Android Q沙盒机制 使用探究
以下基于Android Q Bate3版本,最新版本为bate5 基本没有变化,另外target小于29,并且app没有手动开启沙盒模式,可以不用适配。
适配必看
1、权限有改动
Note: 早先Android Q版本的 READ_MEDIA_IMAGES, READ_MEDIA_AUDIO, and READ_MEDIA_VIDEO被废弃了,还是用原来的权限。
2、媒体文件删除
beta2版本应用无法通过申请存储权限直接删除其他应用生成的多媒体文件,但是beta3应用申请WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE就可以直接删除;
3、图库和音乐角色删除
RoleManager.ROLE_GALLERY和RoleManager.ROLE_GALLERY,应用无法申请成为默认的图库应用和音乐应用
4、公共集合路径
新增MediaStore.Images.Media.RELATIVE_PATH属性
通过该属性应用可以在公共集合目录下设置任意的路径来存储文件
废弃原来的:MediaStore.Images.Media>PRIMARY_DIRECTORY和MediaStore.Images.Media.SECONDARY_DIRECTORY
一、Android Q应用存储特性
Android Q和Aandroid P存储空间管理如下:
Android Q共分为沙盒空间、共享集合空间、外部存储三个分区。应用读写自己沙箱和共享集合目录中应用自己的文件是不需要申请任何权限的,但是如果应用需要读取其他应用生成的多媒体文件就需要申请权限
1、沙盒空间
除了原来的getFilesDir、getCacheDir、getExternalCacheDir等沙盒内路径外,以下三种也会默认为沙盒路径。
| API |
路径 |
|---|---|
| Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES) |
storage/emulated/0/Android/sandbox/packagename/Pictures |
| Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() |
storage/emulated/0/Android/sandbox/packagename/ storage/self/primary/Android/sandbox/packagename/ |
| new File("/sdcard","file.txt") |
storage/emulated/0/Android/sandbox/packagename/file.txt storage/self/primary/Android/sandbox/packagename/file.txt |
适配建议:
1、不推荐直接通过 /sdcard、/data等字符串构造路径如:new File("/sdcard"),推荐使用API的方式获取路径如:Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),此处需要业务方整改适配。
2、对原有沙盒空间的访问,可不进行适配
3、原来存储到沙盒外的文件将默认在沙盒内,是否需要适配需要进行确认。判断标准参照沙盒特性。
沙盒空间特性:
应用卸载会删除沙盒空间(卸载需要保留的文件不能保存在沙盒空间,可通过SAF和MediaStore进行适配)
外部不再能够直接访问(可以通过FileProvider进行适配,或存储到非沙盒空间,业务场景如:分享文件、吊起系统Installer安装APK)
应用访问不需要权限
2、共享集合空间(漏加权限,对data字段没有适配)
Android Q媒体推荐采用分区存储,图片、音频、视频文件将存储到对应的集合中,存储在共享集合中的文件在应用卸载后不会被删除
Q之前,通常使用MediaStore的"_data"字段获取文件的真实路径,该方式在Q及之后将被禁止。
“_data”值变化,返回的值不再是文件真实路径
查询sql语句管控,不合法的查询列会导致返回的查询数据为空,除了mediastore中定义的列以外的信息,其他的信息,无法查询成功
位置信息被删除,无法通过MediaProvider直接查询,适配方式为:需要应用动态申请ACCESS_MEDIA_LOCATION权限,并调用MediaStore的setRequireOriginal方法
MediaStore 通过以下方式获取文件URI,通过URI读写文件(业务方禁止使用data字段获取真实路径)。
// 查询方式没有变化
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, new String[]{MediaStore.Images.Media._ID}, null, null, null);
while (cursor.moveToFirst()){// 以下方式获取媒体文件URI
int id = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex(MediaStore.Images.Media._ID));
Uri photoUri = Uri.parse(MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI.toString()+File.separator+id);
}// 根据URI获取bitmap
private Bitmap getBitmapFromUri(Uri uri) throws IOException {
ParcelFileDescriptor parcelFileDescriptor =
getContentResolver().openFileDescriptor(uri, "r");
FileDescriptor fileDescriptor = parcelFileDescriptor.getFileDescriptor();
Bitmap image = BitmapFactory.decodeFileDescriptor(fileDescriptor);
parcelFileDescriptor.close();
return image;
}
适配建议:
