Spring Ioc(控制反转)以及DI(依赖注入)详解
- Struts2:web层,比较简单(难点:ValueStack值栈、拦截器)
- Hibernate:dao层,知识点杂(学了不用,默认设置够用了)
- Spring:service层,重要,(讲多少用多少)
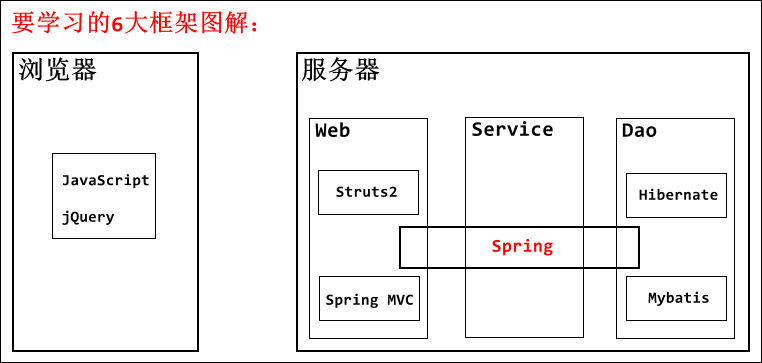
- Spring课程概述:
- Spring day01:基础(IoC控制反转、DI依赖注入)、整合JUnit、整合Web
- Spring day02:AOP切面编程、JDBCTemplate
- Spring day03:事务管理、SSH整合
一、Spring框架概述
1.1、什么是Spring?
- Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个
轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson 在其著作《Expert One-On-One J2EE Development and Design》中阐述的部分理念和原型衍生而来。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。该框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 J2EE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。然而,Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。Spring的核心是控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-stack(一站式)轻量级开源框架。 - 轻量级:与EJB对比,依赖资源少,消耗的资源少。
- 分层:full-stack(一站式),每一个层都提供解决方案。
web层:struts,spring-MVC
service层:spring
dao层:hibernate,mybatis,jdbcTemplate–>spring-data
1.2、Spring由来(两本书)
- 《Expert One-to-One J2EE Design and Development》
- 《Expert One-to-One J2EE Development without EJB》
1.3、Spring核心
- Spring的核心是:控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)
- 官网:http://www.springsource.org
1.4、Spring优点
- 方便解耦,简化开发(高内聚低耦合)
Spring就是一个大工厂(容器),可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理。Spring工厂就是用于生成Bean。
- AOP编程的支持
- Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能。
- 声明式事务的支持
- 只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程。
- 方便程序的测试
- Spring对Junit4 支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring 程序。
- 方便集成各种优秀框架
- Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的直接支持。
- 降低JavaEE API的使用难度
- Spring 对JavaEE 开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低。
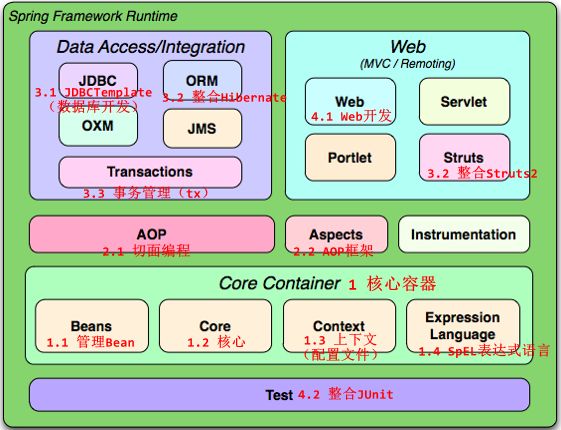
1.5、Spring体系结构
- Spring 框架是一个分层架构,它包含一系列的功能要素,并被分为大约20个模块。这些模块分为Core Container、Data Access/Integration、Web、AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)、Instrumentation和测试部分,如下图所示:
二、Spring入门案例:IoC【掌握】
- 编写流程
- 下载Spring最新开发包
- 复制Spring开发jar包到工程
- 编写Spring核心配置文件
- 在程序中读取Spring配置文件,通过Spring框架获得Bean,完成相应操作
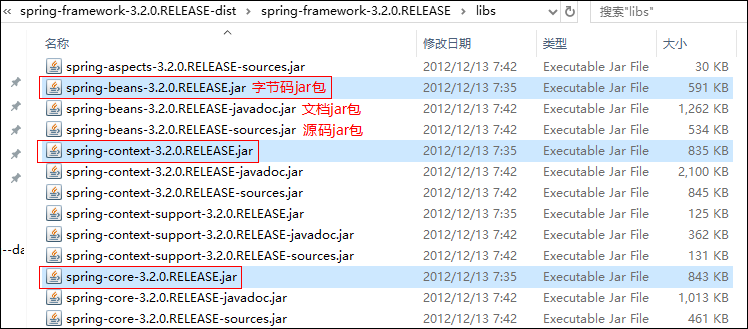
2.1、导入jar包
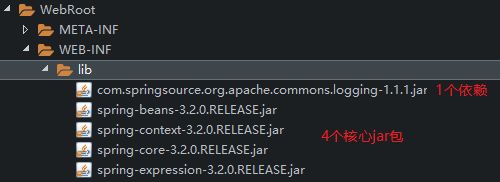
4 + 1:4个核心jar包(beans、core、context、expression)+ 1个依赖jar包(com.springsource.org.apache.commons.logging-1.1.1.jar)
项目中的显示:
Spring核心开发包简介:
- spring-core-3.2.2.RELEASE.jar
- 包含Spring框架基本的核心工具类,Spring其它组件要都要使用到这个包里的类,是其它组件的基本核心。
- spring-beans-3.2.2.RELEASE.jar
- 所有应用都要用到的,它包含访问配置文件、创建和管理bean。
- 以及进行Inversion of Control(IoC) / Dependency Injection(DI)操作相关的所有类。
- spring-context-3.2.2.RELEASE.jar
- Spring提供在基础IoC功能上的扩展服务,此外还提供许多企业级服务的支持。
- 如邮件服务、任务调度、JNDI定位、EJB集成、远程访问、缓存以及各种视图层框架的封装等。
- spring-expression-3.2.2.RELEASE.jar
- Spring表达式语言。
- com.springsource.org.apache.commons.logging-1.1.1.jar
- 第三方的主要用于处理日志。
2.2、编写目标类
- 创建UserService接口和实现类
- 获得UserService实现类的实例
- 在之前开发中,我们是直接new一个对象即可。即:
private IUserDao dao = new IUserDaoImpl(); - 在学习Spring之后,将由Spring来创建对象的实例 –> 即:
IoC 控制反转(Inverse of Control)
之后需要实例对象时,从Spring工厂(容器)中获得即可,需要将实现类的全限定名称配置到xml文件中。
- 在之前开发中,我们是直接new一个对象即可。即:
