list=load_labels_file(file,labels_num,shuffle)
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_record_dir)
for i, [image_name, labels] in enumerate(zip(images_list, labels_list)):
image_path=os.path.join(image_dir,images_list[i])
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print('Err:no image',image_path)
continue
image = read_image(image_path, resize_height, resize_width)
image_raw = image.tostring()
if i%log==0 or i==len(images_list)-1:
print('------------processing:%d-th------------' % (i))
print('current image_path=%s' % (image_path),'shape:{}'.format(image.shape),'labels:{}'.format(labels))
# 这里仅保存一个label,多label适当增加"'label': _int64_feature(label)"项
# label=labels[0]
# labels_raw="0.12,0,15"
labels_raw = np.asanyarray(labels,dtype=np.float32).tostring()
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw),
'height': _int64_feature(image.shape[0]),
'width': _int64_feature(image.shape[1]),
'depth': _int64_feature(image.shape[2]),
'labels': _bytes_feature(labels_raw),
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
def disp_records(record_file,resize_height, resize_width,show_nums=4):
'''
解析record文件,并显示show_nums张图片,主要用于验证生成record文件是否成功
:param tfrecord_file: record文件路径
:return:
'''
# 读取record函数
tf_image, tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height,resize_width,type='normalization')
# 显示前4个图片
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(show_nums):
image,label = sess.run([tf_image,tf_label]) # 在会话中取出image和label
# image = tf_image.eval()
# 直接从record解析的image是一个向量,需要reshape显示
# image = image.reshape([height,width,depth])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(image.shape,image.dtype,label))
# pilimg = Image.fromarray(np.asarray(image_eval_reshape))
# pilimg.show()
show_image("image:{}".format(label),image)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
def batch_test(record_file,resize_height, resize_width):
'''
:param record_file: record文件路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:return:
:PS:image_batch, label_batch一般作为网络的输入
'''
# 读取record函数
tf_image,tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height,resize_width,type='normalization')
image_batch, label_batch= get_batch_images(tf_image,tf_label,batch_size=4,labels_nums=2,one_hot=False,shuffle=True)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess: # 开始一个会话
sess.run(init)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
for i in range(4):
# 在会话中取出images和labels
images, labels = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch])
# 这里仅显示每个batch里第一张图片
show_image("image", images[0, :, :, :])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(images.shape,images.dtype,labels))
# 停止所有线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 参数设置
resize_height = 224 # 指定存储图片高度
resize_width = 224 # 指定存储图片宽度
shuffle=True
log=1000
# 产生train.record文件
image_dir='dataset_regression/images'
train_labels = 'dataset_regression/train.txt' # 图片路径
train_record_output = 'dataset_regression/record/train.tfrecords'
create_records(image_dir,train_labels, train_record_output, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log)
train_nums=get_example_nums(train_record_output)
print("save train example nums={}".format(train_nums))
# 测试显示函数
# disp_records(train_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
# 产生val.record文件
image_dir='dataset_regression/images'
val_labels = 'dataset_regression/val.txt' # 图片路径
val_record_output = 'dataset_regression/record/val.tfrecords'
create_records(image_dir,val_labels, val_record_output, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log)
val_nums=get_example_nums(val_record_output)
print("save val example nums={}".format(val_nums))
#
# # 测试显示函数
# # disp_records(train_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
# batch_test(val_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
2.3 生成分割多个record文件
上述该代码只保存为单个record文件,当图片数据很多时候,会导致单个record文件超级巨大的情况,解决方法就是,将数据分成多个record文件保存,读取时,只需要将多个record文件的路径列表交给“tf.train.string_input_producer”,完整代码如下:
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: tf_record_demo
@File : tf_record_batchSize.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2018-07-27 17:19:54
@desc : 将图片数据保存为多个record文件
"""
##########################################################################
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
from PIL import Image
##########################################################################
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
# 生成字符串型的属性
def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
# 生成实数型的属性
def float_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value))
def show_image(title,image):
'''
显示图片
:param title: 图像标题
:param image: 图像的数据
:return:
'''
# plt.figure("show_image")
# print(image.dtype)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title(title) # 图像题目
plt.show()
def load_labels_file(filename,labels_num=1):
'''
载图txt文件,文件中每行为一个图片信息,且以空格隔开:图像路径 标签1 标签2,如:test_image/1.jpg 0 2
:param filename:
:param labels_num :labels个数
:return:images type->list
:return:labels type->list
'''
images=[]
labels=[]
with open(filename) as f:
for lines in f.readlines():
line=lines.rstrip().split(' ')
label=[]
for i in range(labels_num):
label.append(int(line[i+1]))
images.append(line[0])
labels.append(label)
return images,labels
def read_image(filename, resize_height, resize_width):
'''
读取图片数据,默认返回的是uint8,[0,255]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:return: 返回的图片数据是uint8,[0,255]
'''
bgr_image = cv2.imread(filename)
if len(bgr_image.shape)==2:#若是灰度图则转为三通道
print("Warning:gray image",filename)
bgr_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)#将BGR转为RGB
# show_image(filename,rgb_image)
# rgb_image=Image.open(filename)
if resize_height>0 and resize_width>0:
rgb_image=cv2.resize(rgb_image,(resize_width,resize_height))
rgb_image=np.asanyarray(rgb_image)
# show_image("src resize image",image)
return rgb_image
def create_records(image_dir,file, record_txt_path, batchSize,resize_height, resize_width):
'''
实现将图像原始数据,label,长,宽等信息保存为record文件
注意:读取的图像数据默认是uint8,再转为tf的字符串型BytesList保存,解析请需要根据需要转换类型
:param image_dir:原始图像的目录
:param file:输入保存图片信息的txt文件(image_dir+file构成图片的路径)
:param output_record_txt_dir:保存record文件的路径
:param batchSize: 每batchSize个图片保存一个*.tfrecords,避免单个文件过大
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
PS:当resize_height或者resize_width=0是,不执行resize
'''
if os.path.exists(record_txt_path):
os.remove(record_txt_path)
setname, ext = record_txt_path.split('.')
