spring-security框架源码改造:根据接口参数验证权限
一、背景
spring-security作为一个权限验证框架,还是很好用的(虽然有点“重”),它能拦截请求,根据请求的路径、配置的权限码和定义的权限验证器进行权限拦截,同时能很方便的和spring、sprign-session等集成。但是我现在有个需求:对于同一个接口的某些参数取不同的值时,可能需要不同的权限验证。比如:/test/set?type=?,当type==1或type==2的时候需要拦截的权限是不一样的(由于项目原因,我们目前使用的版本还是 4.x)。
当然,很直观的想,我们有一些解决方案:
1.在代码层面进行控制(一般不会这样做,耦合性较高)
2.通过自定义拦截器实现(一般都这样做,相当于在原权限拦截的基础上又加了一层拦截,可以在框架的基础上加,也可以在容器的基础上加)
3.改造spring-security源码,使其支持根据参数值进行权限验证(本文要介绍的方式,之所以采取这种方式,主要还是为了深入研究框架)
注:虽然本文要介绍如何改造该框架,但是通常情况下,我都不建议这样做。要改造源码,则需要在某一个指定的版本上操作,但是框架可能涉及到更新换代,等你更新框架版本的时候可能就有的事儿做了哦。另外,我们要保证改造不会对框架本身和依赖被改造框架的框架本身造成不良影响(别改出一堆bug出来o(╯□╰)o),就需要我们对框架本身要足够的了解。
好了,废话不多说,下面我们先介绍spring+spring-security的原理,然后再介绍如何改造。(注:不知道高版本的security有没有相关的功能扩展,还没有去研究,这次改造也是在一两年以前弄的了,只是现在才总结到博客中。另外spring系列的原理我会整理到专栏,这里先不做阐述哈)
二、spring、spring-security 原理简介(4.1.6.RELEASE)
由于security的使用在网上一搜一大堆,这里就不浪费篇幅讲解如何配置使用了哈,我们直接进入正题:它包含哪些关键组件,这些组件是如何协同工作的。
首先,servlet容器在处理http请求的时候,会获取对应请求路径的FilterChain,如果获取到的FilterChain不为空,那么则会执行对应的doFilter方法(这个是servlet的内容,这里就先不深究,一样放到专题中总结)。另外,这里还是得提一下spring的一些简单“原理”。
根据servlet3.0的规范,servlet容器在启动应用的时候,会扫描应用下每一个jar包里面,此文件:META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 里配置的ServletContainerInitializer的实现类,启动运行该示例的onStartup方法,另外可通过注解:@HandlesTypes 绑定它所“感兴趣”的类,这些感兴趣的类,会通过参数传入onStartup方法。
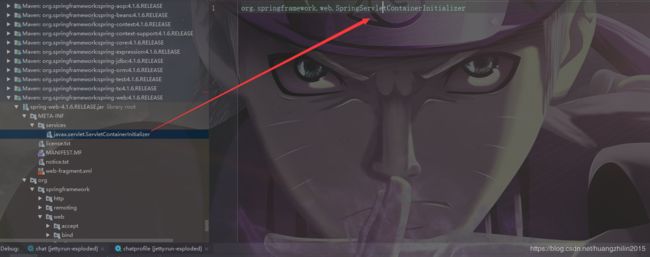
而spring正是利用了这一点,其SpringServletContainerInitializer类实现了ServletContainerInitializer接口,并且将其配置在了spring-web/META-INFO/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer中,如下图所示:
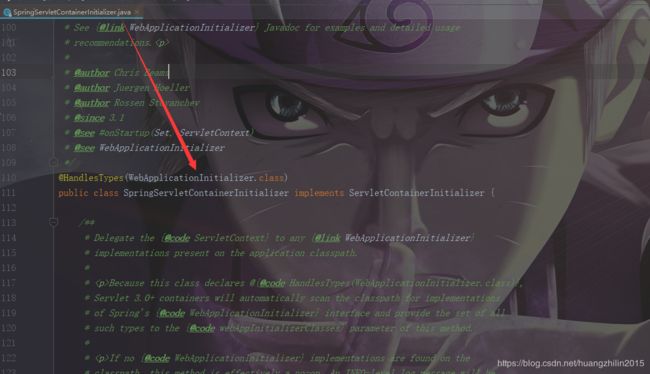
而SpringServletContainerInitializer所感兴趣的类为:WebApplicationInitializer.class:
WebApplicationInitializer是一个接口,它模仿了ServletContainerInitializer,只有一个onStartup方法。SpringServletContainerInitializer在启动(onStartup())的时候,会获取到所有实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的类,并且根据它们各自的@Order排序,然后顺序执行每个WebApplicationInitializer的onStartup方法。
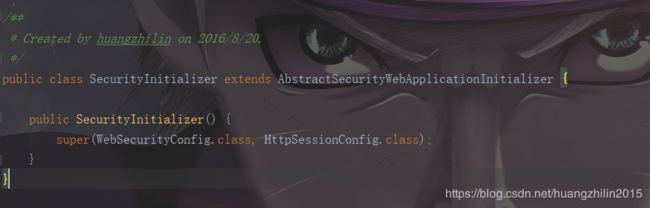
然后再回到我们的spring-security。在我的项目中是通过编码方式集成的spring-security:继承AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer类,通过父类构造方法传递一些配置类,如下所示:
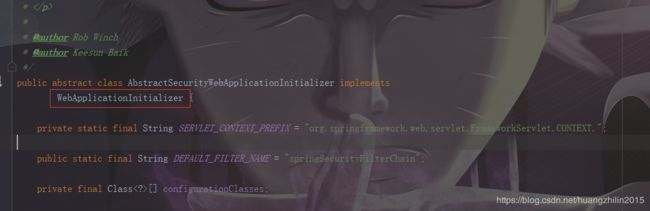
具体的配置不是我们的重点,现在我们来看一下这个AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer是何方神圣。
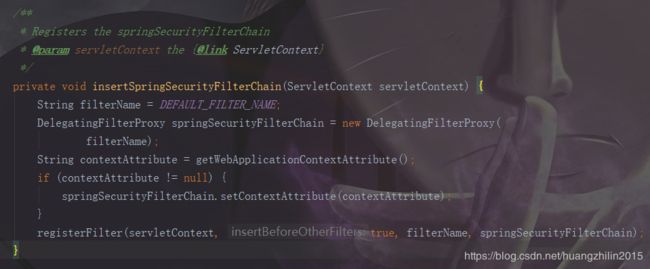
