Java注解解析 整理
为什么要学习注解?学习注解有什么好处?学完能做什么?
1.能够看懂别人的代码,特别是框架相关的代码
2.让编程更加简洁,代码更加清晰
要学会自定义注解 1.5
概念
java提供了一种原程序中的元素关联任何信息和任何元数据的途径和方法。
Java中常用的注解
注解的分类
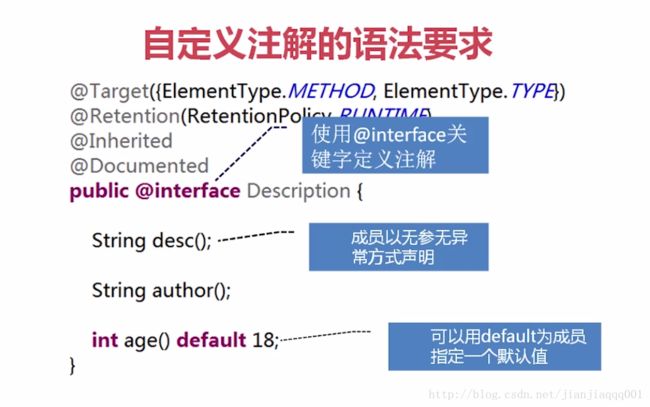
自定义注解
注解的应用实战
Java中常用的注解
jdk自带的注解
重写注解 @Override
会按注解指令 覆盖 父类中的一个类,如果没有覆盖就会报编译错误
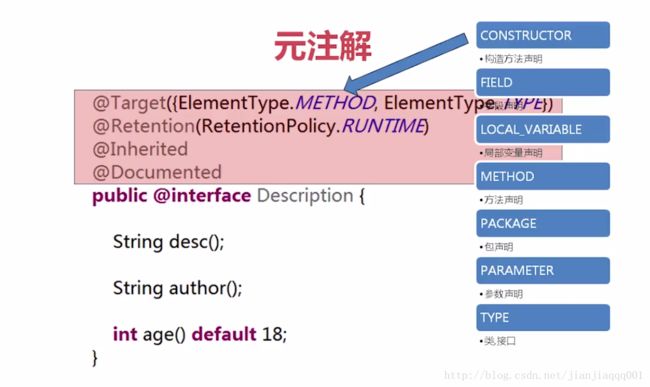
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Override {
}方法过时注解 @Deprecated 这是
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value={CONSTRUCTOR, FIELD, LOCAL_VARIABLE, METHOD, PACKAGE, PARAMETER, TYPE})
public @interface Deprecated {
}
按照运行机制来分
1.源码注解
注解只在源码中存在,编译成.class文件就不存在了
2.编译时注解
注解在源码和.class文件都存在
例如@Override @Deprecated @SuppressWarnings(“”)
3.运行时注解
在运行阶段还起作用,甚至会影响运行逻辑的注解
4.元注解 注解的注解
使用自定义注解
先定义以上的注解 然后再代码中使用定义的注解
注解 是 无参无异常 的声明 可以有默认值
注解只有一个方法时 要用value
当只有一个的时候 可以直接使用
没有任何成员的时候就是标识注解。
@Documented 就是标识注解
解析注解
概念: 通过反射获取类,函数或成员上的运行时注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑。
//描述注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Description {
String value();
}
//父类
public abstract class Person {
public abstract String name();
}
//小孩类 子类
@Description("I am class annotation")
public class Child extends Person{
@Override
@Description("I am method annotation")
public String name() {
return null;
}
}
//注解解析类
public class ParseAnn {
public static void praseAnno(){
//1.使用类加载器加载类
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.danjiang.ann.Child");
//2.找到类上面的注解
boolean isAnnotationPresent = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class);
if (isAnnotationPresent) {
//3.拿到注解实例
Description annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Description.class);
String value = annotation.value();
System.out.println("value==" + value);
}
//4.找到方法上的注解
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//2.找到方法上面的注解
boolean isExit = method.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class);
if (isExit) {
//3.拿到注解实例
Description annotation = method.getAnnotation(Description.class);
String value = annotation.value();
System.out.println("value==" + value);
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParseAnn.praseAnno();
}
运行结果 :
value==I am class annotation
value==I am method annotation
//另外的一种解法
for (Method method : methods) {
Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
if (annotation instanceof Description) {
String value = ((Description) annotation).value();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
这是运行时注解。 假如我们改成Source , Class
运行时就没有了.