UserService.java
public interface UserService {
void addUser();
}
UserServiceImpl.java
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("a_ioc add user");
}
}
2.3、编写spring配置文件
- 位置:任意,开发中一般在classpath下(src)
- 名称:任意,开发中常用 applicationContext.xml
- 内容:添加schema约束
- 约束文件位置:spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html\xsd-config.html
beans.xml
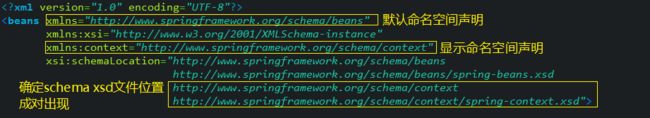
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.a_ioc.UserServiceImpl">bean>
beans>
2.4、测试代码
TestIoC.java
public class TestIoC {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 之前开发,自己手写new出对象
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
userService.addUser();
}
@Test
public void demo02() {
// 现在从spring容器中获得对象实例
// 1 、获得容器
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/a_ioc/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
// 2、获得内容 ,注意此时不需要自己new出对象了,都是从spring容器中获得
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId");
userService.addUser();
}
}
- IoC(Inverse of Control)反转控制的概念,就是将原本在程序中手动创建UserServiceImpl对象的控制权,交由Spring框架管理。
- 简单说,就是创建UserServiceImpl对象的控制权被反转到了Spring框架。
三、Spring入门案例:DI【掌握】
- DI :Dependency Injection :依赖注入
is a :是一个,继承。
has a:有一个,成员变量,依赖。
class B {
private A a; // B类依赖A类,B类使用A类。
}
依赖:一个对象需要使用另一个对象。
注入:通过setter方法进行另一个对象实例设置。
- 例如:
class BookServiceImpl {
// 之前开发:接口 = 实现类(service和dao耦合了,写死了,知道具体的实现类是谁,那么我的具体实现类变化,那么这行代码也得跟着变)
// private BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImpl();
// spring之后(解耦:service实现类使用了dao的接口,这样就不知道具体的实现类是谁了)
private BookDao bookDao;
setter方法
}
模拟spring执行过程
创建service实例:BookService bookService = new BookServiceImpl(); => IoC <bean>
创建dao实例:BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImple(); => IoC
将dao设置给service:bookService.setBookDao(bookDao); => DI <property>
3.1、编写目标类
- 创建BookDao接口和实现类
- 创建BookService接口和实现类
- 将dao和service配置到 xml文件中
- 使用api测试
3.1.1、dao
BookDao.java
public interface BookDao {
void save();
}
BookDaoImpl.java
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("b_di add book");
}
}
3.1.2、service
BookService.java
public interface BookService {
void addBook();
}
BookServiceImpl.java
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
// 方式1:之前,接口 = 实现类
// private BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImpl();
// 方式2:现在,接口 + setter
private BookDao bookDao;
public void setBookDao(BookDao bookDao) {
this.bookDao = bookDao;
}
@Override
public void addBook() {
this.bookDao.save();
}
}
3.2、编写spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
模拟spring执行过程
创建service实例:BookService bookService = new BookServiceImpl(); => IoC <bean>
创建dao实例:BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImple(); => IoC
将dao实例设置给service实例:bookService.setBookDao(bookDao); => DI <property>
<property> 用于进行属性注入
name : Bean的属性名称,通过setter方法获得
setBookDao => BookDao => bookDao
ref :另一个Bean的id值的引用
-->
<!-- 创建service实例 -->
<bean id="bookServiceId" class="com.itheima.b_di.BookServiceImpl">
<!-- 将dao实例设置给service实例 -->
<property name="bookDao" ref="bookDaoId"></property> <!-- 用于进行属性注入 -->
