Android属性动画之ValueAnimator使用
目前Android系统动画包括三类:View动画,帧动画,属性动画,其中属性动画是API Level 11添加的。
本文主要记录属性动画的使用,权当笔记,以供后续自己需要参考。
关于属性动画的博客,强烈推荐:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/43536355,本文一些代码也是搬郭兄的例子
首先简单回顾一下View动画和帧动画:
View动画作用对象只能是View,View类中有个函数:startAnimation(Animation animation),就是开启动画,给View设置一个动画对象。
Animation代表View动画,看一下的它的类结构:
View动画效果包括四类:透明度,旋转,缩放,平移。如果是组合这几动画效果,可以使用AnimationSet。创建该类动画既可以使用相应类的构造函数创建,也可以通过使用xml文件表示。
帧动画实现由AnimationDrawable实现,该对象代表一系列的图片集合,它可以作为的View的背景,实现一张张显示不同的背景的效果。调用它的start()函数即开始动画,同样使用xml文件也可以配置帧动画。它使用的标签就是animation-list
关于View动画和帧动画就介绍这点,没贴对应的demo代码片段了。
下面看属性动画:
属性动画使用Animator来表示:
属性动画作用对象不单限于View,可以是任意对象。
Animator是抽象类,先从它的子类ValueAnimator入手。
先来看一下ValueAnimator的简单使用:
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f,3f);
animator.setDuration(1000);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float value = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
long time = animation.getCurrentPlayTime();
Log.d("Test", "time "+time+"cuurent value is " + value);
}
});
animator.start();setDuration()设置时间间隔,表示第一个值变化到最后一个值的时间。
start()函数就是开启动画。
为了观察ValueAnimator是对这值操作的效果,可以添加一个监听器。
看一下log:
D/Test: time 0cuurent value is 0.0
D/Test: time 2cuurent value is 0.0
D/Test: time 17cuurent value is 0.002138704
D/Test: time 34cuurent value is 0.00805378
D/Test: time 50cuurent value is 0.018467456
D/Test: time 67cuurent value is 0.03310606
D/Test: time 84cuurent value is 0.050705463
D/Test: time 100cuurent value is 0.07341528
D/Test: time 117cuurent value is 0.10019302
D/Test: time 134cuurent value is 0.12904367
D/Test: time 150cuurent value is 0.1634902
D/Test: time 167cuurent value is 0.20174816
D/Test: time 184cuurent value is 0.24113926
D/Test: time 200cuurent value is 0.28647467
D/Test: time 217cuurent value is 0.33527023
D/Test: time 238cuurent value is 0.38423243
D/Test: time 250cuurent value is 0.43933985
D/Test: time 267cuurent value is 0.4974718
D/Test: time 284cuurent value is 0.5547992
D/Test: time 300cuurent value is 0.61832196
D/Test: time 317cuurent value is 0.6843594
D/Test: time 334cuurent value is 0.7486398
D/Test: time 350cuurent value is 0.8190143
D/Test: time 367cuurent value is 0.89133024
D/Test: time 384cuurent value is 0.960982
D/Test: time 400cuurent value is 1.0364745
D/Test: time 420cuurent value is 1.1132891
D/Test: time 434cuurent value is 1.186596
D/Test: time 450cuurent value is 1.2653486
D/Test: time 467cuurent value is 1.3447697
D/Test: time 484cuurent value is 1.4199276
D/Test: time 500cuurent value is 1.5
D/Test: time 517cuurent value is 1.5800724
D/Test: time 534cuurent value is 1.6552303
D/Test: time 550cuurent value is 1.7346514
D/Test: time 567cuurent value is 1.8134034
D/Test: time 584cuurent value is 1.8867109
D/Test: time 601cuurent value is 1.9635255
D/Test: time 617cuurent value is 2.039018
D/Test: time 634cuurent value is 2.1086698
D/Test: time 650cuurent value is 2.1809857
