程序的加载链接和库-目标文件
用汇编的方式实现读取1000号逻辑扇区开始的8个扇区
IDE通道的通讯地址是0x1F0 - 0x1F7
其中0x1F3 - 0x1F6 4个字节的端口是用来写入LBA地址的
LBA就是 logical Block Address
1000的16进制就是0x3E8
向0x1F3 - 0x1F6写入 0x3E8
向0x1F2这个地址写入扇区数量,也就是8
向0X1F7写入要执行的操作命令码,对读操作的命令码是 0x20
具体汇编代码如下
out 0x1F3 0x00
out 0x1F4 0x00
out 0x1F5 0x03
out 0x1F6 0xE8
out 0x1F2 0x08
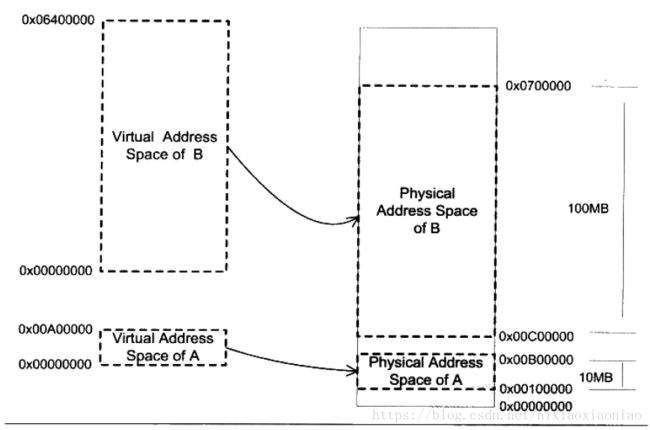
out 0x1F7 0x20假设有128M内存
A程序需要10M,B程序要100M,C程序需要20M
直接这么分配会有问题,不可能三个同时运行,按程序维度切换内存效率低
分配策略需要解决下面一些问题
1.地址空间不隔离
2.内存使用效率低
3.程序运行的地址不确定
解决的方式就是 分段,分页
分段实际是在物理内存之上又加了一个层,是虚拟内存
分页则用来解决上面的第二个问题,效率低
分页开可以解决加载的一些问题,动态链接库的共享,程序段,代码段的读写权限控制等
分页跟操作系统中断也紧密联系
从操作系统角度看 hello world程序的编译,加载,链接过程
预编译cpp
gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i
或者
cpp hello.c > hello.i编译cc1
gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s
或者
cc1 hello.c汇编as
gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o
或者
as hello.s -o hello.o链接 ld ,这里需要加上很多静态,动态库的路径
一个完整的编译过程如下
Using built-in specs.
COLLECT_GCC=gcc
COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/lto-wrapper
Target: x86_64-redhat-linux
Configured with: ../configure --prefix=/usr --mandir=/usr/share/man --infodir=/usr/share/info --with-bugurl=http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla --enable-bootstrap --enable-shared --enable-threads=posix --enable-checking=release --with-system-zlib --enable-__cxa_atexit --disable-libunwind-exceptions --enable-gnu-unique-object --enable-linker-build-id --with-linker-hash-style=gnu --enable-languages=c,c++,objc,obj-c++,java,fortran,ada,go,lto --enable-plugin --enable-initfini-array --disable-libgcj --with-isl=/builddir/build/BUILD/gcc-4.8.5-20150702/obj-x86_64-redhat-linux/isl-install --with-cloog=/builddir/build/BUILD/gcc-4.8.5-20150702/obj-x86_64-redhat-linux/cloog-install --enable-gnu-indirect-function --with-tune=generic --with-arch_32=x86-64 --build=x86_64-redhat-linux
Thread model: posix
gcc version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (GCC)
COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-mtune=generic' '-march=x86-64'
/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/cc1 -quiet -v b.c -quiet -dumpbase b.c -mtune=generic -march=x86-64 -auxbase b -version -o /tmp/ccE6VyWz.s
GNU C (GCC) version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (x86_64-redhat-linux)
compiled by GNU C version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16), GMP version 6.0.0, MPFR version 3.1.1, MPC version 1.0.1
GGC heuristics: --param ggc-min-expand=97 --param ggc-min-heapsize=127051
ignoring nonexistent directory "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include-fixed"
ignoring nonexistent directory "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../x86_64-redhat-linux/include"
#include "..." search starts here:
#include <...> search starts here:
/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include
/usr/local/include
/usr/include
End of search list.
