【Android学习】第四章 · SQLite数据库的使用以及内容显示
SQLite数据库的使用
这里用安卓单元测试框架学习SQLite
在主包下新建一个类myOpenHelper继承SQLiteOpenHelper
在另一个包下新建类test继承AndroidTestCase
并在Mainfest.xml文件下添加
<instrumentation android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner" android:targetPackage="目标包名">instrumentation>
<uses-library android:name="android.test.runner">uses-library>
此时在myOpenHelper中复写onCreate类
创建一个表单
db.execSQL("create table person(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name char(10),phone char(20),salary integer(10))");
在test类调用setUp和tearDown方法
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
super.setUp();
myOpenHelper = new myOpenHelper(getContext(), "student.db", null, 1);
db = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
}
@Override
protected void tearDown() throws Exception {
super.tearDown();
db.close();
}在setUp下新建一个数据库
在tearDown下关闭数据库
数据的增加原始:
db.execSQL("insert into person(name,phone,salary) values (?,?,?)",new Object[]{"三十","110",30000});
db.execSQL("insert into person(name,phone,salary) values (?,?,?)",new Object[]{"二十","120",30000});安卓封装好的方法:
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", "十");
values.put("phone", "119");
values.put("salary", 20000);
db.insert("person", null, values);
数据的删除原始:
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", "十");
values.put("phone", "119");
values.put("salary", 20000);
db.insert("person", null, values);
数据的查询原始:
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from person", null);
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
System.out.println(name);
}安卓封装好的方法:
db.query("person", null, null, null, null, null, null);
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
System.out.println(name);
}百度释义:
query(table, columns, selection, selectionArgs, groupBy, having, orderBy, limit)方法各参数的含义:
table:表名。相当于select语句from关键字后面的部分。如果是多表联合查询,可以用逗号将两个表名分开。
columns:要查询出来的列名。相当于select语句select关键字后面的部分。
selection:查询条件子句,相当于select语句where关键字后面的部分,在条件子句允许使用占位符“?”
selectionArgs:对应于selection语句中占位符的值,值在数组中的位置与占位符在语句中的位置必须一致,否则就会有异常。
groupBy:相当于select语句group by关键字后面的部分
having:相当于select语句having关键字后面的部分
orderBy:相当于select语句order by关键字后面的部分,如:personid desc, age asc;
limit:指定偏移量和获取的记录数,相当于select语句limit关键字后面的部分。
数据的更新原始:
db.execSQL("update person set salary=? where name=?",new Object[]{40000,"二十"});安卓封装好的方法:
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("salary", 88888);
db.update("person", values, "name=?", new String[]{"二十"});
事务用以保证数据的安全性:
public void Transaction(){
try {
db.beginTransaction();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("salary", 12);
db.update("person", values, "name=?", new String[] { "十" });
values.clear();
values.put("salary", 21);
db.update("person", values, "name=?", new String[] { "二十" });
//提交时这段代码如果没有执行过,就会回滚
db.setTransactionSuccessful();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("就是有问题!!!");
}finally{
db.endTransaction();
}
}
在主界面显示数据库内容
方法一:每次读取到一个数据对象new一个view并添加到布局内
此时布局文件中仅有LinearLayout对象用来获取view
peopleList = new ArrayList();
LinearLayout ll =(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.ll);
myOpenHelper oh = new myOpenHelper(this,"student.db",null,1);