我们可以看到,它实现了我们上面提到的WebApplicationInitializer接口,并且实现了onStartup方法。在其onStartup方法里做的工作里就包含有一项操作:注册springSecurity的过滤器,并且该过滤器是通过DelegatingFilterProxy实现的(delegate为FilterChainProxy,是通过上图中的DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME从WebApplicationContext中获取的,而context中的bean是通过WebSecurityConfiguration注入其中的,且指定了名称为该DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME,具体的操作会在spring源码系列中详细总结),感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看相关源码,逻辑很简单。这里贴一下主要代码,具体就是生成一个过滤器,注册到servletContext,之后的所有请求(/*)都会经过它:
同样的,spring-session也是通过类似的操作开始运作的,经过filter注册之后,我们一个请求可能会包含很多的filter,比如我的项目有spring-session、spring-security、spring-MVC、还有编码的过滤器,整个过滤器链看起来是这个样子的:
springSessionRepositoryFilter->springSecurityFilterChain->characterEncodingFilter->dispathcerServlet
其中还有很多细节,但是并不是我们现在的关注重点,我们要改造springSecurity,所以还是看springSecurityFilterChain这个东东。
我们上面说了,springSecurityFilterChain其实是由DelegatingFilterProxy实现的,而其delegate就是个FilterChainProxy,在doFilter的时候会根据当前的request(比如请求/test/set)获取对应的过滤器列表。它缓存了一些路径和其对应的过滤器列表,方便请求来的时候直接匹配,比如我们配置了一些不需要权限拦截的路径,那么它们排在前面,如果匹配成功就没有权限相关的验证了,否则会有另一个filter列表对请求进行过滤处理。而这个filter列表会被封装成一个VirtualFilterChain,由它进行处理。这是典型的责任链模式应用,大家可以参考其实现运用到自己的项目中(如果需要的话)。
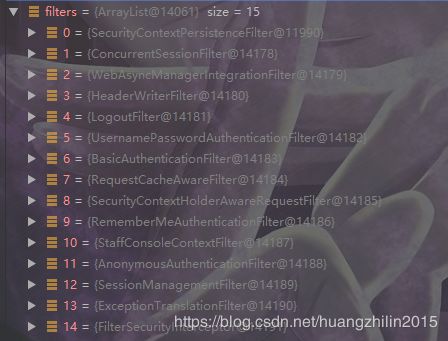
而这个filter列表有很多的filter,下图是我本地项目打断点截的图,可以看到有15个filter(其中有我自己加的filter),每个filter都有自己的作用,密码验证相关的、记住密码的等等,我们主要看和权限验证相关的:FilterSecurityInterceptor(下图中的最后一个)
FilterSecurityInterceptor的主要任务是从缓存中获取当前请求路径的权限配置,这个缓存的配置来源于我们的配置文件。按照我们改造之前的流程的话,是这样的:
1、我们在配置文件中配置了 intercept-url,比如spring-security.xml中有如下配置:
2、框架启动的时候会解析该配置文件,将这些intercept-url的配置缓存起来
3、FilterSecurityInterceptor在过滤请求的时候,会根据请求路径从缓存中获取对应的attribute列表,传递到我们指定的AccessDecisionManager(myAccessDecisionManager)中处理
这里还需要我们详细看看,配置文件是如何加载解析的。首先还是要从spring说起,spring有个基础配置文件,大家都很熟悉:applicationContext.xml(另外还有个ContextLoaderListener),不论是在web.xml配置,还是使用注解,我们会引入这个xml文件,spring在启动的时候会解析该文件,我们集成spring-security的时候会在applicationContext.xml中通过
spring会解析resource标签,然后解析spring-security.xml文件,而spring-security.xml这个文件并不是由解析applicationContext.xml文件的解析器解析的,这里涉及到spring处理子项目xml的一些方式,我们简单介绍一下。
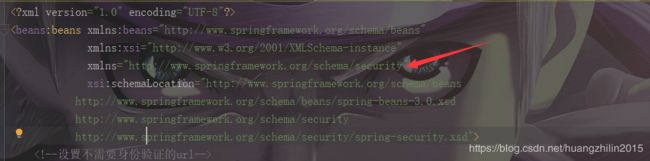
首先,在spring-security.xml中配置有namespaceUri:
就是箭头指向的这个:xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"。它是干嘛的呢?spring在解析该xml的是时候,会先拿到这个namespaceUri,然后根据这个uri去获取它的解析器类全限定名,怎么获取呢?这就要说到spring的:/META-INF/spring.handlers这个文件。这个文件里面配置了一些uri和类全限定名的对应关系,spring会加载这些handlers文件,然后将其放到一个叫做handlerMappings的Map里面,key为uri,value则为类的全限定名。
和spring.handlers相关的主要涉及的类为DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver,它是通过懒加载的方式加载的,感兴趣的可以去看看,这里贴出相关代码 (还涉及到单例的BeanDefinitionDocumentReader和delegate等,具体的流程,这里暂时不深究):
/**
* Load the specified NamespaceHandler mappings lazily.