</bean>
<!-- 创建dao实例 -->
<bean id="bookDaoId" class="com.itheima.b_di.BookDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
3.3、测试代码
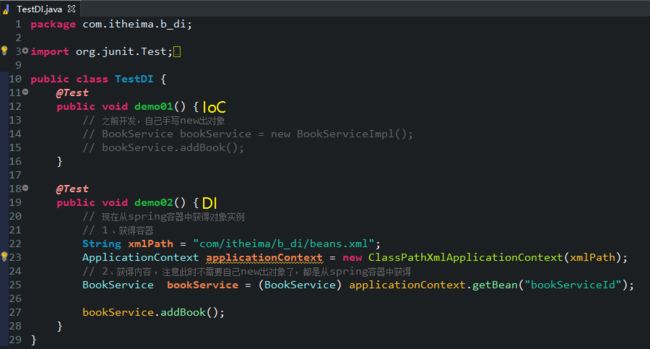
public class TestDI {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 之前开发,自己手写new出对象
// BookService bookService = new BookServiceImpl();
// bookService.addBook();
}
@Test
public void demo02() {
// 现在从spring容器中获得对象实例
// 1 、获得容器
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/b_di/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
// 2、获得内容 ,注意此时不需要自己new出对象了,都是从spring容器中获得
BookService bookService = (BookService) applicationContext.getBean("bookServiceId");
bookService.addBook();
}
}
- DI:Dependency Injection 依赖注入,在Spring框架负责创建Bean对象时,动态的将依赖对象注入到Bean组件。
- getBean(“bookServiceId”); 从spring容器中获得指定名称对象的实例时,会先判断本实例对象是否需要使用其他实例化对象,由于设置了< property name=”bookDao” ref=”bookDaoId”>< /property>,说明需要使用其他实例化对象,所以就根据其他Bean的id值的引用,去spring容器中获得指定名称对象的实例,相当于将dao实例设置给service实例。
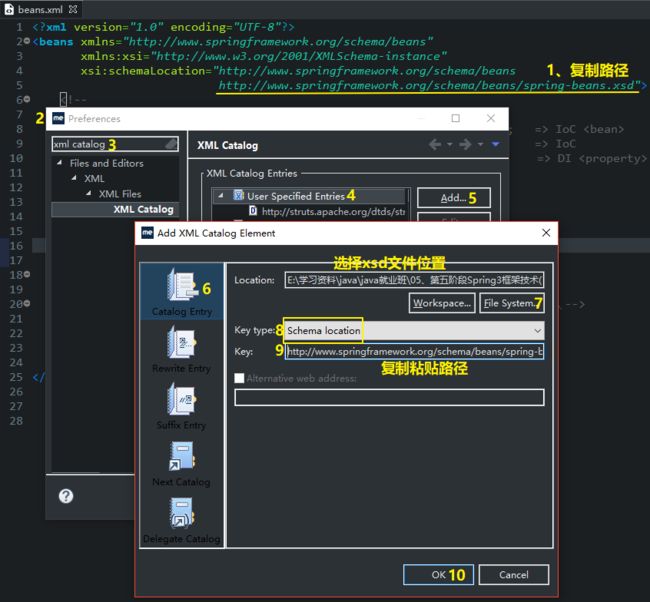
四、MyEclipse中编写applicationContext.xml时的提示设置
- 法一:电脑联网
- 法二:电脑没有联网
五、Spring的核心API(了解)
- api整体了解即可,之后不使用,在学习过程需要。

- BeanFactory :这是一个
工厂,用于生成任意Bean。
采取延迟加载,第一次调用getBean(); 时才会初始化Bean。(即实例化对象) - ApplicationContext :是BeanFactory的子接口,功能更强大。(国际化处理、事件传递、Bean自动装配、各种不同应用层的Context实现)。
采取非延时加载,当配置文件被加载时,就进行对象的实例化。
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 用于加载classpath(类路径/src)下的xml
- 加载xml运行时位置 –> /WEB-INF/classes/xxx.xml
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 用于加载指定盘符下的xml
- 加载xml运行时位置 –> /WEB-INF/xxx.xml
- 通过java web学习过的 ServletContext.getRealPath(); 获得具体盘符
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 用于加载classpath(类路径/src)下的xml
示例代码如下:
public class TestDI {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 之前开发,自己手写new出对象
// BookService bookService = new BookServiceImpl();
// bookService.addBook();
}
@Test
public void demo02() {
// 现在从spring容器中获得对象实例,使用的是ApplicationContext
// 1 、获得容器
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/b_di/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); // 采取非延时加载,当配置文件被加载时,就进行对象的实例化。
// 2、获得内容 ,注意此时不需要自己new出对象了,都是从spring容器中获得
BookService bookService = (BookService) applicationContext.getBean("bookServiceId");
bookService.addBook();
}
@Test
public void demo03() {
// 现在从spring容器中获得对象实例,使用的是BeanFactory,里面需要一个Resource,该Resource又是一个接口,需要找它的实现类ClassPathResource
// 1 、获得容器
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/b_di/beans.xml";
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource(xmlPath));
// 2、获得内容 ,注意此时不需要自己new出对象了,都是从spring容器中获得
BookService bookService = (BookService) beanFactory.getBean("bookServiceId"); // 采取延迟加载,第一次调用getBean(); 时才会初始化Bean(即实例化对象)。
bookService.addBook();
}
}
六、装配Bean:基于XML
6.1、实例化Bean 的三种方式
- 3种bean实例化方式:
- 使用
默认构造方法实例化 - 使用
静态工厂方法实例化 - 使用
实例工厂方法实例化
- 使用
6.1.1、使用默认构造方法实例化
格式:
<bean id="从Spring容器中获得实例时使用的" class="需要创建实例的全限定类名">bean>
例如:<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.a_ioc.UserServiceImpl">bean>
示例中用到的 UserService.java 和 UserServiceImpl.java 代码同上 2.2、编写目标类 的代码,这里不再赘述!