-
共享集合空间的文件访问推荐使用MediaStore、MediaProvider进行适配。
共享集合特性:
-
文件分区存储
-
应用卸载不会删除
-
文件夹通过系统生成(Pictures、DCIM、Movies、Download等)
-
系统只提供了多媒体文件的读权限,没有提供写权限,应用无法通过申请写权限修改其他应用生成的文件
-
访问权限更加细化,详情参考权限变更
权限变更:
bate3版本中,还是用原来权限,以下三个权限被移除
应用读取自己添加的文件不需要权限,读取其他应用的文件需要权限:
-
音乐文件:android.permission.READ_MEDIA_AUDIO
-
照片文件:android.permission.READ_MEDIA_IMAGES
-
视频文件:android.permission.READ_MEDIA_VIDEO
3、外部存储
外部存储空间允许用户自由选择文件目录,并对目录以及目录下的文件进行管理。需要读写指定的任意目录的文件只能通过SAF的方式实现。
适配建议:
-
通过SAF(存储访问)进行适配
二、Android Q外部文件存储适配指引
Android Q的适配方法有:FileProvider、MediaStore&MediaProvider、SAF三种
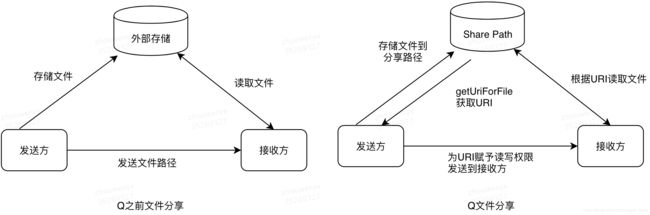
1、FileProvider使用
设计多个应用的文件交流推荐使用FileProvider,使用场景(文件分享、调用系统安装器安装应用)流程图对比如下图:
定义FileProvider
指定分享路径
获取URI
File imagePath = new File(Context.getFilesDir(), "images");
File newFile = new File(imagePath, "default_image.jpg");
Uri contentUri = getUriForFile(getContext(), "com.mydomain.fileprovider", newFile);给URI赋读写权限
//方法一
//mode_flags: FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION, FLAG_GRANT_WRITE_URI_PERMISSION(一个或者两个都行)
Context.grantUriPermission(package, Uri, mode_flags)
//方法二
Intent.setData(Uri)
// FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION, FLAG_GRANT_WRITE_URI_PERMISSION(一个或者两个都行)
Intent.setFlags()分享
//将intent发送给目标(一般通过setResult方法)
setResult()接收
Uri returnUri = intent.getData()
data = getContentResolver.openFIleDescriptor(returnUri,"r")2、MediaStore&MediaProvider
Android Q之前存储图片、视频、音频等文件时,通常在外部存储创建特定一个文件夹,将文件存储在该文件夹下。在Android Q之后,图片等媒体文件推荐存储在共享集合空间,对该结合的访问使用MediaStore&MediaProvider的方式。在Android Q之前就有MediaStore,Android Q之后MediaStore的使用方式发生了调整。
bata3版本 MediaStore的路径发生了变化
bate2中:(路径在Download/secondDir下,primaryDir必须和媒体类型对应,此处为primaryDir=“Download”),并且路径不能够超过2级
values.put(MediaStore.Downloads.PRIMARY_DIRECTORY, primaryDir);
values.put(MediaStore.Downloads.SECONDARY_DIRECTORY, secondDir);bate3中:(路径外部传入,不能以“/”开头,可以有多层嵌套)
values.put(MediaStore.Images.Media.RELATIVE_PATH,"DCIM/path1/path2/");
保存文件:
/**
* @param name
* @param description
* @param mime
* @param path
* @return 文件URI.toString
*/
private String savaPhotoToDownload(String name, String description, String mime,String path) {
if(path.startsWith("/")){
return null;
}
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(MediaStore.Images.Media.DISPLAY_NAME, name);
values.put(MediaStore.Images.Media.MIME_TYPE, mime);
values.put(MediaStore.Images.Media.DESCRIPTION, description);
values.put(MediaStore.Images.Media.RELATIVE_PATH,path);
Uri url = null;
String stringUri = null;
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();
try {
url = cr.insert(MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, values);
if (url == null) {
return null;
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