# 加载文件,仅获取一个label
images_list, labels_list=load_labels_file(file,1)
sample_num = len(images_list)
# 打乱样本的数据
# random.shuffle(labels_list)
batchNum = int(math.ceil(1.0 * sample_num / batchSize))
for i in range(batchNum):
start = i * batchSize
end = min((i + 1) * batchSize, sample_num)
batch_images = images_list[start:end]
batch_labels = labels_list[start:end]
# 逐个保存*.tfrecords文件
filename = setname + '{0}.tfrecords'.format(i)
print('save:%s' % (filename))
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(filename)
for i, [image_name, labels] in enumerate(zip(batch_images, batch_labels)):
image_path=os.path.join(image_dir,batch_images[i])
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print('Err:no image',image_path)
continue
image = read_image(image_path, resize_height, resize_width)
image_raw = image.tostring()
print('image_path=%s,shape:( %d, %d, %d)' % (image_path,image.shape[0], image.shape[1], image.shape[2]),'labels:',labels)
# 这里仅保存一个label,多label适当增加"'label': _int64_feature(label)"项
label=labels[0]
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw),
'height': _int64_feature(image.shape[0]),
'width': _int64_feature(image.shape[1]),
'depth': _int64_feature(image.shape[2]),
'label': _int64_feature(label)
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
# 用txt保存*.tfrecords文件列表
# record_list='{}.txt'.format(setname)
with open(record_txt_path, 'a') as f:
f.write(filename + '\n')
def read_records(filename,resize_height, resize_width):
'''
解析record文件
:param filename:保存*.tfrecords文件的txt文件路径
:return:
'''
# 读取txt中所有*.tfrecords文件
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
files_list=[]
for line in lines:
files_list.append(line.rstrip())
# 创建文件队列,不限读取的数量
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files_list,shuffle=False)
# create a reader from file queue
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
# reader从文件队列中读入一个序列化的样本
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# get feature from serialized example
# 解析符号化的样本
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'height': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'width': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'depth': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)
}
)
tf_image = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)#获得图像原始的数据
tf_height = features['height']
tf_width = features['width']
tf_depth = features['depth']
tf_label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
# tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [-1]) # 转换为行向量
tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [resize_height, resize_width, 3]) # 设置图像的维度
# 存储的图像类型为uint8,这里需要将类型转为tf.float32
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32)
# [1]若需要归一化请使用:
tf_image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(tf_image, tf.float32)# 归一化
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) # 归一化
# [2]若需要归一化,且中心化,假设均值为0.5,请使用:
# tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) - 0.5 #中心化
return tf_image, tf_height,tf_width,tf_depth,tf_label
def disp_records(record_file,resize_height, resize_width,show_nums=4):
'''
解析record文件,并显示show_nums张图片,主要用于验证生成record文件是否成功
:param tfrecord_file: record文件路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param show_nums: 默认显示前四张照片
:return:
'''
tf_image, tf_height, tf_width, tf_depth, tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height, resize_width) # 读取函数
# 显示前show_nums个图片
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(show_nums):
image,height,width,depth,label = sess.run([tf_image,tf_height,tf_width,tf_depth,tf_label]) # 在会话中取出image和label
# image = tf_image.eval()
# 直接从record解析的image是一个向量,需要reshape显示
# image = image.reshape([height,width,depth])
print('shape:',image.shape,'label:',label)
# pilimg = Image.fromarray(np.asarray(image_eval_reshape))
# pilimg.show()
show_image("image:%d"%(label),image)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
def batch_test(record_file,resize_height, resize_width):
'''
:param record_file: record文件路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:return:
:PS:image_batch, label_batch一般作为网络的输入
'''
tf_image,tf_height,tf_width,tf_depth,tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height, resize_width) # 读取函数
# 使用shuffle_batch可以随机打乱输入:
# shuffle_batch用法:https://blog.csdn.net/u013555719/article/details/77679964
min_after_dequeue = 100#该值越大,数据越乱,必须小于capacity
batch_size = 4