在spring容器中进行配置:
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.a_ioc.UserServiceImpl">bean>
beans>
测试代码:
TestIoC.java
public class TestIoC {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 之前开发,自己手写new出对象
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl(); // 直接手动创建实例
userService.addUser();
}
@Test
public void demo02() {
// 现在从spring容器中获得对象实例
// 1 、获得容器
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/a_ioc/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
// 2、获得内容 ,注意此时不需要自己new出对象了,都是从spring容器中获得
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId");
userService.addUser();
}
}
6.1.2、使用静态工厂方法实例化
- 静态工厂:常用与spring整合其他框架(工具)时。
- 静态工厂:用于生成实例对象,所有的方法必须是static。
示例中用到的 UserService.java 和 UserServiceImpl.java 代码同上 2.2、编写目标类 的代码,这里不再赘述!
格式:
<bean id="" class="工厂全限定类名" factory-method="静态方法名称">
在spring容器中进行配置:
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.b_static_factory.MyBeanFactory" factory-method="createService">bean>
beans>
静态工厂类代码:
public class MyBeanFactory {
/**
* 创建实例的静态工厂,所有的方法必须是静态的(static)。
*
* @return
*/
public static UserService createService() {
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
// 还有创建其他实例的静态工厂
// ......
}
测试代码:
TestStaticFactory.java
/**
* 第二种实例化Bean 的方式 :使用静态工厂方法实例化
*
*/
public class TestStaticFactory {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 以前:使用自定义的静态实例工厂
UserService userService = MyBeanFactory.createService();
userService.addUser();
}
@Test
public void demo02() {
// 现在:使用spring 工厂:将自定义的静态工厂创建的实例交给spring管理
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/c_inject/b_static_factory/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId", UserService.class); // 这种方式底层会自动转换
// UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId");
userService.addUser();
}
}
注意:当使用JDK版本为1.8时,运行上面的测试代码会出现一个问题: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException,
问题解决链接:使用Junit测试一个 spring静态工厂实例化bean 的例子,所有代码都没有问题,但是出现java.lang.IllegalArgumentException异常
小结:在以后的开发中,工厂类不需要我们去手写,因为别人已经写好了,我们通过编写配置文件,把别人写好的工厂类拿来,写上要用的方法名,然后把它生产后的实例给Spring存起来,以后我们要用什么实例,跟Spring说一下,去拿就可以了。
6.1.3、使用实例工厂方法实例化
- 实例工厂:必须先有工厂的实例对象,然后通过实例对象去创建对象。特点:提供所有的方法都是“非静态”的。
示例中用到的 UserService.java 和 UserServiceImpl.java 代码同上 2.2、编写目标类 的代码,这里不再赘述!
在spring容器中进行配置:
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myBeanFactoryId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.c_factory.MyBeanFactory" >bean>
<bean id="userServiceId" factory-bean="myBeanFactoryId" factory-method="createService">bean>
beans>
静态工厂类代码:
public class MyBeanFactory {
/**
* 创建实例的工厂,所有方法非静态
*
* @return
*/
public UserService createService() {
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
// 还有创建其他实例的工厂
// ......