*/
private Map getHandlerMappings() {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
try {
Properties mappings =
PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.handlerMappingsLocation, this.classLoader);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded NamespaceHandler mappings: " + mappings);
}
Map handlerMappings = new ConcurrentHashMap(mappings.size());
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, handlerMappings);
this.handlerMappings = handlerMappings;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable to load NamespaceHandler mappings from location [" + this.handlerMappingsLocation + "]", ex);
}
}
}
}
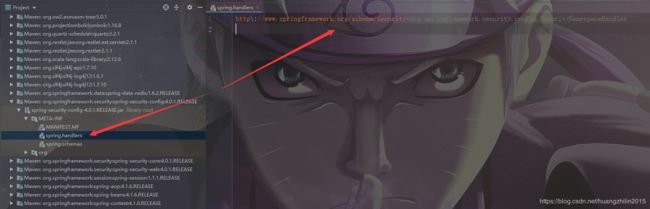
return this.handlerMappings; 再说spring-security的jar包,它下面有个这个文件:
如上图所示,spring-security的jar包里配置有该文件,并且将http://www.springframework.org/schema/security指向了org.springframework.security.config.SecurityNamespaceHandler这个类,按照上面说的,最终将由SecurityNamespaceHandler来处理我们的spring-security.xml配置文件。接下来我们重心放到它上就行了。
SecurityNamespaceHandler里有很多的parser,针对于一些的节点处理,而我们目前就只关心
package org.springframework.security.config.http;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.BeanComponentDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ManagedMap;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ParserContext;
import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig;
import org.springframework.security.config.Elements;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.expression.DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.expression.ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.xml.DomUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
/**
* Allows for convenient creation of a {@link FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource} bean
* for use with a FilterSecurityInterceptor.
*
* @author Luke Taylor
*/
public class FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
private static final String ATT_USE_EXPRESSIONS = "use-expressions";
private static final String ATT_HTTP_METHOD = "method";
private static final String ATT_PATTERN = "pattern";
private static final String ATT_ACCESS = "access";
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser.class);
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 首先获取所有的intercept-url元素
List interceptUrls = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element,
"intercept-url");
// 有些配置不允许在这里出现,当然,我们的例子中没有配置requires-channel和filters
for (Element elt : interceptUrls) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(elt
.getAttribute(HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_REQUIRES_CHANNEL))) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"The attribute '"
+ HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_REQUIRES_CHANNEL
+ "' isn't allowed here.", elt);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(elt
.getAttribute(HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_FILTERS))) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"The attribute '" + HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_FILTERS
+ "' isn't allowed here.", elt);
}
}
//创建MetadataSource的具体逻辑,具体见下面该方法
BeanDefinition mds = createSecurityMetadataSource(interceptUrls, false, element,
parserContext);
String id = element.getAttribute(AbstractBeanDefinitionParser.ID_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(id)) {
parserContext.registerComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(mds, id));
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, mds);
}
return mds;
}
static RootBeanDefinition createSecurityMetadataSource(List interceptUrls,
boolean addAllAuth, Element httpElt, ParserContext pc) {
//获取指定的request-matcher,如果没有指定,则使用默认的AntPathRequestMatcher.class,我们的例子中没有指定
MatcherType matcherType = MatcherType.fromElement(httpElt);
//看是否配置了use-expressions,默认为true,我们的例子中没有配置
boolean useExpressions = isUseExpressions(httpElt);
//真正的解析逻辑在parseInterceptUrlsForFilterInvocationRequestMap方法里,具体见下面该方法
ManagedMap requestToAttributesMap = parseInterceptUrlsForFilterInvocationRequestMap(
matcherType, interceptUrls, useExpressions, addAllAuth, pc);
BeanDefinitionBuilder fidsBuilder;
if (useExpressions) {
Element expressionHandlerElt = DomUtils.getChildElementByTagName(httpElt,
Elements.EXPRESSION_HANDLER);
String expressionHandlerRef = expressionHandlerElt == null ? null
: expressionHandlerElt.getAttribute("ref");
if (StringUtils.hasText(expressionHandlerRef)) {
logger.info("Using bean '" + expressionHandlerRef
+ "' as web SecurityExpressionHandler implementation");
}
else {
//如果没有指定expression-handler,那么注册默认的处理器
expressionHandlerRef = registerDefaultExpressionHandler(pc);
}
//绑定到ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource.class
fidsBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource.class);
fidsBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(requestToAttributesMap);
fidsBuilder.addConstructorArgReference(expressionHandlerRef);
}
else {
fidsBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource.class);
fidsBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(requestToAttributesMap);
}
fidsBuilder.getRawBeanDefinition().setSource(pc.extractSource(httpElt));
return (RootBeanDefinition) fidsBuilder.getBeanDefinition();
}
static String registerDefaultExpressionHandler(ParserContext pc) {
BeanDefinition expressionHandler = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(
DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler.class).getBeanDefinition();
String expressionHandlerRef = pc.getReaderContext().generateBeanName(
expressionHandler);
pc.registerBeanComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(expressionHandler,
expressionHandlerRef));
return expressionHandlerRef;
}
static boolean isUseExpressions(Element elt) {
String useExpressions = elt.getAttribute(ATT_USE_EXPRESSIONS);
return !StringUtils.hasText(useExpressions) || "true".equals(useExpressions);
}
/**
*循环所有的interceptor-url配置,会返回一个map:其key和value都为BeanDefinition类型,其中,key的root为对应的matcherType,
*本例中为AntPathRequestMatcher.class;而value的root为SecurityConfig.class,它以字符串的形式保存一个我们上面提到的ConfigAttribute
*后面会交由 ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource处理
*/
private static ManagedMap parseInterceptUrlsForFilterInvocationRequestMap(
MatcherType matcherType, List urlElts, boolean useExpressions,
boolean addAuthenticatedAll, ParserContext parserContext) {
ManagedMap filterInvocationDefinitionMap = new ManagedMap();
for (Element urlElt : urlElts) {
//每一个urlElt就是一个
//获取access属性,也就是我们需要的权限
String access = urlElt.getAttribute(ATT_ACCESS);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(access)) {
//如果access不为有效字符串,则忽略此项
continue;
}
//获取pattern属性,也就是我们需要拦截的路径比如:/test/set
String path = urlElt.getAttribute(ATT_PATTERN);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(path)) {
//如果path不为有效字符串,当做异常处理
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"path attribute cannot be empty or null", urlElt);
}
//获取method字段,当然我们的例子中并没有配置
String method = urlElt.getAttribute(ATT_HTTP_METHOD);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(method)) {
method = null;
}
//根据path和method创建一个matcher(将path和method添加到构造参数),
//该返回值是一个BeanDefinition(注:spring中,BeanDefinition用于描述一个类示例,属性、构造器参数等等),rootBean为传入的matcherType
BeanDefinition matcher = matcherType.createMatcher(path, method);
//SecurityConfig主要就是以字符串的形式保存一个我们上面提到的ConfigAttribute
BeanDefinitionBuilder attributeBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(SecurityConfig.class);
if (useExpressions) {
logger.info("Creating access control expression attribute '" + access
+ "' for " + path);
// The single expression will be parsed later by the
// ExpressionFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource
//只有一个构造参数就是access,以数组形式传入
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(new String[] { access });
//构造方法为createList
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createList");
}
else {
//和上面相比就是factoryMethod不一样,当然我们的情况是useExpressions is true
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(access);
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createListFromCommaDelimitedString");
}
if (filterInvocationDefinitionMap.containsKey(matcher)) {
logger.warn("Duplicate URL defined: " + path
+ ". The original attribute values will be overwritten");
}
filterInvocationDefinitionMap.put(matcher,
attributeBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
if (addAuthenticatedAll && filterInvocationDefinitionMap.isEmpty()) {
//没有对应配置的处理情况
BeanDefinition matcher = matcherType.createMatcher("/**", null);
BeanDefinitionBuilder attributeBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(SecurityConfig.class);
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(new String[] { "authenticated" });
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createList");
filterInvocationDefinitionMap.put(matcher,
attributeBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
//返回整个map
return filterInvocationDefinitionMap;
}
}
从源码中我们都能看出一些熟悉的字段了,比如method、pattern、access这些,其实就是我们
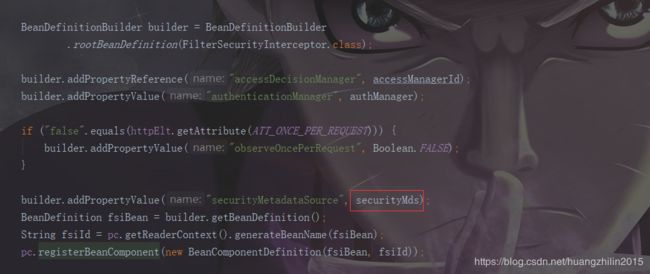
该返回结果会绑定到FilterSecurityInterceptor.class的构造参数上,具体实施的类为HttpConfigurationBuilder.java,由于代码太多,这里只贴我们关注的代码块,图中红框框起来的securityMds就是上步中返回的BeanDefinition。
上图的这个Builder就是用于创建FilterSecurityInterceptor的,其有一个metadataSource属性,它会在创建阶段将securityMds绑定到该参数上。还记得我们之前提到的,过滤一个请求的时候会根据该请求获取对应的ConfigAttribute吗?这个东西就来源于securityMds,也就是FilterSecurityInterceptor的metadataSource属性,核心操作为:
Collection attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object); 三、改造
到这里,我们已经明白了spring-security是如何运作起来的。那么再来说我们的扩展。我们目前在配置文件中是这样配置的:
这个是不支持根据参数来拦截权限的,那么通过源码分析,我们目前有几种方式可以达到我们的目的呢?