@Inhrited
是一个标记注解,@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一个使用了@Inherited修饰的annotation类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation将被用于该class的子类。
@Inherited annotation类型是被标注过的class的子类所继承。类并不从它所实现的接口继承annotation,方法并不从它所重载的方法继承annotation
当@Inherited annotation类型标注的annotation的Retention是RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,则反射API增强了这种继承性。如果我们使用java.lang.reflect去查询一个@Inherited annotation类型的annotation时,反射代码检查将展开工作:检查class和其父类,直到发现指定的annotation类型被发现,或者到达类继承结构的顶层。
@Description("I am class Person annotation")
public abstract class Person {
@Description("I am method annotation")
public abstract String name();
}
public class Child extends Person{
@Override
public String name() {
return null;
}
}
运行结果:value==I am class Person annotation
抽象类 Person 改成接口后什么也不输出
在接口上是不起做用的,在父类上会起作用 而且只继承了类上的注解,没有继承方法上的注解。
公司取自一个公司的持久层框架,用来代替Hibernate的解决方案,核心代码用注解来实现。
需求:
1.用户有一张表,字段包括用户ID,用户名,昵称,年龄,性别,所在城市,邮箱,手机号。
2.方便的对每个字段或字段的组合条件进行检索,并打印SQL
3.使用的方式要足够简单
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Table {
String value();
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Column {
String value();
}
package com.danjian.test;
@Table("user")
public class Filter {
@Column("id")
private int id;
@Column("user_name")
private String userName;
@Column("nick_name")
private String nickName;
@Column("age")
private int age;
@Column("city")
private String city;
@Column("email")
private String email;
@Column("mobile")
private String mobile;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Filter filter1 = new Filter();
Filter filter2 = new Filter();
Filter filter3 = new Filter();
filter1.setId(10); //查询id为10的用户
filter2.setUserName("lucy"); //查询用户名为Lucy的用户
filter2.setNickName("jiang"); //查询用户名为Lucy的用户
filter3.setEmail("[email protected],[email protected],[email protected]");//查询邮箱为其中任意一个的
String sql1 = query(filter1);
String sql2 = query(filter2);
String sql3 = query(filter3);
System.out.println(sql1);
System.out.println(sql2);
System.out.println(sql3);
FilterTest filterTest = new FilterTest();
filterTest.setLeader("danjiang");
String sql4 = query(filterTest);
System.out.println(sql4);
}
private static String query(Object filter) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//1.获取到class
Class clazz = filter.getClass();
//2.获取Table的名字
boolean isAnnotationPresent = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Table.class);
if (isAnnotationPresent) {
Table annotation = (Table) clazz.getAnnotation(Table.class);
String tableName = annotation.value();
stringBuilder.append("select * from ")
.append(tableName).append(" where 1 = 1");
//3.遍历所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
//4.处理每个字段对应的sql
//4.1拿到字段名
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
boolean isexit = field.isAnnotationPresent(Column.class);
if (isexit) {
//4.1拿到字段名
Column annotationColumn = field.getAnnotation(Column.class);
String columName = annotationColumn.value();
// System.out.println("columName == " + columName);
//4.2拿到字段的值
String fielfName = field.getName();
// System.out.println("fielfName == " + fielfName);
//4.3拼接方法
String getMerhodName = "get" + fielfName.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + fielfName.substring(1);
// System.out.println("getMerhodName == " + getMerhodName);
Object fieldValue = null;
try {
Method method = clazz.getMethod(getMerhodName);
fieldValue = method.invoke(filter);
// System.out.println("fieldValue == " + fieldValue);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 4.4拼装sql
if (fieldValue == null || (fieldValue instanceof Integer && (Integer)fieldValue == 0)) {
continue;
}
stringBuilder.append(" and ").append(columName);
if (fieldValue instanceof String) {
String newfieldValue = (String) fieldValue;
if (newfieldValue.contains(",")) {
String[] splits = newfieldValue.split(",");
stringBuilder.append(" in (");
for (String string : splits) {
stringBuilder.append("'").append(string).append("'").append(",");
}
stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(stringBuilder.length() -1);
stringBuilder.append(")");
// System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
} else {
stringBuilder.append(" = ").append("'").append(newfieldValue).append("'");
// System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}
} else if (fieldValue instanceof Integer) {
stringBuilder.append(" = ").append(fieldValue);
// System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
}
}
String sql = stringBuilder.toString();
return sql;
}
}
package com.danjian.test;
@Table("tepartment")
public class FilterTest {
@Column("id")
private int id;
@Column("name")
private String name;
@Column("leader")
private String leader;
@Column("amount")
private int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getLeader() {
return leader;
}
public void setLeader(String leader) {
this.leader = leader;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
//运行结果:
select * from user where 1 = 1 and id = 10
select * from user where 1 = 1 and user_name = 'lucy' and nick_name = 'jiang'
select * from user where 1 = 1 and email in ('[email protected]','[email protected]','[email protected]')
select * from tepartment where 1 = 1 and leader = 'danjiang'其中前面博客,IOC框架里面也用到了注解
之后 有编译时注解,和源码注解,学习总结整理。