ParcelFileDescriptor descriptor = cr.openFileDescriptor(url, "w");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(descriptor.getFileDescriptor());
InputStream inputStream = getResources().getAssets().open("success.png");
while (true) {
int readSize = inputStream.read(buffer);
if (readSize == -1) {
break;
}
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, readSize);
}
outputStream.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (url != null) {
cr.delete(url, null, null);
}
}
if (url != null) {
stringUri = url.toString();
}
return stringUri;
}
// 保存文件 存储位置:/storage/emulated/0/DICM/path1/path2/new_photo_file.png
String path = savaPhoto("new_photo_file", "new photo file descrition", "image/png", "DCIM/path1/path2/");
读取文件
private List loadPhoto() {
List photos = new ArrayList<>();
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI,
new String[]{MediaStore.Images.Media._ID}, null, null, null);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
int id = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex(MediaStore.Images.Media._ID));
Uri uri = Uri.parse(MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI.toString() + File.separator + id);
photos.add(uri);
}
return photos;
}
// 读取文件
List photos = loadPhoto();
if (photos != null && photos.size() > 0) {
showBitmap(iv, loadPhoto().get(0));
} 3、SAF(存储访问框架)
SAF(存储访问框架)简介
-
文档提供程序 — 一种内容提供程序,允许存储服务(如 Google Drive)显示其管理的文件。 文档提供程序作为DocumentsProvider 类的子类实现。文档提供程序的架构基于传统文件层次结构,但其实际数据存储方式由您决定。Android 平台包括若干内置文档提供程序,如 Downloads、Images 和 Videos。
-
客户端应用 — 一种自定义应用,它调用 ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT 和/或 ACTION_CREATE_DOCUMENT Intent 并接收文档提供程序返回的文件;
-
选取器 — 一种系统 UI,允许用户访问所有满足客户端应用搜索条件的文档提供程序内的文档。
SAF 提供的部分功能
-
允许用户浏览所有文档提供程序而不仅仅是单个应用中的内容;
-
让您的应用获得对文档提供程序所拥有文档的长期、持久性访问权限。 用户可以通过此访问权限添加、编辑、保存和删除提供程序上的文件;
-
支持多个用户帐户和临时根目录,如只有在插入驱动器后才会出现的 USB 存储提供程序。
SAF 架构流程图
SAF客户端
1、搜索文档
请注意以下事项:
-
当应用触发 ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT Intent 时,后者会启动一个选取器来显示所有匹配的文档提供程序
-
在 Intent 中添加类别 CATEGORY_OPENABLE 可对结果进行过滤,以仅显示可以打开的文档(如图像文件)
-
语句 intent.setType("image/*") 可做进一步过滤,以仅显示 MIME 数据类型为图像的文档
private static final int READ_REQUEST_CODE = 42;
...
/**
* Fires an intent to spin up the "file chooser" UI and select an image.
*/
public void performFileSearch() {
// ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT is the intent to choose a file via the system's file
// browser.
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT);
// Filter to only show results that can be "opened", such as a
// file (as opposed to a list of contacts or timezones)
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE);
// Filter to show only images, using the image MIME data type.
// If one wanted to search for ogg vorbis files, the type would be "audio/ogg".