1、加一个servlet的Filter。放在我们的springSecurityFilterChain之后,实现在springSecurity拦截的基础上进行二次拦截
2、在springSecurityFilterChain的内部增加一个filter。放在FilterSecurityInterceptor之后,实现在springSecurity拦截的基础上二次拦截
3、直接修改access的表达式,结合自定义ExpressionParse进行表达式的解析,然后在myAccessDesisiionManager中根据attribute进行权限拦截。比如access="[{type=1,privilege=1},{type=2,privilege=2}]"(随便写的啊)
4、修改源码,以支持我们的自定义操作。
我现在介绍第4种方式,修改源码,因为我想要达到一个目的:更改spring-security.xml的配置方式。比如修改后的结构变成下面这样:
表示/test/set这个接口,要根据type参数的具体值进行权限拦截,如果type==1,那么需要access为1(这个access是和具体的权限结构相关的哈,只是我的系统中权限码为数字);如果type==2,那么需要access为2,依次类推。我们还可以对access进行扩展,比如access="1&2&3"表示同时需要1、2、3权限;access="1|2|3"表示需要1、2、3中的任意一个权限等等。说干就开干。
第一步、我们需要改造xml的解析器:FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser。使它支持我们新增的item子项解析:在解析每个interceptor-url节点时候,如果其下有item节点列表,那么解析列表,并且每个子项的matcher和之前不同,它需要4个构造器参数,分别是path、method、paramName、paramValue,子项的attribute则是一样的,我们目前简单设置为字符串,然后将它们放到filterInvocationDefinitionMap中,最终绑定到FilterSecurityInterceptor的成员变量,其它逻辑则不变。
第二步、自定义RequestMatcher,使其支持:
1、接收第一步提到的path、method、paramName、paramValue参数构造matcher的BeanDefinition;
2、其matches方法需要支持paramName和paramValue的比对支持
第三步、修改xsd文件。由于我们在xml文件中新增了item节点,所以需要将新增的节点定义到XML的结构定义文件中。
第四步、让jvm加载我们修改之后的文件,而不是jar包中的源码文件
我们先来一步一步实施前三步操作:
1、修改FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser.java,主要修改了parseInterceptUrlsForFilterInvocationRequestMap方法,使其支持item子节点解析:
package org.springframework.security.config.http;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.BeanComponentDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ManagedMap;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ParserContext;
import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig;
import org.springframework.security.config.Elements;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.expression.DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.expression.ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.xml.DomUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Allows for convenient creation of a {@link FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource} bean
* for use with a FilterSecurityInterceptor.