D/Test: time 667cuurent value is 2.25136
D/Test: time 684cuurent value is 2.3156412
D/Test: time 700cuurent value is 2.381678
D/Test: time 717cuurent value is 2.445201
D/Test: time 734cuurent value is 2.5025282
D/Test: time 750cuurent value is 2.5606604
D/Test: time 767cuurent value is 2.6157675
D/Test: time 784cuurent value is 2.6647298
D/Test: time 801cuurent value is 2.7135253
D/Test: time 817cuurent value is 2.7588606
D/Test: time 834cuurent value is 2.7982516
D/Test: time 851cuurent value is 2.8365097
D/Test: time 867cuurent value is 2.8709564
D/Test: time 884cuurent value is 2.899807
D/Test: time 901cuurent value is 2.9265847
D/Test: time 917cuurent value is 2.9492946
D/Test: time 934cuurent value is 2.9668941
D/Test: time 951cuurent value is 2.9815326
D/Test: time 967cuurent value is 2.9919462
D/Test: time 984cuurent value is 2.9978614
D/Test: time 1001cuurent value is 3.0
通过log可以发现,我们设置的从0到3耗时1000ms确实是做了相应的变化。
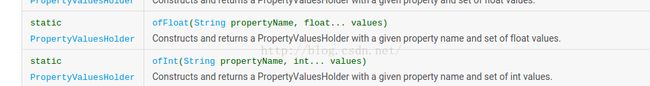
ValueAnimator除了可以对浮点型值操作外,还可以对int值操作,它有方法ofInt(int... values)
虽然看到这些值变化了,但是变化的这些中间值是如何得出的呢?
那么先看两个类PropertyValuesHolder和TypeEvaluator。
PropertyValuesHolder看类名应该是对属性及属性值的封装,看一下源码:
在frameworks/base/core/java/android/animation/ValueAnimator.java中
public static ValueAnimator ofFloat(float... values) {
ValueAnimator anim = new ValueAnimator();
anim.setFloatValues(values);
return anim;
}public void setFloatValues(float... values) {
..
setValues(new PropertyValuesHolder[]{PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("", values)});
...
// New property/values/target should cause re-initialization prior to starting
mInitialized = false;
}利用属性和属性值构造了一个PropertyValuesHolder对象
看一下PropertyValuesHolder的ofFloat()函数
因为这里我们只对值操作,没有属性可言,所以属性直接传入“”。ValueAnimator的子类ObjectAnimator可以对一个对象的属性进行变化,就会传入属性值,这个后面再讲。
而TypeEvaluator的作用就是告诉动画系统如何从初始值过度到结束值,计算出中间值。PropertyValuesHolder内部就包含该类的两个子类对象
在frameworks/base/core/java/android/animation/PropertyValuesHolder.java中
// type evaluators for the primitive types handled by this implementation
private static final TypeEvaluator sIntEvaluator = new IntEvaluator();
private static final TypeEvaluator sFloatEvaluator = new FloatEvaluator();PropertyValuesHolder会根据操作是int值还是float值来选择哪一个TypeEvaluator,
看一下TypeEvaluator这个接口
在frameworks/base/core/java/android/animation/TypeEvaluator.java中
public interface TypeEvaluator {
/**
* This function returns the result of linearly interpolating the start and end values, with
* fraction representing the proportion between the start and end values. The
* calculation is a simple parametric calculation: result = x0 + t * (v1 - v0),
* where x0 is startValue, x1 is endValue,
* and t is fraction.
*
* @param fraction The fraction from the starting to the ending values
* @param startValue The start value.
* @param endValue The end value.
* @return A linear interpolation between the start and end values, given the
* fraction parameter.