SQLiteDatabase db = oh.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query("person", null, null, null, null, null, null);
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
String phone = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("phone"));
int salary = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("salary"));
people people = new people(name, phone, salary);
peopleList.add(people);
}
for(people people:peopleList){
TextView tv = new TextView(this);
tv.setText(people.toString());
ll.addView(tv);
}
缺点:当数据过多程序会崩溃,由于所有的数据都new一个TextView,不显示的view占用系统资源导致崩溃
解决方法二:通过ListView方法显示
在xml文件下新建一个listview组件
再在mainactivity.java下获取
ListView lv = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.lv);
//设置适配器(此处有三种,均可以通过自定义xml布局构图)
第一种:自定义适配器继承自BaseAdapter
lv.setAdapter(new myAdapter());
//适配器主要完成getCount和getView方法
class myAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
//系统调用,用来获知模型层(list)有多少数据
public int getCount() {
return peopleList.size();
}
//系统调用,返回的view作为listview的一个条目显示在屏幕上
//position:getview返回的view对象在listview是第几个条目
//covertview:系统之前缓存的条目
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
System.out.println("方法调用"+position);
/*获取布局填充器方法1:
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this);
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_listview, null);
方法2:把布局文件填充为view对象
View view = View.inflate(MainActivity.this, R.layout.item_listview, null);*/
//获取布局填充器方法3
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater)getSystemService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View view = null;
//此时要设置缓存
if(convertView ==null){
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_listview, null);
//只要系统中有条目缓存,在新条目出现时就会调用
}
else{
view = convertView;
}
TextView tv_1 = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.tv1);
tv_1.setText(peopleList.get(position).getName());
TextView tv_2 = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.tv2);
tv_2.setText(peopleList.get(position).getPhone());
TextView tv_3 = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.tv3);
tv_3.setText(peopleList.get(position).getSalary()+"");//文本需要获取的是String类型
return view;
}
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
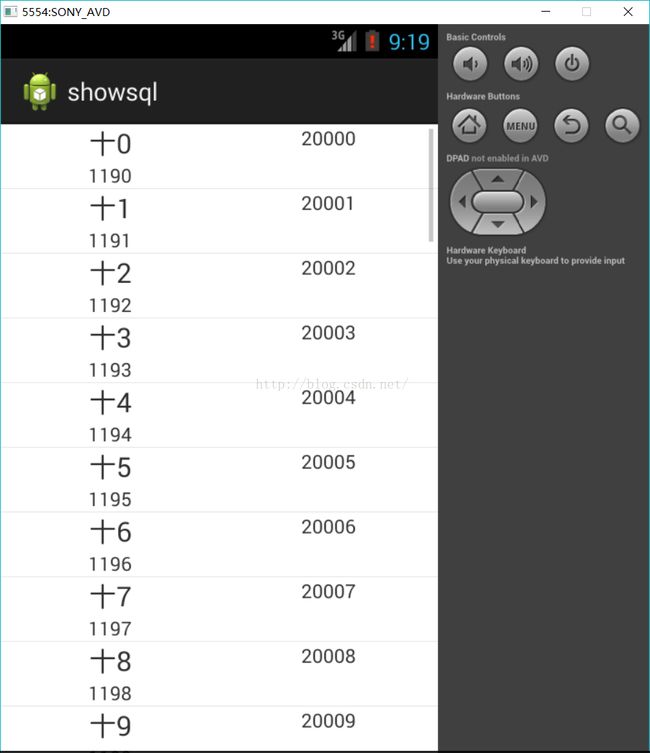
}}效果图:
再介绍两种adapter
ArrayAdapter指定更改的组件对象类型,并添加对象
String[] objects = new String[]{
"小明",
"小红",
"煞笔",
"小刚"
};
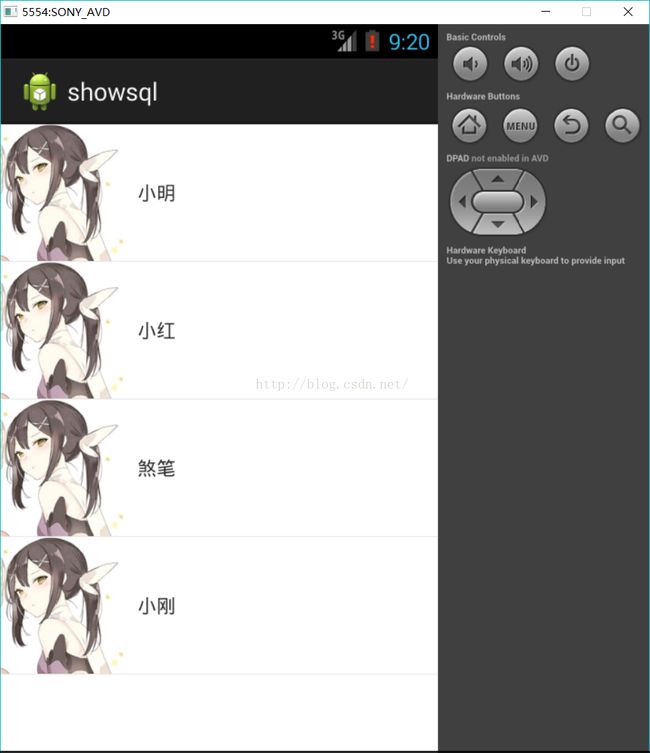
lv.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter(this, R.layout.item_listview, R.id.tv, objects));
效果图:
SimpleAdapter
//把每个条目需要处理的所有数据封装到map中,把map封装到list中
//这样就保证每个list元素包含一个条目需要的所有数据
List> data = new ArrayList>();
Map map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put("name", "周杰伦");
map1.put("photo", R.drawable.p1);
data.add(map1);
Map map2 = new HashMap();
map2.put("name", "薛之谦");
map2.put("photo", R.drawable.p2);
data.add(map2);
Map map3 = new HashMap();
map3.put("name", "林俊杰");
map3.put("photo", R.drawable.p3);
data.add(map3);
ListView lv = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.lv);
lv.setAdapter(new SimpleAdapter(this, data, R.layout.item_listview, new String[]{"name","photo"}, new int[]{R.id.tv,R.id.iv})); 效果图: