章节3.1和3.2----栈的表示、实现和应用
文章目录
- 1、存储结构 P46
- 2、顺序栈实现
- 3、链栈的实现
- 4、进制转换
- 5、括号匹配
- 6、行编辑程序
- 7、迷宫求解
- 8、表达式求值
- 9、斐波那契数列
- 10、汉诺塔问题
1、存储结构 P46
typedef struct{
int *base;
int *top;
int StackSize;
}SqStack;
2、顺序栈实现
会了顺序表和链表的话,栈就简单的多了
下面我给出的这个小例子,里面包含了顺序栈的初始化、压栈、弹栈、遍历操作
#include3、链栈的实现
关于链栈的实现,其实前面我们在写链表的时候,最终我们优化出来的终极版本,其实就已经很像一个链式栈了。只是操作上再加以限制就好了
栈要遵循先进后出的原则:
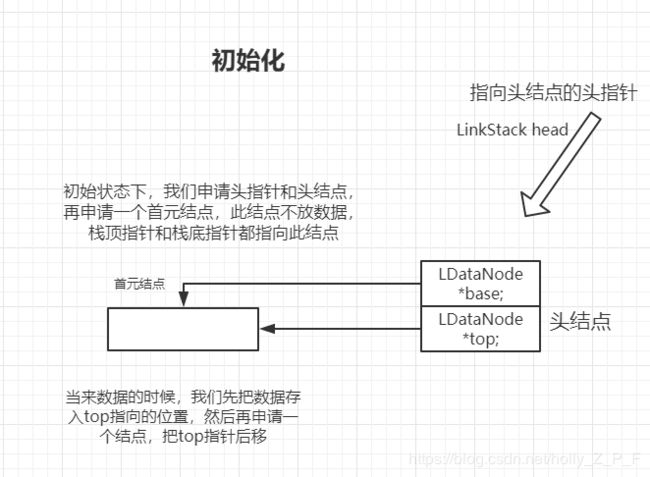
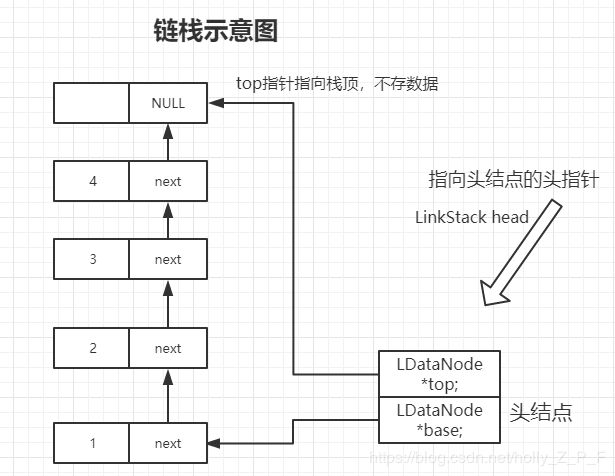
需要注意的是,我们在弹栈的时候,也就相当于删除链表末尾元素,所以要先找到末尾元素的前驱,如果这是个双向链栈,那么我们可以直接通过top指针找到他的前驱,单向链栈的话,我们就需要遍历找到最后了。
这里我用的是单向链栈,显然用双向效率更高,有兴趣可以试试实现双向链栈。
实现代码:
#include4、进制转换
注意:这里我写的三个程序,均实现的是一个十进制数转化成n进制数,n<10.
如果要转换十六进制,需要略作修改。
C语言实现
#include数组模拟栈实现:
#includeC++(STL)实现
/******
author: 1900
language: C++
******/
#include5、括号匹配
注意:括号是字符型数据
#include6、行编辑程序
#include7、迷宫求解
关于这个迷宫求解,建议后边学了图之后,再回过头来写,会更明白些
这里贴出一个我之前学的时候写的
两种写法:
迷宫求解解法详解
8、表达式求值
关于最后这三个问题,我先更新下边的东西,这个回过头第二遍的时候再写吧,我太懒了,要跟不上进度了。。。/大哭