# capacity = (min_after_dequeue + (num_threads + a small safety margin∗batchsize)
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size#容量:一个整数,队列中的最大的元素数
image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([tf_image, tf_label],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess: # 开始一个会话
sess.run(init)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
for i in range(4):
# 在会话中取出images和labels
images, labels = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch])
# 这里仅显示每个batch里第一张图片
show_image("image", images[0, :, :, :])
print(images.shape, labels)
# 停止所有线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 参数设置
image_dir='dataset/train'
train_file = 'dataset/train.txt' # 图片路径
output_record_txt = 'dataset/record/record.txt'#指定保存record的文件列表
resize_height = 224 # 指定存储图片高度
resize_width = 224 # 指定存储图片宽度
batchSize=8000 #batchSize一般设置为8000,即每batchSize张照片保存为一个record文件
# 产生record文件
create_records(image_dir=image_dir,
file=train_file,
record_txt_path=output_record_txt,
batchSize=batchSize,
resize_height=resize_height,
resize_width=resize_width)
# 测试显示函数
disp_records(output_record_txt,resize_height, resize_width)
# batch_test(output_record_txt,resize_height, resize_width)
3. 直接文件读取方式
上面的都是将数据转存为tfrecord文件,训练时再读取,如果不想转为record文件,想直接读取图像文件进行训练,可以使用下面的方法:
filename.txt
0.jpg 0
1.jpg 0
2.jpg 0
3.jpg 0
4.jpg 0
5.jpg 1
6.jpg 1
7.jpg 1
8.jpg 1
9.jpg 1
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: tf_record_demo
@File : tf_read_files.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2018-10-14 10:44:06
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import glob
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
def show_image(title, image):
'''
显示图片
:param title: 图像标题
:param image: 图像的数据
:return:
'''
# plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title(title) # 图像题目
plt.show()
def tf_read_image(filename, resize_height, resize_width):
'''
读取图片
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:return:
'''
image_string = tf.read_file(filename)
image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string, channels=3)
# tf_image = tf.cast(image_decoded, tf.float32)
tf_image = tf.cast(image_decoded, tf.float32) * (1. / 255.0) # 归一化
if resize_width>0 and resize_height>0:
tf_image = tf.image.resize_images(tf_image, [resize_height, resize_width])
# tf_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(tf_image) # 标准化[0,1](减均值除方差)
return tf_image
def get_batch_images(image_list, label_list, batch_size, labels_nums, resize_height, resize_width, one_hot=False, shuffle=False):
'''
:param image_list:图像
:param label_list:标签
:param batch_size:
:param labels_nums:标签个数
:param one_hot:是否将labels转为one_hot的形式
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序,一般train时shuffle=True,验证时shuffle=False
:return:返回batch的images和labels
'''
# 生成队列
image_que, tf_label = tf.train.slice_input_producer([image_list, label_list], shuffle=shuffle)
tf_image = tf_read_image(image_que, resize_height, resize_width)
min_after_dequeue = 200
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size # 保证capacity必须大于min_after_dequeue参数值
if shuffle:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([tf_image, tf_label],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue)
else:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.batch([tf_image, tf_label],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity)
if one_hot:
labels_batch = tf.one_hot(labels_batch, labels_nums, 1, 0)
return images_batch, labels_batch
def load_image_labels(filename):
'''
载图txt文件,文件中每行为一个图片信息,且以空格隔开:图像路径 标签1,如:test_image/1.jpg 0
:param filename:
:return:
'''
images_list = []
labels_list = []
with open(filename) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
# rstrip:用来去除结尾字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、' ',即:换行、回车、制表符、空格)
content = line.rstrip().split(' ')
name = content[0]
labels = []
for value in content[1:]:
labels.append(int(value))
images_list.append(name)
labels_list.append(labels)
return images_list, labels_list
def batch_test(filename, image_dir):
labels_nums = 2
batch_size = 4
resize_height = 200
resize_width = 200
image_list, label_list = load_image_labels(filename)
image_list=[os.path.join(image_dir,image_name) for image_name in image_list]
image_batch, labels_batch = get_batch_images(image_list=image_list,
label_list=label_list,
batch_size=batch_size,
labels_nums=labels_nums,