}
测试代码:
TestFactory.java
package com.itheima.c_inject.c_factory;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 第三种实例化Bean 的方式 :使用实例工厂方法实例化
* */
public class TestFactory {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 以前:使用自定义的实例工厂
// 1、创建工厂实例
MyBeanFactory myBeanFactory = new MyBeanFactory();
// 2、通过工厂实例,获得对象
UserService userService = myBeanFactory.createService();
userService.addUser();
}
@Test
public void demo02() {
// 现在:使用spring 工厂:将自定义的实例工厂创建的实例交给spring管理
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/c_inject/c_factory/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId", UserService.class); // 这种方式底层会自动转换
// UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId");
userService.addUser();
}
}
6.2、Bean 的种类
- 普通bean :之前操作的都是普通bean。例如:
< bean id="xxx" class="A" >,这句代码的意思是:Spring直接创建A的实例,并返回。 - FactoryBean :是一个特殊的bean,
具有工厂生成对象能力,但是只能生成特定的对象。
想要生产对象的bean 必须实现FactoryBean 接口,此接口提供方法getObject(); 用于获得特定bean。
- 示例:
< bean id="xxx" class="FB">,这句代码的意思是:Spring会先创建FB实例,然后调用getObject(); 方法,并返回方法的返回值。
即相当于如下两行代码:
FB fb = new FB();
return fb.getObject();
- 示例:
- BeanFactory 和 FactoryBean 对比?
- BeanFactory :是一个生产bean的工厂,用于生成任意的bean。
- FactoryBean :是一个特殊的bean,用于生成另一个特定的bean。
- 例如:ProxyFactoryBean ,此工厂bean用于生产代理对象的实例。
< bean id="xxx" class="....ProxyFactoryBean">,这句代码的意思是:获得代理对象的实例。即AOP使用。
- 例如:ProxyFactoryBean ,此工厂bean用于生产代理对象的实例。
spring容器中bean元素id和name属性的区别?
- 在spring容器中添加以下配置:
示例:< bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.a_ioc.UserServiceImpl"> - bean节点中id和name的区别:
- 区别一:
- id : 指定唯一实例引用
- name : 可以指定多个实例引用,例如name=”名称1, 名称2”
区别二:
- id :id的命名要满足XML对ID属性命名规范
例如:必须以字母开始,可以使用字母、数字、连字符、下划线、句话、冒号 name : 如果Bean的名称中含有特殊字符,就需要使用name属性
例如 :< bean name="# boy" class="cn.itheima.ioc.Boy"/>因为name属性可以相同,所以后出现Bean会覆盖之前出现的同名的Bean。
总结:项目开发的时候,强烈要求用id,因为id可以表示唯一引用。
6.3、Bean 的作用域
- Bean 的作用域:用于确定spring所创建bean 的实例个数。

- 取值:
- singleton 单例,默认值。
- prototype 多例,每执行一次getBean() 将获得一个实例。例如:在struts整合spring时,需要配置action为多例。
- 配置示例:
- 例如:
< bean id="xxx" class="xxx" scope="xxx">
- 例如:
- 默认情况下会在容器启动时初始化bean,但我们可以指定Bean节点的
lazy-init="true"来延迟初始化bean,这时候,只有第一次获取bean会才初始化bean。
例如:< bean id="xxx" class="cn.itheima.UserServiceImpl" lazy-init="true"> - 如果想对所有bean都应用延迟初始化,可以在根节点beans设置
default-lazy-init="true",
例如:< beans default-lazy-init="true“> - Portlet是基于java的web组件,由portlet容器管理,并由容器处理请求,生产动态内容。
- Portals使用portlets作为可插拔用户接口组件,提供信息系统的表示层。
- 作为利用servlets进行web应用编程的下一步,portlets实现了web应用的模块化和用户中心化。
示例代码如下:
示例中用到的 UserService.java 和 UserServiceImpl.java 代码同上 2.2、编写目标类 的代码,这里不再赘述!
在spring容器中进行配置:
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.d_scope.UserServiceImpl" scope="prototype">bean>
beans>
测试代码:
TestScope.java
public class TestScope {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 现在:使用spring 工厂
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/d_scope/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService1 = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId", UserService.class); // 这种方式底层会自动转换
UserService userService2 = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId", UserService.class); // 这种方式底层会自动转换
// 默认Bean的作用域是单例,所以打印的对象的地址是一样的
// System.out.println(userService1); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@2ac273d3
// System.out.println(userService2); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@2ac273d3
// 现在在配置文件中添加scope属性,值为prototype,此时Bean的作用域变为多例了,再次打印,输出地址不一样了
System.out.println(userService1); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@66480dd7
System.out.println(userService2); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@52a86356
}
}
6.4、Bean 的生命周期
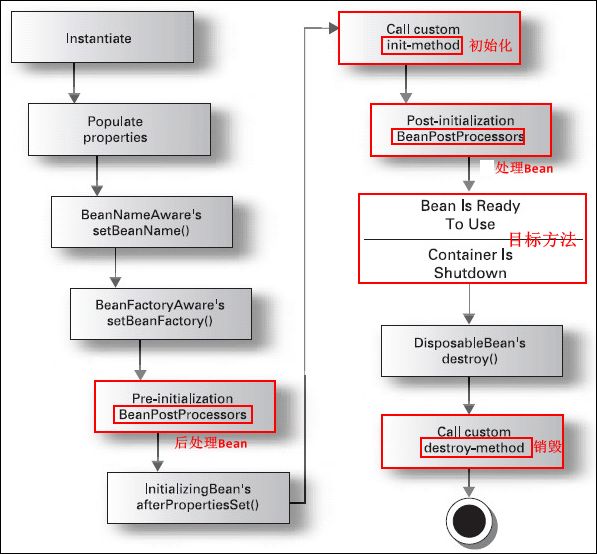
6.4.1、Bean 的生命周期详情
- instantiate bean 对象实例化。
- populate properties 封装属性。
- 如果Bean实现 BeanNameAware,则表示执行
setBeanName。- 如果Bean实现 BeanFactoryAware 或者 ApplicationContextAware,则表示设置实例工厂(
setBeanFactory)或者上下文对象(setApplicationContext)。- 如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean),则表示执行
postProcessBeforeInitialization。- 如果Bean实现 InitializingBean,则表示执行
afterPropertiesSet。- 调用
,则表示指定初始化方法init。- 如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean),则表示执行