GNU C (GCC) version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (x86_64-redhat-linux)
compiled by GNU C version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16), GMP version 6.0.0, MPFR version 3.1.1, MPC version 1.0.1
GGC heuristics: --param ggc-min-expand=97 --param ggc-min-heapsize=127051
Compiler executable checksum: 25c276d835072ed72bab97eea8b3b665
COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-mtune=generic' '-march=x86-64'
as -v --64 -o /tmp/ccmR5XjD.o /tmp/ccE6VyWz.s
GNU assembler version 2.25.1 (x86_64-redhat-linux) using BFD version version 2.25.1-32.base.el7_4.2
COMPILER_PATH=/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/
LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/:/lib/../lib64/:/usr/lib/../lib64/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../:/lib/:/usr/lib/
COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-mtune=generic' '-march=x86-64'
/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/collect2 --build-id --no-add-needed --eh-frame-hdr --hash-style=gnu -m elf_x86_64 -dynamic-linker /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/crti.o /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/crtbegin.o -L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5 -L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64 -L/lib/../lib64 -L/usr/lib/../lib64 -L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../.. /tmp/ccmR5XjD.o -lgcc --as-needed -lgcc_s --no-as-needed -lc -lgcc --as-needed -lgcc_s --no-as-needed /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/crtend.o /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/crtn.o/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/cc1 -quiet -v b.c -quiet -dumpbase b.c -mtune=generic -march=x86-64 -auxbase b -version -o /tmp/ccE6VyWz.s
GNU C (GCC) version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (x86_64-redhat-linux)
compiled by GNU C version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16), GMP version 6.0.0, MPFR version 3.1.1, MPC version 1.0.1
GGC heuristics: --param ggc-min-expand=97 --param ggc-min-heapsize=127051
ignoring nonexistent directory "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include-fixed"
ignoring nonexistent directory "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../x86_64-redhat-linux/include"
#include "..." search starts here:
#include <...> search starts here:
/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include
/usr/local/include
/usr/include
End of search list.
GNU C (GCC) version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (x86_64-redhat-linux)
compiled by GNU C version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16), GMP version 6.0.0, MPFR version 3.1.1, MPC version 1.0.1
GGC heuristics: --param ggc-min-expand=97 --param ggc-min-heapsize=127051
Compiler executable checksum: 25c276d835072ed72bab97eea8b3b665
COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-mtune=generic' '-march=x86-64'
as -v --64 -o /tmp/ccmR5XjD.o /tmp/ccE6VyWz.s
GNU assembler version 2.25.1 (x86_64-redhat-linux) using BFD version version 2.25.1-32.base.el7_4.2
COMPILER_PATH=/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/
LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/:/lib/../lib64/:/usr/lib/../lib64/:/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../:/lib/:/usr/lib/
COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-mtune=generic' '-march=x86-64'