*
* @author Luke Taylor
*/
public class FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
private static final String ATT_USE_EXPRESSIONS = "use-expressions";
private static final String ATT_HTTP_METHOD = "method";
private static final String ATT_PATTERN = "pattern";
private static final String ATT_ACCESS = "access";
//paramName,paramValue,item为我们新增的常量定义,表示我们在XML中新增的节点
private static final String ATT_PARAMNAME = "paramName";
private static final String ATT_PARAMVALUE = "paramValue";
private static final String SUB_ITEM = "item";
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser.class);
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
List interceptUrls = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element,
"intercept-url");
// Check for attributes that aren't allowed in this context
for (Element elt : interceptUrls) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(elt
.getAttribute(HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_REQUIRES_CHANNEL))) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"The attribute '"
+ HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_REQUIRES_CHANNEL
+ "' isn't allowed here.", elt);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(elt
.getAttribute(HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_FILTERS))) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"The attribute '" + HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser.ATT_FILTERS
+ "' isn't allowed here.", elt);
}
}
BeanDefinition mds = createSecurityMetadataSource(interceptUrls, false, element,
parserContext);
String id = element.getAttribute(AbstractBeanDefinitionParser.ID_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(id)) {
parserContext.registerComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(mds, id));
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, mds);
}
return mds;
}
static RootBeanDefinition createSecurityMetadataSource(List interceptUrls,
boolean addAllAuth, Element httpElt, ParserContext pc) {
MatcherType matcherType = MatcherType.fromElement(httpElt);
boolean useExpressions = isUseExpressions(httpElt);
ManagedMap requestToAttributesMap = parseInterceptUrlsForFilterInvocationRequestMap(
matcherType, interceptUrls, useExpressions, addAllAuth, pc);
BeanDefinitionBuilder fidsBuilder;
if (useExpressions) {
Element expressionHandlerElt = DomUtils.getChildElementByTagName(httpElt,
Elements.EXPRESSION_HANDLER);
String expressionHandlerRef = expressionHandlerElt == null ? null
: expressionHandlerElt.getAttribute("ref");
if (StringUtils.hasText(expressionHandlerRef)) {
logger.info("Using bean '" + expressionHandlerRef
+ "' as web SecurityExpressionHandler implementation");
} else {
expressionHandlerRef = registerDefaultExpressionHandler(pc);
}
fidsBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource.class);
fidsBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(requestToAttributesMap);
fidsBuilder.addConstructorArgReference(expressionHandlerRef);
} else {
fidsBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource.class);
fidsBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(requestToAttributesMap);
}
fidsBuilder.getRawBeanDefinition().setSource(pc.extractSource(httpElt));
return (RootBeanDefinition) fidsBuilder.getBeanDefinition();
}
static String registerDefaultExpressionHandler(ParserContext pc) {
BeanDefinition expressionHandler = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(
DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler.class).getBeanDefinition();
String expressionHandlerRef = pc.getReaderContext().generateBeanName(
expressionHandler);
pc.registerBeanComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(expressionHandler,
expressionHandlerRef));
return expressionHandlerRef;
}
static boolean isUseExpressions(Element elt) {
String useExpressions = elt.getAttribute(ATT_USE_EXPRESSIONS);
return !StringUtils.hasText(useExpressions) || "true".equals(useExpressions);
}
private static ManagedMap parseInterceptUrlsForFilterInvocationRequestMap(
MatcherType matcherType, List urlElts, boolean useExpressions,
boolean addAuthenticatedAll, ParserContext parserContext) {
ManagedMap filterInvocationDefinitionMap = new ManagedMap();
for (Element urlElt : urlElts) {
String path = urlElt.getAttribute(ATT_PATTERN);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(path)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"path attribute cannot be empty or null", urlElt);
}
String method = urlElt.getAttribute(ATT_HTTP_METHOD);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(method)) {
method = null;
}
//在处理每一个interceptor-url节点的时候,如果下面有item子项,那么解析它的子项列表
List items = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(urlElt, SUB_ITEM);
if (items != null && items.size() > 0) {
//item子节点处理
for (Element item : items) {
String paramName = item.getAttribute(ATT_PARAMNAME);
String paramValue = item.getAttribute(ATT_PARAMVALUE);
String access = item.getAttribute(ATT_ACCESS);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(paramName) || !StringUtils.hasText(paramValue) || !StringUtils.hasText(access)) {
continue;
}
BeanDefinition matcher = matcherType.createMatcher(path, method, paramName, paramValue);
BeanDefinitionBuilder attributeBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(SecurityConfig.class);
if (useExpressions) {
logger.info("Creating access control expression attribute '" + access
+ "' for [path=" + path + ",paramName=" + paramName + "]");
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(new String[]{access});
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createList");
} else {
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(access);
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createListFromCommaDelimitedString");
}
if (filterInvocationDefinitionMap.containsKey(matcher)) {
logger.warn("Duplicate URL defined: " + path
+ ". The original attribute values will be overwritten");
}
filterInvocationDefinitionMap.put(matcher,
attributeBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
continue;
}
String access = urlElt.getAttribute(ATT_ACCESS);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(access)) {
continue;
}
BeanDefinition matcher = matcherType.createMatcher(path, method);
BeanDefinitionBuilder attributeBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(SecurityConfig.class);
if (useExpressions) {
logger.info("Creating access control expression attribute '" + access
+ "' for " + path);
// The single expression will be parsed later by the
// ExpressionFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(new String[]{access});
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createList");
} else {
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(access);
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createListFromCommaDelimitedString");
}
if (filterInvocationDefinitionMap.containsKey(matcher)) {
logger.warn("Duplicate URL defined: " + path
+ ". The original attribute values will be overwritten");
}
filterInvocationDefinitionMap.put(matcher,
attributeBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
if (addAuthenticatedAll && filterInvocationDefinitionMap.isEmpty()) {
BeanDefinition matcher = matcherType.createMatcher("/**", null);
BeanDefinitionBuilder attributeBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.rootBeanDefinition(SecurityConfig.class);
attributeBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(new String[]{"authenticated"});
attributeBuilder.setFactoryMethod("createList");
filterInvocationDefinitionMap.put(matcher,
attributeBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
return filterInvocationDefinitionMap;
}
}
2、自定义RequestMatcher,由于我们当前改动较少,而且是为了讲解原理,我也就难得去重新定义一个RequestMatcher了哈,直接在默认使用的AntPathRequestMatcher上更改:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
* an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* Matcher which compares a pre-defined ant-style pattern against the URL (
* {@code servletPath + pathInfo}) of an {@code HttpServletRequest}. The query string of
* the URL is ignored and matching is case-insensitive or case-sensitive depending on the
* arguments passed into the constructor.
