Linux操作系统实践中的实验(1)
首先是简单的系统调用,类似于当前的进程号,组号,用户名等等
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char **argv){
pid_t my_pid, parent_pid;
uid_t my_uid, my_euid;
gid_t my_gid, my_egid;
struct passwd *my_info;
my_pid = getpid(); //process id
parent_pid = getppid(); //parent process id
my_uid = getuid(); //user id
my_euid = geteuid(); //effective user id
my_gid = getgid(); //group id
my_egid = getegid(); //effective group id
my_info = getpwuid(my_uid); //user information
printf("Process ID:%1d\n", my_pid);
printf("Parent ID:%1d\n", parent_pid);
printf("User ID:%1d\n", my_uid);
printf("Effective User ID:%1d\n", my_euid);
printf("Group ID:%1d\n", my_gid);
printf("Effective group ID:%1d\n", my_egid);
if(my_info){
printf("My login name:%s\n", my_info->pw_name);
printf("My password:%s\n", my_info->pw_passwd);
printf("My user ID:%1d\n", my_info->pw_uid);
printf("My group ID:%1d\n", my_info->pw_gid);
printf("My real name:%s\n", my_info->pw_gecos);
printf("My home dir:%s\n", my_info->pw_dir);
printf("My work shell:%s\n", my_info->pw_shell);
}
return 0;
} 接下来是进程的基本操作,比如kill
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(void){
pid_t childpid;
int status;
int retval;
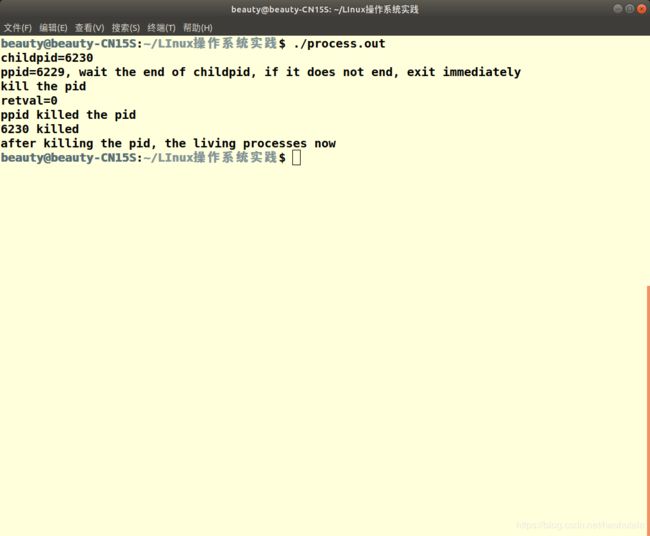
childpid = fork(); //clone a new process
printf("childpid=%d\n", childpid);
if(childpid == -1){ //fail to create a new process
perror("fork()");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if(childpid == 0){
puts("In child process\n");
printf("pid=%d, sleep 100 sec\n", (int)getpid());
sleep(100);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else{
printf("ppid=%d, wait the end of childpid, if it does not end, exit immediately\n", (int)getpid());
if(waitpid(childpid, &status, WNOHANG)==0){
//pid does not end
printf("kill the pid\n");
retval = kill(childpid, SIGKILL);
printf("retval=%d\n", retval);
printf("ppid killed the pid\n");
if(retval){
puts("kill failed.\n");
perror("kill");
waitpid(childpid, &status, 0);
}
else{
printf("%d killed\n", childpid);
printf("after killing the pid, the living processes now\n");
}
}
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
return 0;
} 然后是简单的多线程操作
#include
#include
/*
* you should add -lpthread while compiling this file
* like gcc multiThreads.c -o multiThreads.out -lpthread
*/
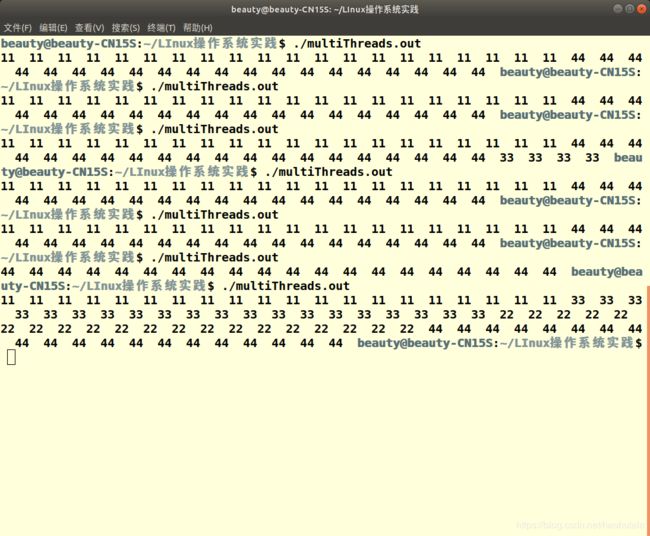
void *printyou(void* unused){
int c=20;
while(c--) printf("11 ", stderr);
return NULL;
}
void *printme(void* unused){
int c=20;
while(c--) printf("22 ", stderr);
return NULL;
}
void *printhim(void* unused){
int c=20;
while(c--) printf("33 ", stderr);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
int c=20;
pthread_t t1, t2, t3;
//create new thread
/*
* param1 thread identifier
* param2 the attribute of the thread
* param3 the starting addr of function
* param4 the running attribute
*/
pthread_create (&t1, NULL, &printyou, NULL);
pthread_create (&t2, NULL, &printme, NULL);
pthread_create (&t3, NULL, &printhim, NULL);
while(c--) printf("44 ", stderr);
return 0;
} 不知道为什么每次结果都不太一样。。
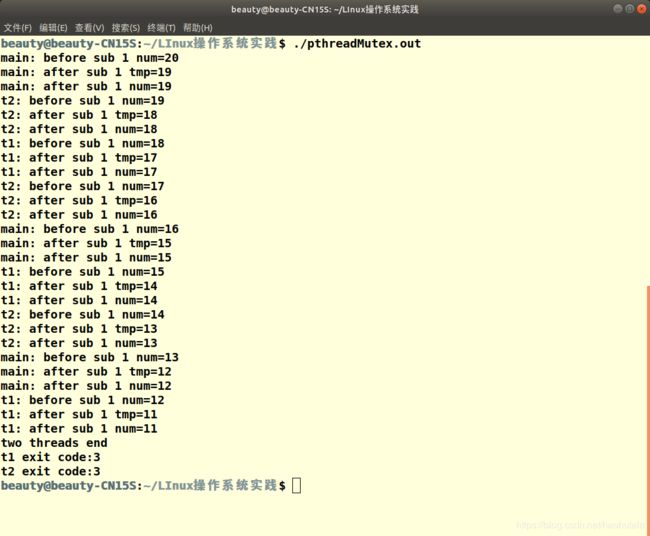
最后是有锁保护的多线程访问理解资源
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int num=20,count=3;
pthread_mutex_t mylock=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void *sub1(){
int i=0,tmp;
for(;i