postProcessAfterInitialization。- 执行业务处理
- 如果Bean实现 DisposableBean,则表示执行
destroy。- 调用
,则表示指定销毁方法customerDestroy。
6.4.2、Bean 的初始化和销毁
目标方法执行前和执行后,将进行Bean的初始化或销毁。
示例:
示例代码如下:
编写目标类代码:
UserService.java
public interface UserService {
void addUser();
}
UserServiceImpl.java
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("e_lifecycle add user");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("我的初始化方法");
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("我的销毁方法");
}
}
编写配置文件:
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.e_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl"
init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory">bean>
beans>
编写测试代码:
public class TestLifecycle {
@Test
public void demo01() throws Exception {
// 现在:使用spring 工厂(spring 容器)
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/c_inject/e_lifecycle/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId");
userService.addUser();
// 要想使我的销毁方法也执行,必须要求:
// 1.容器必须先close,我的销毁方法才会执行;
// 2.必须是单例的(spring所创建该bean的实例个数只有一个)即bean中的scope配置成默认即可。
// 因为此close方法在接口 ApplicationContext 中没有定义,而在实现类中提供了该方法,我们可以使用反射,因为反射最后执行的就是实现类中的方法。
applicationContext.getClass().getMethod("close").invoke(applicationContext);
}
}
6.4.3、BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean
- 是由spring提供的一种机制,只要实现类实现此接口BeanPostProcessor,并将该实现类提供给spring容器,spring容器将自动执行两个方法:在初始化方法前执行before()方法,在初始化方法后执行after()方法。配置格式:

- Factory hook(勾子) that allows for custom modification of new bean instances, e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
- spring提供工厂勾子,用于修改实例对象,可以生成代理对象。(是AOP底层)
谷歌翻译:Factory hook(勾子),允许自定义修改新的bean实例,例如:检查标记接口或用代理包装它们。
我们来模拟这句话的意思:
before() => postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
after() => postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
A a = new A();
a = B.before(a); // 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以什么都没做,也可以做一些事情,比如:生成jdk代理对象并返回给a,这样a就从实例对象变成代理对象了,此时的a就具有了AOP功能;再比如,如果把null返回给a,再用a去调用方法,就会出现空指针异常。
a.init();
a = B.after(a);
// 以下是AOP演示:
// 我们现在在后处理Bean 代码执行完之后,把jdk代理对象返回给a。让a在调用addUser()之前先做一些事情
// 之前要做的事情
a.addUser(); // 在目标方法的前后可以做一些事情,例如:开启事务、提交事务、性能监控(前后时间)等等
// 之后要做的事情
a.destroy();
目标类示例代码如下:
UserService.java
public interface UserService {
void addUser();
}
UserServiceImpl.java
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("e_lifecycle add user");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("我的初始化方法");
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("我的销毁方法");
}
}
实现类示例代码如下:
MyBeanPostProcessor.java
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行了前方法:" + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行了后方法:" + beanName);
// 传入的参数bean是我们的目标对象,此时我们的目标对象只有一个接口,那么我们的代理对象也只有一个接口
// 生成jdk代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
MyBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), // 代理对象
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), // 目标对象
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("---开启事务---");
Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args); // 执行目标方法,本例中的目标方法是addUser
System.out.println("---关闭事务---");
return obj;
}
}); // 代理的处理程序
}
}
配置文件示例代码如下:
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.e_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl"
init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory">bean>
<bean class="com.itheima.e_lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor">bean>
beans>
测试示例代码如下:
TestLifecycle.java
public class TestLifecycle {
@Test
public void demo01() throws Exception {
// 现在:使用spring 工厂(spring 容器)
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/e_lifecycle/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId");
userService.addUser();
// 要想使我的销毁方法也执行,必须要求:
// 1.容器必须先close,我的销毁方法才会执行;
// 2.必须是单例的(spring所创建该bean的实例个数只有一个)即bean中的scope配置成默认即可。
// 因为此close方法在接口 ApplicationContext 中没有定义,而在实现类中提供了该方法,我们可以使用反射,因为反射最后执行的就是实现类中的方法。
applicationContext.getClass().getMethod("close").invoke(applicationContext);
}
}
- 运行结果截图:
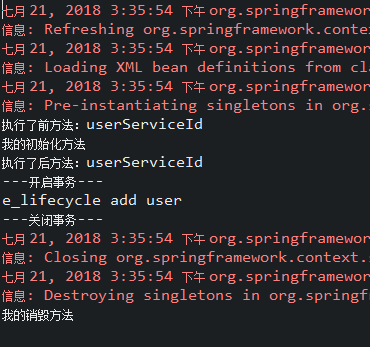
- 问题1:后处理bean作用某一个目标类,还是所有目标类?