/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/collect2 --build-id --no-add-needed --eh-frame-hdr --hash-style=gnu -m elf_x86_64 -dynamic-linker /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/crti.o /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/crtbegin.o -L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5 -L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64 -L/lib/../lib64 -L/usr/lib/../lib64 -L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../.. /tmp/ccmR5XjD.o -lgcc --as-needed -lgcc_s --no-as-needed -lc -lgcc --as-needed -lgcc_s --no-as-needed /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/crtend.o /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/../../../../lib64/crtn.o编译过程
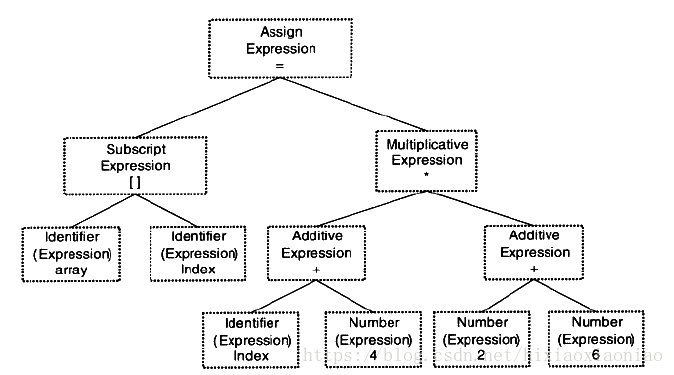
编译的语法树
编译的步骤
1.词法分析
2.语法分析
3.语义分析
4.中间语言产生
5.目标代码生成和优化
整个编译和链接的过程如下:
Linux的可执行文件是 ELF格式的
Executable Linkable Format 都是COFF common file format格式的变种
通过file命令查看 一些不同的ELF格式文件结果如下
file link.o
link.o: ELF 64-bit LSB relocatable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), not stripped
file libfoo.so
libfoo.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, BuildID[sha1]=871ecaf438d2ccdcd2e54cd8158b9d09a9f971a7, not stripped
file p1
p1: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=37f75ef01273a9c77f4b4739bcb7b63a4545d729, not stripped
file libfoo.so
libfoo.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, BuildID[sha1]=871ecaf438d2ccdcd2e54cd8158b9d09a9f971a7, stripped
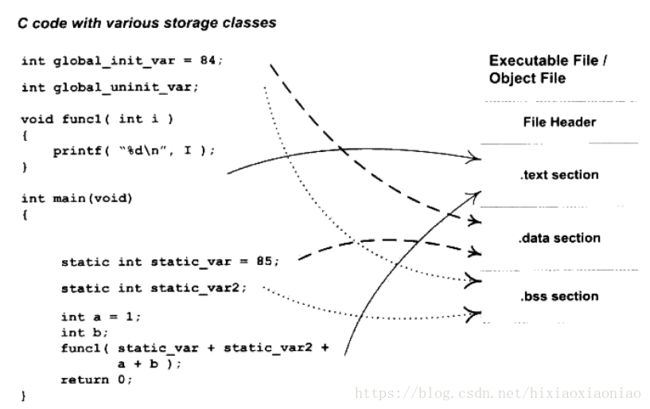
一段C代码对应的各种类型的 section如下
代码放到 .text段中,数据放到 .data段中,未初始化的全局变量和局部变量放到 .bss中
一个专门用来分析ELF内容的c程序
#include
extern char __executable_start[];
extern char etext[], _etext[], __etext[];
extern char edata[], _edata[];
extern char end[], _end[];
int main() {
printf("executable start %X\n",__executable_start);
printf("text end %X %X %X\n",etext, _etext, __etext);
printf("data end %X %X\n",edata, _edata);
printf("exxecutable end %X %X\n",end , _end);
} objdump -h SpecialSymbol.o
SpecialSymbol.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Sections:
Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn
0 .text 0000006a 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000040 2**0
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, RELOC, READONLY, CODE
1 .data 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 000000aa 2**0
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
2 .bss 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 000000aa 2**0
ALLOC
3 .rodata 0000004f 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 000000aa 2**0
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
4 .comment 0000002e 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 000000f9 2**0
CONTENTS, READONLY
5 .note.GNU-stack 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000127 2**0
CONTENTS, READONLY
6 .eh_frame 00000038 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000128 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, RELOC, READONLY, DATA将一个图片拷贝成二进制格式文件
objcopy -I binary -O elf64 -B i386 xx.jpg image.o
自定义的段,加上 __atribute__ 前缀,如
__attribute__((section("foo"))) int global = 42;
__attribute__((section("bar"))) void foo(){}查看SpecialSymbol.o的头文件
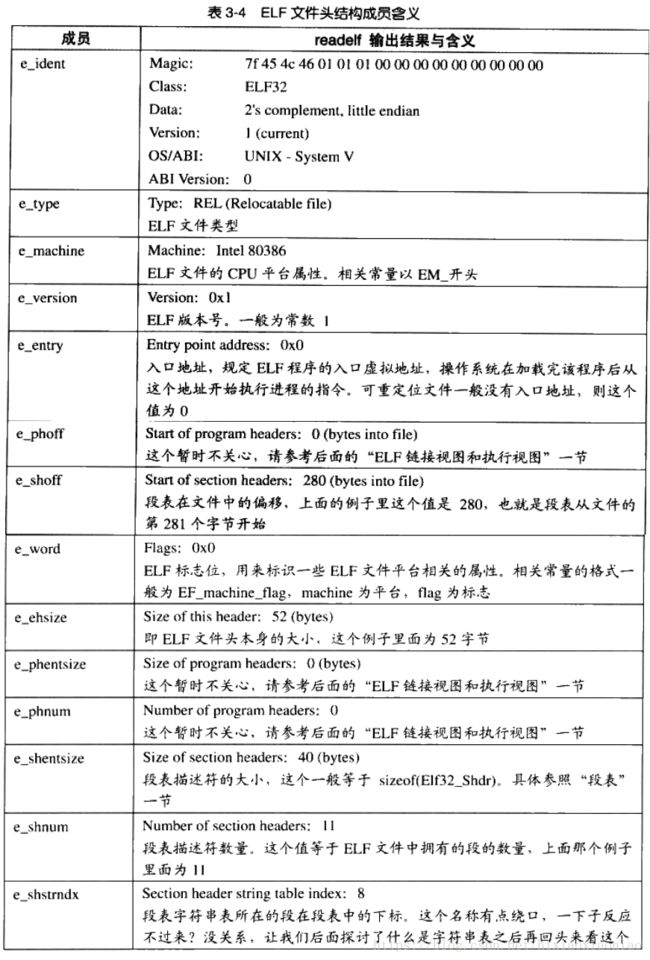
readelf -h SpecialSymbol.o
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 0 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 1416 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 0 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 0
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 13
Section header string table index: 10
ELF头文件定义
SpecialSymbol的段表如下
readelf -S SpecialSymbol.o
There are 13 section headers, starting at offset 0x588:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Offset
Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0
[ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000040
000000000000006a 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 1
[ 2] .rela.text RELA 0000000000000000 000003f0
0000000000000180 0000000000000018 I 11 1 8
[ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000aa
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1
[ 4] .bss NOBITS 0000000000000000 000000aa
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1
[ 5] .rodata PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000aa
000000000000004f 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[ 6] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000f9
000000000000002e 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1
[ 7] .note.GNU-stack PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000127
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[ 8] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000128
0000000000000038 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[ 9] .rela.eh_frame RELA 0000000000000000 00000570
0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 11 8 8
[10] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000160
0000000000000061 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[11] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 000001c8
00000000000001c8 0000000000000018 12 9 8
[12] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000390
000000000000005b 0000000000000000 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), l (large)
I (info), L (link order), G (group), T (TLS), E (exclude), x (unknown)
O (extra OS processing required) o (OS specific), p (processor specific)ELF头文件会指向shstrtab段表
shstrtab是段名称字符串表,里面包含了所有段的名称,比如.text,.bss,.note等
ELF头文件中的重定位信息
readelf -r SpecialSymbol.o
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x3f0 contains 16 entries:
Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend
000000000005 000a0000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 __executable_start + 0
00000000000a 00050000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 .rodata + 0
000000000014 000b00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 printf - 4
000000000019 000c0000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 __etext + 0
00000000001e 000d0000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 _etext + 0
000000000023 000e0000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 etext + 0
000000000028 00050000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 .rodata + 15
000000000032 000b00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 printf - 4
000000000037 000f0000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 _edata + 0
00000000003c 00100000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 edata + 0
000000000041 00050000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 .rodata + 28
00000000004b 000b00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 printf - 4
000000000050 00110000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 _end + 0
000000000055 00120000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 end + 0
00000000005a 00050000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 .rodata + 38
000000000064 000b00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 printf - 4
强符号和弱符号
对于已经初始化数据的变量就是强符号,没有初始化的就是弱符号,函数是强符号
定义规则如下
1.不允许有多个强符号,否则报错
2.如果有一个强符号多个弱符号则选择强符号
3.如果有多个弱符号,则选择占用空间最大的一个,比如A是int类型,B是double则选择B
调试信息,用如下方式编译就会产生调试信息
gcc -g -c -o SpecialSymbol.o SpecialSymbol.c
readelf -S SpecialSymbol.o
There are 21 section headers, starting at offset 0xbc8:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Offset
Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0
[ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000040
000000000000006a 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 1
[ 2] .rela.text RELA 0000000000000000 000007a8
0000000000000180 0000000000000018 I 19 1 8
[ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000aa
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1
[ 4] .bss NOBITS 0000000000000000 000000aa
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1
[ 5] .rodata PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000aa
000000000000004f 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[ 6] .debug_info PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000f9
00000000000000f4 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[ 7] .rela.debug_info RELA 0000000000000000 00000928
0000000000000240 0000000000000018 I 19 6 8
[ 8] .debug_abbrev PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000001ed
0000000000000072 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[ 9] .debug_aranges PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000025f
0000000000000030 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[10] .rela.debug_arang RELA 0000000000000000 00000b68
0000000000000030 0000000000000018 I 19 9 8
[11] .debug_line PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000028f
000000000000004a 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[12] .rela.debug_line RELA 0000000000000000 00000b98
0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 19 11 8
[13] .debug_str PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000002d9
0000000000000118 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1
[14] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000003f1
000000000000002e 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1
[15] .note.GNU-stack PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000041f
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[16] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000420
0000000000000038 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[17] .rela.eh_frame RELA 0000000000000000 00000bb0
0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 19 16 8
[18] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000458
00000000000000b0 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[19] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 00000508
0000000000000240 0000000000000018 20 14 8
[20] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000748
000000000000005b 0000000000000000 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), l (large)
I (info), L (link order), G (group), T (TLS), E (exclude), x (unknown)
O (extra OS processing required) o (OS specific), p (processor specific)
查看SpecialSymbol.o中的符号,U就是未定义的,在启动程序的时候会动态链接进来
nm SpecialSymbol.o
U edata
U _edata
U end
U _end
U etext
U _etext
U __etext
U __executable_start
0000000000000000 T main
U printf
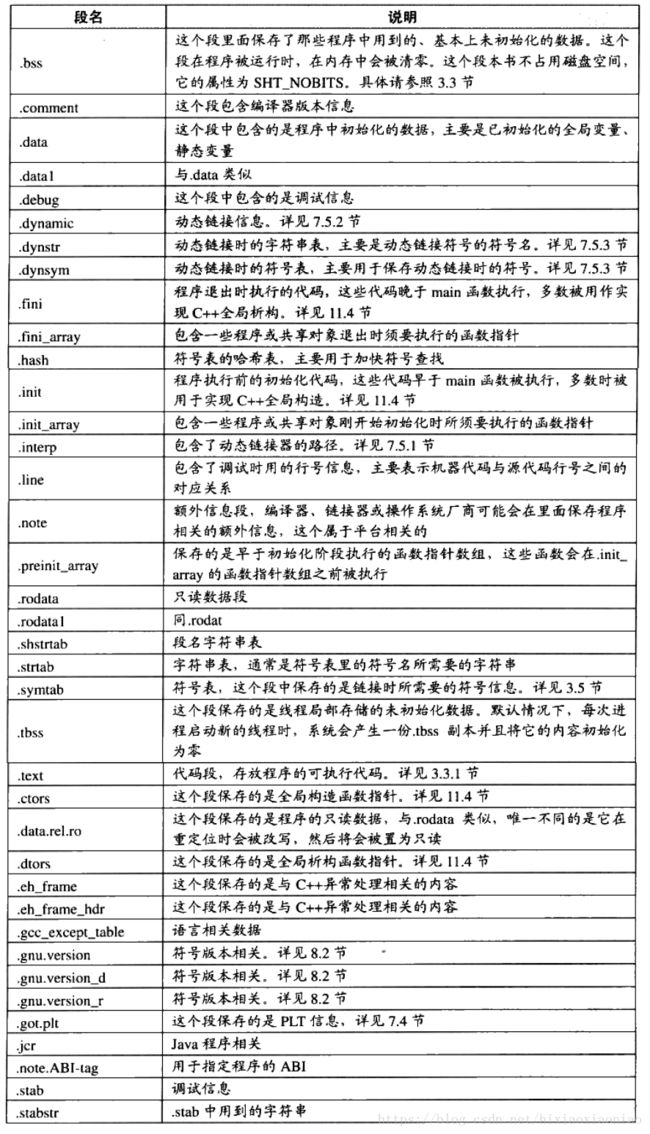
ELF常见的 section如下:
一些相关的命令
| 名称 | 含义 |
| ar | 创建静态库,插入删除列出和提取成员 |
| ldd | 列出一个可执行文件在运行时所需要的共享库 |
| gcc | 强大的编译工具 |
| nm | 列出一个目标文件的符号表中定义的符号 |
| size | 列出目标文件中section的名字和大小 |
| objdump | 所有二进制工具之母 能够显示一个目标文件中所有的信息 最大的作用是反汇编.text 片段中的二进制指令 |
| readelf | 显示一个目标文件的完整结构 包括ELF头中编码的所有信息,包含size和nm的功能 |
| strace | 跟踪调试工具 |
| strip | 删除多余的段 |
| objcopy | 将一个目标文件中的内容拷贝到另一个中 |
| dumpe2fs | 查询文件系统状态格式 |
| tune2fs | 调整和查看文件系统格式 |
参考
关于Linux静态库和动态库的分析
程序的编译链接过程
程序运行流程——链接、装载及执行