resize_height=resize_height, resize_width=resize_width,
one_hot=False, shuffle=True)
with tf.Session() as sess: # 开始一个会话
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
for i in range(4):
# 在会话中取出images和labels
images, labels = sess.run([image_batch, labels_batch])
# 这里仅显示每个batch里第一张图片
show_image("image", images[0, :, :, :])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(images.shape, images.dtype, labels))
# 停止所有线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
if __name__ == "__main__":
image_dir = "./dataset/train"
filename = "./dataset/train.txt"
batch_test(filename, image_dir)
4.数据输入管道:Pipeline机制
TensorFlow引入了tf.data.Dataset模块,使其数据读入的操作变得更为方便,而支持多线程(进程)的操作,也在效率上获得了一定程度的提高。使用tf.data.Dataset模块的pipline机制,可实现CPU多线程处理输入的数据,如读取图片和图片的一些的预处理,这样GPU可以专注于训练过程,而CPU去准备数据。
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/u014061630/article/details/80776975
(五星推荐)TensorFlow全新的数据读取方式:Dataset API入门教程:http://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1583657817436843385&wfr=spider&for=pc
Dataset支持一类特殊的操作:Transformation。一个Dataset通过Transformation变成一个新的Dataset。通常我们可以通过Transformation完成数据变换,打乱,组成batch,生成epoch等一系列操作。常用的Transformation有:map、batch、shuffle和repeat。
下面就分别进行介绍。
map
使用 tf.data.Dataset.map,我们可以很方便地对数据集中的各个元素进行预处理。因为输入元素之间时独立的,所以可以在多个 CPU 核心上并行地进行预处理。map 变换提供了一个 num_parallel_calls参数去指定并行的级别。
dataset = dataset.map(map_func=parse_fn, num_parallel_calls=FLAGS.num_parallel_calls)
prefetch
tf.data.Dataset.prefetch 提供了 software pipelining 机制。该函数解耦了 数据产生的时间 和 数据消耗的时间。具体来说,该函数有一个后台线程和一个内部缓存区,在数据被请求前,就从 dataset 中预加载一些数据(进一步提高性能)。prefech(n) 一般作为最后一个 transformation,其中 n 为 batch_size。 prefetch 的使用方法如下:
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size)
dataset = dataset.prefetch(buffer_size=FLAGS.prefetch_buffer_size) # last transformation
return datasetrepeat
repeat的功能就是将整个序列重复多次,主要用来处理机器学习中的epoch,假设原先的数据是一个epoch,使用repeat(5)就可以将之变成5个epoch:
如果直接调用repeat()的话,生成的序列就会无限重复下去,没有结束,因此也不会抛出tf.errors.OutOfRangeError异常
完整代码
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: fine tuning
@File : pipeline.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2018-11-17 20:18:54
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import glob
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
width=0
height=0
def show_image(title, image):
'''
显示图片
:param title: 图像标题
:param image: 图像的数据
:return:
'''
# plt.figure("show_image")
# print(image.dtype)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title(title) # 图像题目
plt.show()
def tf_read_image(filename, label):
image_string = tf.read_file(filename)
image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string, channels=3)
image = tf.cast(image_decoded, tf.float32)
if width>0 and height>0:
image = tf.image.resize_images(image, [height, width])
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255.0) # 归一化
return image, label
def input_fun(files_list, labels_list, batch_size, shuffle=True):
'''
:param files_list:
:param labels_list:
:param batch_size:
:param shuffle:
:return:
'''
# 构建数据集
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((files_list, labels_list))
if shuffle:
dataset = dataset.shuffle(100)
dataset = dataset.repeat() # 空为无限循环
dataset = dataset.map(tf_read_image, num_parallel_calls=4) # num_parallel_calls一般设置为cpu内核数量
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size)
dataset = dataset.prefetch(2) # software pipelining 机制
return dataset
if __name__ == '__main__':
data_dir = 'dataset/image/*.jpg'
# labels_list = tf.constant([0,1,2,3,4])
# labels_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
files_list = glob.glob(data_dir)
labels_list = np.arange(len(files_list))
num_sample = len(files_list)
batch_size = 1
dataset = input_fun(files_list, labels_list, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
# 需满足:max_iterate*batch_size <=num_sample*num_epoch,否则越界
max_iterate = 3
with tf.Session() as sess:
iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator()
init_op = iterator.make_initializer(dataset)
sess.run(init_op)
iterator = iterator.get_next()
for i in range(max_iterate):
images, labels = sess.run(iterator)
show_image("image", images[0, :, :, :])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(images.shape, images.dtype, labels))
5.参考资料:
[1]https://blog.csdn.net/happyhorizion/article/details/77894055 (五星推荐)
[2]https://blog.csdn.net/ywx1832990/article/details/78462582
[3]https://blog.csdn.net/csuzhaoqinghui/article/details/51377941