// To search for all documents available via installed storage providers,
// it would be "*/*".
intent.setType("image/*");
startActivityForResult(intent, READ_REQUEST_CODE);
}2、处理结果
用户在选取器中选择文档后,系统就会调用 onActivityResult()。指向所选文档的 URI 包含在 resultData 参数中。使用 getData() 提取 URI。获得 URI 后,即可使用它来检索用户想要的文档。例如:
@Override
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode,
Intent resultData) {
// The ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT intent was sent with the request code
// READ_REQUEST_CODE. If the request code seen here doesn't match, it's the
// response to some other intent, and the code below shouldn't run at all.
if (requestCode == READ_REQUEST_CODE && resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK) {
// The document selected by the user won't be returned in the intent.
// Instead, a URI to that document will be contained in the return intent
// provided to this method as a parameter.
// Pull that URI using resultData.getData().
Uri uri = null;
if (resultData != null) {
uri = resultData.getData();
Log.i(TAG, "Uri: " + uri.toString());
showImage(uri);
}
}
}3、检查文档数据
获得文档的 URI 后,即可获得对其元数据的访问权限。以下代码段用于获取 URI 所指定文档的元数据并将其记入日志:
public void dumpImageMetaData(Uri uri) {
// The query, since it only applies to a single document, will only return
// one row. There's no need to filter, sort, or select fields, since we want
// all fields for one document.
Cursor cursor = getActivity().getContentResolver()
.query(uri, null, null, null, null, null);
try {
// moveToFirst() returns false if the cursor has 0 rows. Very handy for
// "if there's anything to look at, look at it" conditionals.
if (cursor != null && cursor.moveToFirst()) {
// Note it's called "Display Name". This is
// provider-specific, and might not necessarily be the file name.
String displayName = cursor.getString(
cursor.getColumnIndex(OpenableColumns.DISPLAY_NAME));
Log.i(TAG, "Display Name: " + displayName);
int sizeIndex = cursor.getColumnIndex(OpenableColumns.SIZE);
// If the size is unknown, the value stored is null. But since an
// int can't be null in Java, the behavior is implementation-specific,
// which is just a fancy term for "unpredictable". So as
// a rule, check if it's null before assigning to an int. This will
// happen often: The storage API allows for remote files, whose
// size might not be locally known.
String size = null;
if (!cursor.isNull(sizeIndex)) {
// Technically the column stores an int, but cursor.getString()
// will do the conversion automatically.
size = cursor.getString(sizeIndex);
} else {
size = "Unknown";
}
Log.i(TAG, "Size: " + size);
}
} finally {
cursor.close();
}
}4、打开文档
获得文档的 URI 后,即可打开文档或对其执行任何其他您想要执行的操作。
private Bitmap getBitmapFromUri(Uri uri) throws IOException {
ParcelFileDescriptor parcelFileDescriptor =
getContentResolver().openFileDescriptor(uri, "r");
FileDescriptor fileDescriptor = parcelFileDescriptor.getFileDescriptor();
Bitmap image = BitmapFactory.decodeFileDescriptor(fileDescriptor);
parcelFileDescriptor.close();
return image;
}private String readTextFromUri(Uri uri) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = getContentResolver().openInputStream(uri);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
inputStream));
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(line);
}
fileInputStream.close();
parcelFileDescriptor.close();
return stringBuilder.toString();
}5、创建新文档
// Here are some examples of how you might call this method.
// The first parameter is the MIME type, and the second parameter is the name
// of the file you are creating:
//
// createFile("text/plain", "foobar.txt");
// createFile("image/png", "mypicture.png");
// Unique request code.
private static final int WRITE_REQUEST_CODE = 43;
...
private void createFile(String mimeType, String fileName) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CREATE_DOCUMENT);
// Filter to only show results that can be "opened", such as
// a file (as opposed to a list of contacts or timezones).
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE);
// Create a file with the requested MIME type.
intent.setType(mimeType);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TITLE, fileName);
startActivityForResult(intent, WRITE_REQUEST_CODE);
}6、删除文档
DocumentsContract.deleteDocument(getContentResolver(), uri);7、编辑文档
private static final int EDIT_REQUEST_CODE = 44;
/**
* Open a file for writing and append some text to it.