*/
public T evaluate(float fraction, T startValue, T endValue);
} 下面看一下FloatEvaluator源码
在frameworks/base/core/java/android/animation/FloatEvaluator.java中
public class FloatEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator {
/**
* This function returns the result of linearly interpolating the start and end values, with
* fraction representing the proportion between the start and end values. The
* calculation is a simple parametric calculation: result = x0 + t * (v1 - v0),
* where x0 is startValue, x1 is endValue,
* and t is fraction.
*
* @param fraction The fraction from the starting to the ending values
* @param startValue The start value; should be of type float or
* Float
* @param endValue The end value; should be of type float or Float
* @return A linear interpolation between the start and end values, given the
* fraction parameter.
*/
public Float evaluate(float fraction, Number startValue, Number endValue) {
float startFloat = startValue.floatValue();
return startFloat + fraction * (endValue.floatValue() - startFloat);
}
} 重写了 evaluate()函数,evaluate()方法当中传入了三个参数,第一个参数fraction非常重要,这个参数用于表示动画的完成度的,我们应该根据它来计算当前动画的值应该是多少,第二第三个参数分别表示动画的初始值和结束值。那么上述代码的逻辑就比较清晰了,用结束值减去初始值,算出它们之间的差值,然后乘以fraction这个系数,再加上初始值,那么就得到当前动画的值了。返回值就是在监听器里通过getAnimatedValue()获取的值。
知道上面这些,我们使用ValueAnimator的ofFloat()和ofInt()函数时,就没必要去考虑TypeEvaluator了,因为android已经给我写好了。
ValueAnimator不仅可以操作一些数值,也可以操作对象,它有这样一个函数:
ofObject(TypeEvaluator evaluator, Object... values)
该函数是用于对任意对象进行动画操作的。但是相比于浮点型或整型数据,对象的动画操作明显要更复杂一些,因为系统将完全无法知道如何从初始对象过度到结束对象,因此这个时候我们就需要实现一个自己的TypeEvaluator来告知系统如何进行过度。
下面看一个demo,http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/43816093
下面来先定义一个Point类,如下所示:
public class Point {
private float x;
private float y;
public Point(float x, float y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public float getX() {
return x;
}
public float getY() {
return y;
}
} Point类非常简单,只有x和y两个变量用于记录坐标的位置,并提供了构造方法来设置坐标,以及get方法来获取坐标。接下来定义PointEvaluator,如下所示:
