【英文】Osmosis【翻译】@尔墨 【校对】itsmelan
【Quizlet】词表【上篇】生理、病理
人体如何避免自由基损伤?
既然损伤在病理和生理状况下均可发生,既然我们的身体是如此聪明,我们一定有办法避免这种情况,对吧?当然!
Okay so since this can happen in both pathologic AND physiologic settings, since our bodies are so smart, it’s totally reasonable that we have ways of getting rid of them right? Yes! It is!
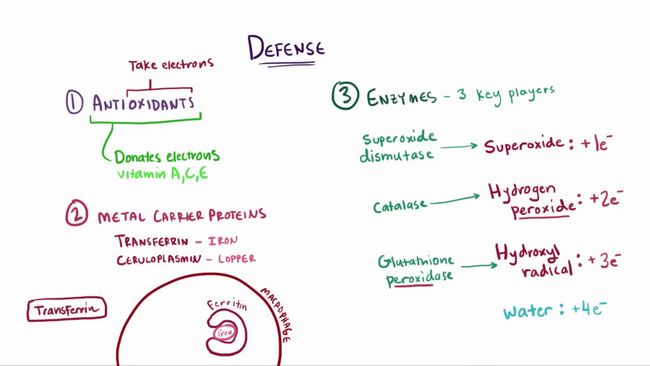
1. 抗氧化剂
抵抗氧化剂的第一道防线就是抗氧化剂。当然如此了,不是吗?由于自由基等等氧化剂能够夺取电子,那么维生素A、C、E等抗氧化剂就能够通过提供电子而清除自由基。
The first defense against these oxidants are uhhh antioxidants! That makes sense, right? Because oxidants, like free radicals, can take electrons, so antioxidants, like vitamin A and vitamin C, vitamin E, which can all eliminate free radicals by donating electrons.
2. 金属载体蛋白
另一条规避的途径是金属载体蛋白,比如转铁蛋白和铜蓝蛋白。它们分别和血液中的铁或铜结合。举个例子,转铁蛋白将铁转运到肝脏和巨噬细胞内,它们可以和铁蛋白结合。类似于隐藏起来,这样就不能产生自由基了。
Another way that we can get rid of them, which we touched on, are metal carrier proteins, like transferrins and ceruloplasmin, which respectively bind or carry iron and copper in the blood. For example, transferrin carries and delivers it to the liver and macrophages. And then when bound in macrophages or the liver by a molecule called ferritin, it’s sort of like hidden away and so it’s not able to generate free radicals.
3. 通过酶类
最后一条规避自由基的途径是通过酶类,有三种非常重要的蛋白在清除自由基中发挥作用。没有电子的氧和有四个电子的水的中间,分别是有一个自由电子的超氧化物,有2个自由电子的过氧化氢、最后有3个电子的羟基自由基,然后就是有4个电子的水。
And finally, another way we can get rid of free radicals is by enzymes, and there are three super important players in the free radical game. So remember that in between oxygen and water, you’ve got superoxide with one electron, then hydrogen peroxide with 2, and finally hydroxyl with 3, and then water with four, right, okay.
这三种酶类分别针对其中一种自由基发挥作用。超氧化物歧化酶负责超氧化物,这很容易记。然后是过氧化氢酶负责过氧化氢,最后是谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶负责羟基自由基。这并不是很好记,因为也许你本来想的是它应该负责过氧化氢。但是记住谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶负责羟基自由基。
Now, our three enzymes are each going to have the job of focusing on one of these free radicals. Superoxide is taken care of by superoxide dismutase, that ones easy; an enzyme called catalase takes hydrogen peroxide, and then hydroxyl free radical is taken by glutathione peroxidase, which is less intuitive, because maybe you’d think that that one should be for hydrogen peroxide, but it’s not.
临床案例:四氯化碳
我们已经学习了自由基,现在通过一个关于四氯化碳的临床案例来进行复习。四氯化碳由一个碳和四个氯组成,通常用于干洗行业。如果它进入血液,就会转化为三氯甲基(CCl3·),这是一种自由基。这个过程在肝脏的P450系统中发生。既然它是一种自由基,那它就可以在肝脏细胞中肆虐,对吧?
Okay let’s quick go over a clinical examples about a chemical called carbon tetrachloride, so one carbon, then four chlorides - and this guys actually used in the dry cleaning industry. If it gets into the blood, it’s converted to trichloromethyl radical, or CCl3 which is a free radical, and this happens in the P450 system of the liver. Now that it’s a free radical, it starts wreaking havoc on the hepatocytes of your liver, right?
它会损伤蛋白质、DNA和细胞膜。在早期阶段,这种损伤是可以逆转的。肉眼可见的病理改变是细胞水肿。这会导致细胞的粗面内质网也水肿。在粗面内质网上有许多核糖体,对吧?它们帮助合成蛋白质。当它粗面内质网水肿时,核糖体脱落,蛋白质合成也随之减少。
It can start damaging proteins, DNA, and cell membranes. In the early stages, this damage is actually reversible, and one way you can tell is by looking for cellular swelling, so the cells are actually swelling. This causes the rough endoplasmic reticulum of the cell to also swell. And remember how on your Rough endoplasmic reticulum, you’ve got all your ribosomes right? Which help make proteins. So when it swells they pop off and your protein synthesis goes down.
还记得肝脏的作用是什么嘛?对,它会从膳食中聚集脂肪和胆固醇,然后重新包装并原路送回。这种重新组装的过程通过我们的好朋友载脂蛋白来完成。载脂蛋白帮助接收、包装和送回脂肪和胆固醇。所以如果四氯化碳或者三氯甲基自由基损伤了肝细胞,并导致水肿和核糖体的丢失,从而减少蛋白质的产生,包括我们的好朋友载脂蛋白。现在这些进入脂肪进入肝脏,但是没有被重新包装和送回。你瞧,脂肪就不能逃逸,肝脏就出现了脂肪变性。
And what does our liver do again? OH right, right it gathers up fat and cholesterol from the diet right? and repackages it and sends it back on it’s way. This repackaging process is done by our good friends the apolipoproteins. apolipoPROTEINS. Proteins that help receive, pack, and send back out the fats and cholesterol. So if CCl4 or rather the trichloromethyl radical damages the liver cell, and causes swelling and loss of ribosomes, then you’ll decreased production of proteins...and decreases our friends the apolipoproteins. Now all the sudden you’ve got these fats coming into the liver but not being repackaged and sent back out...and lo and behold, the fat doesn’t escape and you get this fatty change in the liver.
看看这些肝细胞的组织学切片,这些圆形的空泡代表着脂肪的聚集或者脂肪肝。
Check out this histology of some hepatocytes. These circular spaces represent the accumulation of fat, or fatty liver.
因此肝脏的脂肪累积归根结底其实是自由基导致的。
So this fat buildup in the liver is ultimately caused by free radical damage. Alright, another free radical injury example region, all because of free radical generation.
Meducal! 本期医理闪充结束啦~听说充满电还送大拇指儿、小钢镚儿、小花瓣儿的都是学仙~~咱下期见啦~~~我们的文集叫「Osmosis双语医学」