答:所有。 - 问题2:如何只作用一个?
答:通过获取”参数2”beanName进行控制。例如:”xxx”.equals(method.getName());
6.5、依赖注入Bean 的属性(xml)
- 注入依赖对象可以采用:
手工装配或自动装配。
- 手动装配:一般进行配置信息都采用手动装配。
- 基于xml装配
- 构造方法注入
- 属性setter方法注入
- 接口注入(spring不支持)
- 基于注解装配 => 之后讲解
- 基于xml装配
- 自动装配:在struts 和spring 整合的时候使用自动装配。
- byType:按类型装配
- byName:按名称装配
- constructor:按构造装配
- autodetect:不确定装配(即自动装配)
- 手动装配:一般进行配置信息都采用手动装配。
- 在
实际应用中建议使用手工装配,因为自动装配会产生未知情况,开发人员无法预见最终的装配结果。
6.5.1、构造方法
Bean对象类:
public class User {
private Integer uid;
private String username;
private Integer age;
public User(Integer uid, String username) { // 构造方法一
super();
this.uid = uid;
this.username = username;
}
public User(String username, Integer age) { // 构造方法二
super();
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
}
// 省略getter 和 setter 方法
// ......
spring的配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.a_constructor.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="1">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.Integer" value="2">constructor-arg>
bean>
beans>
6.5.2、setter方法
spring的配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="personId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Person">
<property name="pname" value="晓艺">property>
<property name="age">
<value>26value>
property>
<property name="homeAddr" ref="homeAddrId">property>
<property name="companyAddr">
<ref bean="companyAddrId">ref>
property>
bean>
<bean id="homeAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Address">
<property name="addr" value="山西运城">property>
<property name="tel" value="911">property>
bean>
<bean id="companyAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Address">
<property name="addr" value="百子湾">property>
<property name="tel" value="120">property>
bean>
beans>
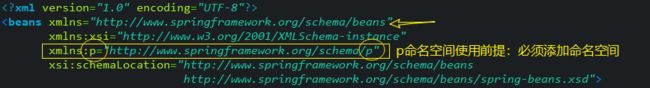
6.5.3、P命名空间 [了解]
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="personId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Person"
p:pname="明军"
p:age="26"
p:homeAddr-ref="homeAddrId"
p:companyAddr-ref="companyAddrId">
bean>
<bean id="homeAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Address"
p:addr="河南信阳"
p:tel="119">
bean>
<bean id="companyAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Address"
p:addr="青年路"
p:tel="110">
bean>
beans>
6.5.4、SpEL [了解]
- 对
格式:
#{123}、#{‘bruce’}、#{2e5} :数字、字符串、科学计数法(常量)
#{beanId} :引用另一个Bean
#{beanId.propName} :引用Bean 的属性(操作数据)
#{beanId.toString()} :引用Bean 的方法(执行方法)
#{T(类).字段|方法} :引用静态方法或字段,例如:T(java.lang.Math).PI
#{3 lt 4 == 4 ge 3} :运算符支持
#{user.name matches ‘[a-z]{6,}’} :正则表达式支持
#{likes[3]} :集合支持
示例代码如下:
spring的配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="customerId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.d_SpEL.Customer">
<property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname?.toUpperCase()}">property>
<property name="pi" value="#{T(java.lang.Math).PI}">property>
bean>
beans>
6.5.5、集合注入
spring的配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="collectionDataId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.e_collection.CollectionData">
<property name="arrayData">
<array>
<value>cmjvalue>
<value>lxyvalue>3
<value>明军value>
<value>晓艺value>
array>
property>
<property name="listData">
<list>
<value>琴棋书画value>
<value>撸哑铃value>
<value>花鸟鱼虫value>
<value>撸娃娃value>
list>
property>
<property name="setData">
<set>
<value>看电影value>
<value>运动value>
<value>创作value>
<value>旅行value>
set>
property>
<property name="mapData">
<map>
<entry key="bruce" value="布鲁斯">entry>
<entry>
<key><value>lucyvalue>key>
<value>露西value>
entry>
map>
property>
<property name="propsData">
<props>
<prop key="处女座">内心善良prop>
<prop key="天蝎座">宅心仁厚prop>
<prop key="缘定今生">此生不悔prop>
props>
property>
bean>
beans>
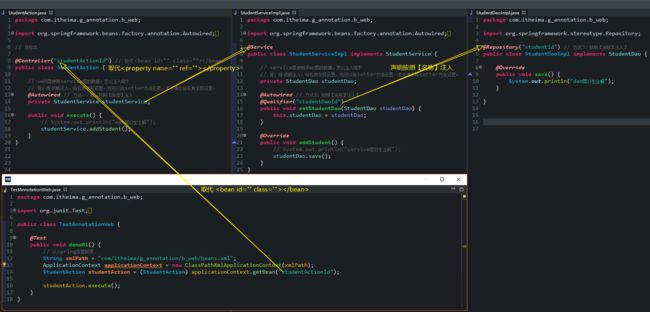