*/
private void editDocument() {
// ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT is the intent to choose a file via the system's
// file browser.
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT);
// Filter to only show results that can be "opened", such as a
// file (as opposed to a list of contacts or timezones).
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE);
// Filter to show only text files.
intent.setType("text/plain");
startActivityForResult(intent, EDIT_REQUEST_CODE);
}private void alterDocument(Uri uri) {
try {
ParcelFileDescriptor pfd = getActivity().getContentResolver().
openFileDescriptor(uri, "w");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream =
new FileOutputStream(pfd.getFileDescriptor());
fileOutputStream.write(("Overwritten by MyCloud at " +
System.currentTimeMillis() + "\n").getBytes());
// Let the document provider know you're done by closing the stream.
fileOutputStream.close();
pfd.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}三、SAF和MediaStore对比,合理使用Download下载集合实现静默访问
1、SAF VS MediaStore
访问范围:MediaStore只能访问共享集合,表现在只能访问Pictures、DCIM、Videos、Audio、Download目录,SAF可以访问共享集合和外部空间,访问范围更广。
访问方式:MediaStore对文件的访问是独立的不需要借助系统文件选择器,文件读写过程是静默的,SAF是存储访问框架,需要借助系统文件选择器进行增删改查操作。
文件移动:MediaStore需要通过copy-delete模式实现,SAF直接改变目录树,无copy过程
2、外部存储静默访问
目前外部存储的的访问推荐使用SAF方式,但是该方式必须使用系统的文件选择器,通过系统功能界面间接操纵文件,在大多业务场景下这种方式是不友好的。
MediaStore能够操作Pictures、DCIM、Videos、Audio、Download目录,分别对应图片、视频、音频和下载文件,对应Download目录任何文件都可以进行存储,业务方可以将文件存储在Download目录下
需要注意Download中目录只能有二级目录,即:Download/path/fileDownload/path/path/file是不允许的 (bate3版本通过MediaStore.Images.Media.RELATIVE_PATH可以指定任意子目录,和/sdcard 目录用法一致)
示意图如下:
四、常见适配场景解决方案
需要适配场景
-
文件共享
问题:应用通过其他通信社交软件分享文件给好友,提示文件不存在;应用使用其他应用打开文件,提示文件不存在。
适配方案:1、平台分享团队会磨平和第三方分享SDK的适配点,但是需要业务方确保分享的文件来自于沙盒内。分享业务方提供沙盒内文件,分享组件能够直接读取,分享组件对文件进行转化(URL,base64等)磨平适配点进行适配。
2、如果使用自定义的分享组件,建议通过FileProvider进行适配。
-
读取沙箱外非多媒体文件
问题:文件管理器只能看到应用自己生成的文件,无法查看其他应用的文件; 社交类应用给好友分享本地文件出现本地文件找不到的问题。
适配方案:使用SAF适配解决
-
读取沙箱外多媒体文件
问题:读取本地多媒体文件为空问题。
适配方案:
MediaProvider的“_data”返回值变更导致的问题,Q版本“_data”值不再是多媒体文件的真实路径,应用通过该返回值判断文件是否存在是有问题的,修改方案参考MediaProvider使用说明章节。
-
应用内安装
问题:通过向系统安装器提供 /sdcar/file.apk的方式安装应用,会提示文件无法找到。
适配方案:
应用内安装采用FileProvider方式,步骤如下:
(注意,安装包需要为Release版本)
1、安装吊起方,实现FileProvider,指定分享路径
2、将文件放到分享路径下
3、调用系统安装器,将APK URI发送给安装器,并赋予安装器读取权限
4、安装器读取文件,进行安装。
不需要适配场景
-
应用数据(缓存数据&临时数据)
-
原来数据存储在“/data/data”,“/data/user"等内部存储空间
-
数据不需要分享
-
数据仅应用内使用
参考文档:
https://download.csdn.net/download/hongye_main/11656766