*
* Using a pattern value of {@code /**} or {@code **} is treated as a universal match,
* which will match any request. Patterns which end with {@code /**} (and have no other
* wildcards) are optimized by using a substring match — a pattern of
* {@code /aaa/**} will match {@code /aaa}, {@code /aaa/} and any sub-directories, such as
* {@code /aaa/bbb/ccc}.
*
*
* For all other cases, Spring's {@link AntPathMatcher} is used to perform the match. See
* the Spring documentation for this class for comprehensive information on the syntax
* used.
*
*
* @author Luke Taylor
* @author Rob Winch
* @see AntPathMatcher
* @since 3.1
*/
public final class AntPathRequestMatcher implements RequestMatcher {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(AntPathRequestMatcher.class);
private static final String MATCH_ALL = "/**";
private final Matcher matcher;
private final String pattern;
private final HttpMethod httpMethod;
private final boolean caseSensitive;
private String paramValue;
private String paramName;
/**
* 新增的构造方法,支持上文提到的四个参数
*
* @param pattern
* @param httpMethod
* @param paramName
* @param paramValue
*/
public AntPathRequestMatcher(String pattern, String httpMethod, String paramName, String paramValue) {
this(pattern, httpMethod, false);
this.paramName = paramName;
this.paramValue = paramValue;
}
/**
* Creates a matcher with the specific pattern which will match all HTTP methods in a
* case insensitive manner.
*
* @param pattern the ant pattern to use for matching
*/
public AntPathRequestMatcher(String pattern) {
this(pattern, null);
}
/**
* Creates a matcher with the supplied pattern and HTTP method in a case insensitive
* manner.
*
* @param pattern the ant pattern to use for matching
* @param httpMethod the HTTP method. The {@code matches} method will return false if
* the incoming request doesn't have the same method.
*/
public AntPathRequestMatcher(String pattern, String httpMethod) {
this(pattern, httpMethod, false);
}
/**
* Creates a matcher with the supplied pattern which will match the specified Http
* method
*
* @param pattern the ant pattern to use for matching
* @param httpMethod the HTTP method. The {@code matches} method will return false if
* the incoming request doesn't doesn't have the same method.
* @param caseSensitive true if the matcher should consider case, else false
*/
public AntPathRequestMatcher(String pattern, String httpMethod, boolean caseSensitive) {
Assert.hasText(pattern, "Pattern cannot be null or empty");
this.caseSensitive = caseSensitive;
if (pattern.equals(MATCH_ALL) || pattern.equals("**")) {
pattern = MATCH_ALL;
matcher = null;
} else {
if (!caseSensitive) {
pattern = pattern.toLowerCase();
}
// If the pattern ends with {@code /**} and has no other wildcards or path
// variables, then optimize to a sub-path match
if (pattern.endsWith(MATCH_ALL)
&& (pattern.indexOf('?') == -1 && pattern.indexOf('{') == -1 && pattern
.indexOf('}') == -1)
&& pattern.indexOf("*") == pattern.length() - 2) {
matcher = new SubpathMatcher(pattern.substring(0, pattern.length() - 3));
} else {
matcher = new SpringAntMatcher(pattern);
}
}
this.pattern = pattern;
this.httpMethod = StringUtils.hasText(httpMethod) ? HttpMethod
.valueOf(httpMethod) : null;
}
/**
* Returns true if the configured pattern (and HTTP-Method) match those of the
* supplied request.
*
* @param request the request to match against. The ant pattern will be matched
* against the {@code servletPath} + {@code pathInfo} of the request.
*/
public boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (httpMethod != null && StringUtils.hasText(request.getMethod())
&& httpMethod != valueOf(request.getMethod())) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request '" + request.getMethod() + " "
+ getRequestPath(request) + "'" + " doesn't match '" + httpMethod
+ " " + pattern);
}
return false;
}
if (pattern.equals(MATCH_ALL)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request '" + getRequestPath(request)
+ "' matched by universal pattern '/**'");
}
return true;
}
String url = getRequestPath(request);
String param = null;
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(paramName)) {
//如果此项matcher配置的了paramName,则需要从request中获取该参数
//注:这里仅仅演示通过getParameter直接获取哈
try {
param = request.getParameter(paramName);
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Checking match of request : '" + url + "'; against '" + pattern
+ "'");
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(param)) {
//在原来matches的基础上增加param的比对
return matcher.matches(url) && param.equals(paramValue);
} else {
//如果没有获取到对应的param参数就走原来的matches逻辑
return matcher.matches(url);
}
}
private String getRequestPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String url = request.getServletPath();
if (request.getPathInfo() != null) {
url += request.getPathInfo();
}
if (!caseSensitive) {
url = url.toLowerCase();
}
return url;
}
public String getPattern() {
return pattern;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (!(obj instanceof AntPathRequestMatcher)) {
return false;
}
AntPathRequestMatcher other = (AntPathRequestMatcher) obj;
return this.pattern.equals(other.pattern) && this.httpMethod == other.httpMethod
&& this.caseSensitive == other.caseSensitive;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int code = 31 ^ pattern.hashCode();
if (httpMethod != null) {
code ^= httpMethod.hashCode();
}
if (paramName != null) {
code ^= paramName.hashCode();
}
if (paramValue != null) {
code ^= paramValue.hashCode();
}
return code;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Ant [pattern='").append(pattern).append("'");
if (httpMethod != null) {
sb.append(", ").append(httpMethod);
}
if (paramName != null) {
sb.append(", ").append(paramName);
}
if (paramValue != null) {
sb.append(", ").append(paramValue);
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Provides a save way of obtaining the HttpMethod from a String. If the method is
* invalid, returns null.