七、装配Bean:基于annotation(注解)
- 注解:就是一个类,格式:@注解名称
- 开发中:使用注解 取代 xml配置文件。
1. @Component 取代 示例代码:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.g_annotation.a_ioc">context:component-scan>
beans>
演示:
单例、多例、初始化、销毁
UserService.java
package com.itheima.g_annotation.c_other;
public interface UserService {
void addUser();
}
UserServiceImpl.java
@Service("userServiceId") // 单例
@Scope("prototype") // 多例
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("c_other add user");
}
@PostConstruct // 初始化
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("我的初始化方法");
}
@PreDestroy // 销毁
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("我的销毁方法");
}
}
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.g_annotation.c_other">context:component-scan>
beans>
测试代码:
TestOther.java
package com.itheima.g_annotation.c_other;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestOther {
@Test
public void demo01() {
// 现在:使用spring 工厂
String xmlPath = "com/itheima/g_annotation/c_other/beans.xml";
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService1 = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId", UserService.class); // 这种方式底层会自动转换
UserService userService2 = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId", UserService.class); // 这种方式底层会自动转换
// 默认Bean的作用域是单例,所以打印的对象的地址是一样的
// System.out.println(userService1); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@2ac273d3
// System.out.println(userService2); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@2ac273d3
// 现在在配置文件中添加scope属性,值为prototype,此时Bean的作用域变为多例了,再次打印,输出地址不一样了
System.out.println(userService1); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@66480dd7
System.out.println(userService2); // com.itheima.c_inject.d_scope.UserServiceImpl@52a86356
applicationContext.close();
}
}
八、学习回顾
1、导入jar包:4 + 1 --> beans/core/context/expression + commons-logging
2、编写目标类:dao 和 service
3、 Spring配置文件
IoC:
<bean id="" class="">bean>
DI:
<bean><property name="" value="" | ref="">property>bean>
实例化方式:
默认构造
静态工厂:
<bean id="" class="工厂类全限定类名" factory-method="静态方法名称">bean>
实例工厂:
<bean id="工厂的id" class="工厂类">bean>
<bean id="" factory-bean="工厂的id" factory-method="方法名称">bean>
作用域:
<bean id="" class="" scope="singleton | prototype">bean>
生命周期:
<bean id="" class="" init-method="" destroy-method="">bean>
后处理bean:实现BeanPostProcessor接口,,对容器中所有的bean都生效。
属性注入:
构造方法注入:
<bean><constructor-arg index="" type="">bean>
setter方法注入:
<bean><property name="" value="" | ref="">bean>bean>
p命名空间:简化
<bean p:属性名="普通值" p:属性名-ref="引用值">bean>
注意:使用p命名空间需要先声明命名空间。
SpEL:
<property name="" value="#{表达式}">
#{123} #{‘abc’}
#{beanId.propName?.methodName()}
#{T(类).静态方法|字段}
集合注入
数组 ...
List ...
Set ...
Map
Properties
4、核心api
BeanFactory,延迟实例化bean,第一次调用getBean(); 时才会初始化Bean。
ApplicationContext 一般常用,功能更强,采取非延时加载,当配置文件被加载时,就进行对象的实例化。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 加载classpath中的xml文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 加载指定盘符的文件,ServletContext.getRealPath()
5、使后处理bean 只对一个生效
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 使后处理bean 只对一个生效
if("userServiceId".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("执行了前方法:" + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
6、注解
1、先配置扫描含有注解的类
2、常见的注解
@Component 组件,注入任意bean
WEB
@Controller web层
@Service service层
@Repository dao层
注入字段或setter方法
普通值:@Value
引用值:
按类型:@Autowired
按名称1:@Autowired @Qualifier("名称")
按名称2:@Resource("名称")
作用域:@Scope("prototype")
生命周期:
初始化:@PostConstruct
销毁方法:@PreDestroy
7、注解和xml混合使用
1.将所有的bean都配置xml中
<bean id="" class="">bean>
2.将所有的依赖都使用注解
@Autowired
默认不生效。为了生效,需要在xml配置:
总结:
注解1:
注解2:
1、一般情况两个注解不一起使用。
2、 “注解1”扫描含有注解(@Component 等)类,注入的注解自动生效。
“注解2”只在xml和注解(注入)混合使用时,使注入的注解生效
摘自传智播客系列课程笔记