public class PointEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator{
@Override
public Object evaluate(float fraction, Object startValue, Object endValue) {
Point startPoint = (Point) startValue;
Point endPoint = (Point) endValue;
float x = startPoint.getX() + fraction * (endPoint.getX() - startPoint.getX());
float y = startPoint.getY() + fraction * (endPoint.getY() - startPoint.getY());
Point point = new Point(x, y);
return point;
}
} 可以看到,PointEvaluator同样实现了TypeEvaluator接口并重写了evaluate()方法。其实evaluate()方法中的逻辑还是非常简单的,先是将startValue和endValue强转成Point对象,然后同样根据fraction来计算当前动画的x和y的值,最后组装到一个新的Point对象当中并返回。
这样我们就将PointEvaluator编写完成了,接下来我们就可以非常轻松地对Point对象进行动画操作了,比如说我们有两个Point对象,现在需要将Point1通过动画平滑过度到Point2,就可以这样写:
Point point1 = new Point(0, 0);
Point point2 = new Point(300, 300);
ValueAnimator anim = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new PointEvaluator(), point1, point2);
anim.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
Point point = (Point) animation.getAnimatedValue();//注意这里的返回值类型是PointEvaluator的evaluate函数返回值类型
long time = animation.getCurrentPlayTime();
Log.d("Test", "time "+time+" x=" + point.getX()+" y="+point.getY());
}
});
anim.setDuration(5000);
anim.start();
D/Test: time 0 x=0.0 y=0.0
D/Test: time 6 x=0.0 y=0.0
D/Test: time 18 x=0.2138704 y=0.2138704
D/Test: time 34 x=0.8548826 y=0.8548826
D/Test: time 50 x=1.8467456 y=1.8467456
D/Test: time 68 x=3.310606 y=3.310606
D/Test: time 84 x=5.1927567 y=5.1927567
D/Test: time 100 x=7.341528 y=7.341528
D/Test: time 117 x=10.019302 y=10.019302
D/Test: time 134 x=13.09627 y=13.09627
D/Test: time 151 x=16.34902 y=16.34902
D/Test: time 167 x=20.174816 y=20.174816
D/Test: time 184 x=24.370802 y=24.370802
D/Test: time 201 x=28.647467 y=28.647467
D/Test: time 217 x=33.527023 y=33.527023
D/Test: time 234 x=38.738724 y=38.738724
D/Test: time 250 x=43.933983 y=43.933983
D/Test: time 267 x=49.74718 y=49.74718
D/Test: time 284 x=55.84631 y=55.84631
D/Test: time 300 x=61.832195 y=61.832195