*
* @param method the HTTP method to use.
* @return the HttpMethod or null if method is invalid.
*/
private static HttpMethod valueOf(String method) {
try {
return HttpMethod.valueOf(method);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
}
return null;
}
private static interface Matcher {
boolean matches(String path);
}
private static class SpringAntMatcher implements Matcher {
private static final AntPathMatcher antMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private final String pattern;
private SpringAntMatcher(String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
public boolean matches(String path) {
return antMatcher.match(pattern, path);
}
}
/**
* Optimized matcher for trailing wildcards
*/
private static class SubpathMatcher implements Matcher {
private final String subpath;
private final int length;
private SubpathMatcher(String subpath) {
assert !subpath.contains("*");
this.subpath = subpath;
this.length = subpath.length();
}
public boolean matches(String path) {
return path.startsWith(subpath)
&& (path.length() == length || path.charAt(length) == '/');
}
}
}
3.在xsd文件(spring-security-4.0.xsd)中增加节点,这里主要更新intercept-url节点:
首先定义item和它的attlist
Add additional headers to the response.
The name of the item to add.
The value for the item.
loren add
然后将item绑定到 intercept-url 的complexType中:
Specifies the access attributes and/or filter list for a particular set of URLs.
我们还剩下最后一步,我们修改了源码,肯定不能把代码打成一个新的jar包然后替换项目中原引用的jar包,该怎么做呢?这里涉及到一个JVM加载类的机制,也是我们通过这种方式演示功能扩展要抛出的一个细节。
JVM通过类的全限定名根据双亲委派的方式加载class,一个class被加载之后就不会再被加载了。明显,我们的servlet容器可不能这样,我们一个容器可以运行多个web项目,而不同的项目可以依赖不同版本的同类jar包,所以它有“自己的一套”类加载机制(当然还有很多其它场景,比如JSP的热更新等,但这不是我们现在的重点),可以说它违反了双亲委派机制。如果我们要项目使用我们自己修改后的class,我们可以把修改的源码类拷贝出来修改,再在项目中创建一个和原类package相同的package,将修改的类放到新建的package中,这样对于我们修改的源码类,编译之后,系统中就存在了两个同包同名的class了(只是我们修改的class位于classes,原class位于lib的jar包中),我们只需要保证自己修改的class被先加载即可,那么怎么保证呢?容器会优先加载classes中的class,所以像上面说的那样操作即可。
但是有另外一个情况,比如笔者的情况就是,该项目最终会生成一个jar包交给其它项目使用。情况就变成了:lib中的两个jar包中存在了同包同名的class。这种情况下,具体先加载哪个class就依托于具体的操作系统文件排序了,我们可以使用maven的maven-dependency-plugin插件将自己修改的class解压到classes中,如下图配置,笔者项目的class都在com.test包下,其它包都是重写的一些框架的类,把除了com.test包以外的所有class都拷贝到classes中(由于我们也修改了xsd文件,所以也要把xsd文件拷贝到classes中):
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-dependency-plugin
unpack
generate-resources
unpack
com.testGroup
testArtifact
1.0
jar
true
target/classes
**/*.class,**/*.xsd
com/test/**/*.class
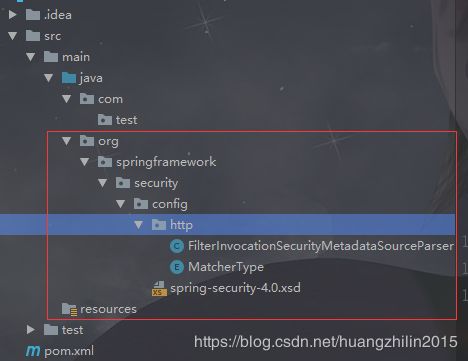
如下图,为项目结构概况,红框内的为我们重写的3个源码类(包括了xsd文件):
最后的最后,AccessDecisionManager的实现就是业务相关的了,比如本例中是如何处理access的值的,这里就不做阐述了哈。
四、总结
本文主要讲解了spring+spring-security的一些简单原理,然后在security的基础上进行了源码改造,实现了我们的“个性化”需求。虽然这样做能达到目的,但我们的主要目的还是是学习知识。通常情况下,如果有更好的解决方案,我们最好还是不要这样做哈。
注:本文是博主的个人理解,如果有错误的地方,希望大家不吝指出,谢谢