mybatis 源码分析(四) 自带连接池-
mybatis 源码分析(四) 自带连接池
- mybatis 源码分析(一) Xml解析,容器初始化
- mybatis 源码分析(二) sql执行路径分析
- mybatis 源码分析(三) 插件原理
- mybatis 源码分析(四) 自带连接池
mybatis 连接池
mybatis 支持3种数据源
1) jndi
顾名思义 支持JNDI创建数据源
2) pooled
连接池实现
3) unpooled
来一个请求连接一个数据库连接本篇重点介绍pooled的实现
pooled
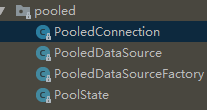
**pooled 主要是由4个类构成
简单解释下:
| 类名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| PooledConnection | 连接对象 实现了 InvocationHandler 动态代理接口 |
| PooledDataSource | 数据源 实现了 DataSource 接口 |
| PooledDataSourceFactory | dataSource生产工厂 |
| PoolState | 记录连接池的状态 (活动连接数 空闲连接数 请求数 …) |
我们先从工厂类开始
PooledDataSourceFactory
public class PooledDataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory {
/** 很简单 构造方法初始化了dataSource */
public PooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
}
}PooledDataSource
这个类东西有点多,关注重点
1.实现了dataSource接口(javax.sql.DataSource)
2.构造函数中使用的都是 UnpooledDataSource(可以理解为就是建立一个连接)
3.实现接口的getConnection 拿到的都是动态代理类
4.关注pushConnection,popConnection 2个方法 连接池的核心实现
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
public PooledDataSource() {
dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
/** 省略其他函数 */
/** 返回的都是一个动态代理类 */
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
/** popConnection 从空闲连接池中获取连接 */
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
/** 返回的都是一个动态代理类 */
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
/** popConnection 从空闲连接池中获取连接 */
return popConnection(username, password).getProxyConnection();
}
/** 省略 */
/** 把当前连接对象从活跃池中移除 放回到空闲池中 */
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
synchronized (state) {
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
state.notifyAll();
} else {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
/** 从空闲连接池中获取连接 删除部分代码*/
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) {
if (state.idleConnections.size() > 0) {
// Pool has available connection
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
} else {
// 判断活跃连接池数量
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// 创建一个新的连接
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
//used in logging, if enabled
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
} else {
// Cannot create new connection
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
/** 连接活跃检查 */
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
//...........
}
} else {
// Must wait
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + 3)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
return conn;
}
}重点 重点
getConnection 获取是一个 getProxyConnection 这是个什么类?动态代理类 具体的实现是在 PooledConnection
PooledConnection
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler {
private static final String CLOSE = "close";
private static final Class[] IFACES = new Class[]{Connection.class};
//最重要的就是 一个构造函数 和 invoke
public PooledConnection(Connection connection, PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.hashCode = connection.hashCode();
this.realConnection = connection;
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.createdTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastUsedTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.valid = true;
this.proxyConnection = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
/** 判断method方法是不是close 如果是就调用 pushConnection 放回连接池*/
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
} else {
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// issue #579 toString() should never fail
// throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime
checkConnection();
}
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
}通过构造函数 动态代理实现Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this)
代理的是Connection 接口 返回连接池是通过代理close方法实现的.
那什么时候 调用的connection.close()呢?
谁执行了connection.close方法
我们通过 第一章 知道最终注入mapper接口的bean都是通过 MapperFactoryBean 生成的 MapperProxy 的动态代理类.
在MapperProxy 中 需要一个sqlSession的实例. 从第一章 我们知道 这里的实例对象是 SqlSessionTemplate.
我们看下 SqlSessionTemplate 怎么做的
SqlSessionTemplate
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession {
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
/** 生成了一个动态代理类 具体实现在 SqlSessionInterceptor */
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
/** 动态代理的实现 invoke 代理了全部的 SqlSession 方法*/
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/** getSqlSession 具体实现请看SqlSessionUtils
* 首先会从事务中获取sqlSession
* 如果没有 就从SqlSeesionFactory获取(默认是DefaultSqlSession)
*/
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
//....
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
//....
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
/** 这个方法很重要 具体实现 请移步
* (org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils)
* 最重要是调用了 session.close()
* 上面提到 sqlSession的实例对象是DefaultSqlSession
* 那我们看下 close都干了什么
*/
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
}DefaultSqlSession
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
public void close() {
try {
/** executor 默认实现是SimpleExecutor
* close方法 在父类BaseExecutor
*/
executor.close(isCommitOrRollbackRequired(false));
dirty = false;
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}BaseExecutor
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
try {
rollback(forceRollback);
} finally {
/** 这里的实例对象是 JdbcTransaction */
if (transaction != null) transaction.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Ignore. There's nothing that can be done at this point.
log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e);
} finally {
transaction = null;
deferredLoads = null;
localCache = null;
localOutputParameterCache = null;
closed = true;
}
}
}JdbcTransaction
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null) {
resetAutoCommit();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.close();
}
}
}大家已经看到了 这段代码 回答了上面的问题:
谁执行了 connection.close
我们再来结合下 第一章 第二章内容 复盘下整个SQL执行流程
Created with Raphaël 2.1.2 MapperProxyFactory MapperProxyFactory MapperProxy MapperProxy SqlSessionTemplate SqlSessionTemplate SqlSessionInterceptor SqlSessionInterceptor mapperMethod mapperMethod DefaultSqlSession DefaultSqlSession BaseExecutor BaseExecutor JdbcTransaction JdbcTransaction Connection Connection 生成spring注入的bean 注入sqlSession实例 代理了sqlSession所有方法 bean调用方法 proxy代理 交于mapperMethod.execute执行 执行SQL 调用代理类 代理SqlSession 执行SQL 并调用close 调用executor.close()方法 调用JdbcTransaction.close()方法 调用Connection的close()方法