D/Test: time 317 x=68.435936 y=68.435936
D/Test: time 334 x=75.272224 y=75.272224
D/Test: time 350 x=81.90143 y=81.90143
D/Test: time 367 x=89.133026 y=89.133026
D/Test: time 384 x=96.538246 y=96.538246
D/Test: time 400 x=103.64744 y=103.64744
D/Test: time 417 x=111.32891 y=111.32891
D/Test: time 434 x=119.12061 y=119.12061
D/Test: time 451 x=126.53486 y=126.53486
D/Test: time 467 x=134.47696 y=134.47696
D/Test: time 484 x=142.46333 y=142.46333
D/Test: time 501 x=150.0 y=150.0
D/Test: time 517 x=158.00723 y=158.00723
D/Test: time 534 x=165.99164 y=165.99164
D/Test: time 551 x=173.46515 y=173.46515
D/Test: time 567 x=181.34035 y=181.34035
D/Test: time 584 x=189.12622 y=189.12622
D/Test: time 601 x=196.35255 y=196.35255
D/Test: time 617 x=203.9018 y=203.9018
D/Test: time 634 x=211.29738 y=211.29738
D/Test: time 651 x=218.09857 y=218.09857
D/Test: time 667 x=225.136 y=225.136
D/Test: time 684 x=231.95915 y=231.95915
D/Test: time 701 x=238.1678 y=238.1678
D/Test: time 717 x=244.52008 y=244.52008
D/Test: time 734 x=250.60283 y=250.60283
D/Test: time 751 x=256.066 y=256.066
D/Test: time 767 x=261.57675 y=261.57675
D/Test: time 784 x=266.76932 y=266.76932
D/Test: time 801 x=271.35254 y=271.35254
D/Test: time 817 x=275.88605 y=275.88605
D/Test: time 834 x=280.0606 y=280.0606
D/Test: time 850 x=283.65097 y=283.65097
D/Test: time 867 x=287.09564 y=287.09564
D/Test: time 884 x=290.14935 y=290.14935
D/Test: time 901 x=292.65848 y=292.65848
D/Test: time 917 x=294.92944 y=294.92944
D/Test: time 934 x=296.78714 y=296.78714
D/Test: time 951 x=298.15326 y=298.15326
D/Test: time 967 x=299.1946 y=299.1946
D/Test: time 984 x=299.81055 y=299.81055
D/Test: time 1001 x=300.0 y=300.0
好的,这就是自定义TypeEvaluator的全部用法,掌握了这些知识之后,我们就可以来尝试一下如何通过对Point对象进行动画操作,从而实现整个自定义View的动画效果。
新建一个MyAnimView继承自View,代码如下所示:
public class MyAnimView extends View {
public static final float RADIUS = 100f;
private Point currentPoint;
private Paint mPaint;
public MyAnimView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (currentPoint == null) {
currentPoint = new Point(RADIUS, RADIUS);
drawCircle(canvas);
startAnimation();
} else {
drawCircle(canvas);
}
}
private void drawCircle(Canvas canvas) {
float x = currentPoint.getX();
float y = currentPoint.getY();
canvas.drawCircle(x, y, RADIUS, mPaint);
}
private void startAnimation() {
Point startPoint = new Point(RADIUS, RADIUS);
Point endPoint = new Point(getWidth() - RADIUS, getHeight() - RADIUS);
ValueAnimator anim = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new PointEvaluator(), startPoint, endPoint);
anim.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
currentPoint = (Point) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
anim.setDuration(5000);
anim.start();
}
}
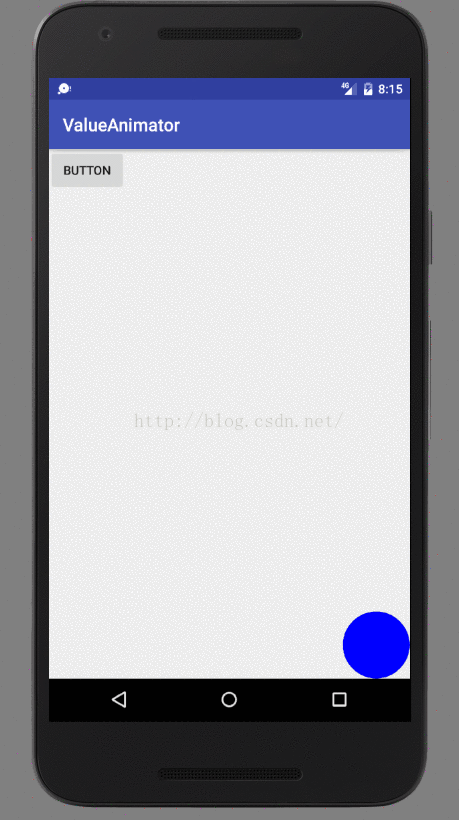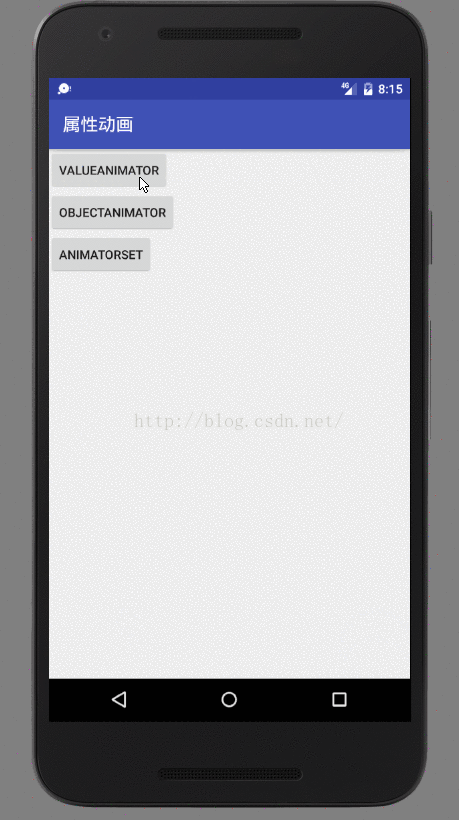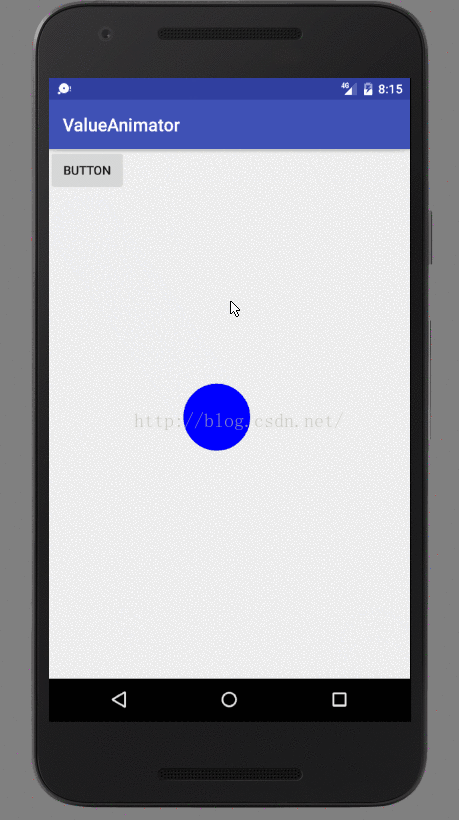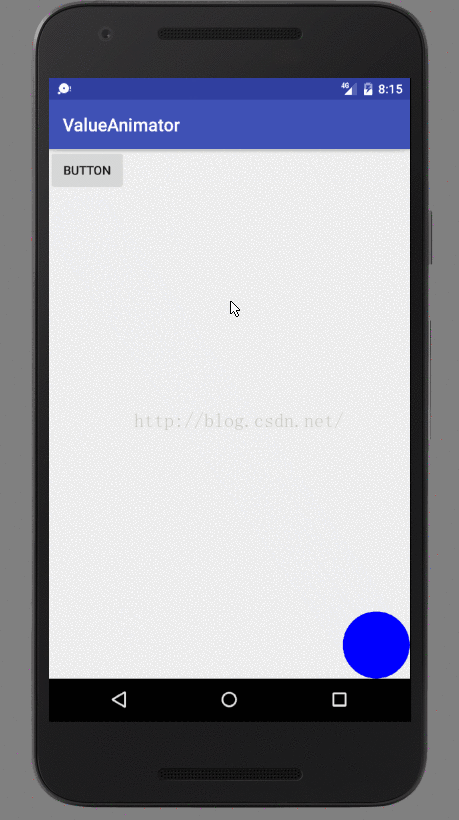
基本上还是很简单的,总共也没几行代码。首先在自定义View的构造方法当中初始化了一个Paint对象作为画笔,并将画笔颜色设置为蓝色,接着在onDraw()方法当中进行绘制。这里我们绘制的逻辑是由currentPoint这个对象控制的,如果currentPoint对象不等于空,那么就调用drawCircle()方法在currentPoint的坐标位置画出一个半径为50的圆,如果currentPoint对象是空,那么就调用startAnimation()方法来启动动画。
那么我们来观察一下startAnimation()方法中的代码,其实大家应该很熟悉了,就是对Point对象进行了一个动画操作而已。这里我们定义了一个startPoint和一个endPoint,坐标分别是View的左上角和右下角,并将动画的时长设为5秒。然后有一点需要大家注意的,就是我们通过监听器对动画的过程进行了监听,每当Point值有改变的时候都会回调onAnimationUpdate()方法。在这个方法当中,我们对currentPoint对象进行了重新赋值,并调用了invalidate()方法,这样的话onDraw()方法就会重新调用,并且由于currentPoint对象的坐标已经改变了,那么绘制的位置也会改变,于是一个平移的动画效果也就实现了。
下面我们只需要在布局文件当中引入这个自定义控件:
看了上面,大家应该还有一个疑问,就是evaluate()函数的fraction参数是谁传进来的,这个又要讲到Interpolator这个东西,该文就没有去讲这个东西了,知道是它是控制动画的变化率的,动画系统内部已有这个东西,而且fraction值是由它得来的,推荐博文http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/44171115。
ValueAnimator其他一些方法,我们可以调用setStartDelay()方法来设置动画延迟播放的时间,调用setRepeatCount()和setRepeatMode()方法来设置动画循环播放的次数以及循环播放的模式,循环模式包括RESTART和REVERSE两种,分别表示重新播放和倒序播放的意思。
ValueAnimator同样也可以使用xml文件来配置,在res目录下面新建一个animator文件夹
例如这样:
后面会继续几句ValueAnimator的子类ObjectAnimator的使用,这个类在我们写项目涉及动画的时候应该用得比较多。