python读取文本文件数据
本文要点刚要:
(一)读文本文件格式的数据函数:read_csv,read_table
1.读不同分隔符的文本文件,用参数sep
2.读无字段名(表头)的文本文件 ,用参数names
3.为文本文件制定索引,用index_col
4.跳行读取文本文件,用skiprows
5.数据太大时需要逐块读取文本数据用chunksize进行分块。
(二)将数据写成文本文件格式函数:to_csv
范例如下:
(一)读取文本文件格式的数据集
1.read_csv和read_table的区别:
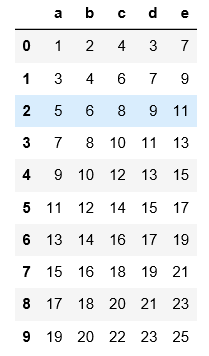
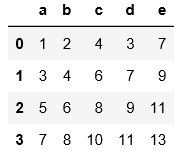
#read_csv默认读取用逗号分隔符的文件,不需要用sep来指定分隔符
|
1
|
import
pandas as pdpd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.csv'
)
|
|
1
2
3
|
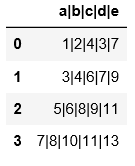
#read_csv如果读的是用非逗号分隔符的文件,必须要用sep指定分割符,不然读出来的是原文件的样子,数据没被分割开
import
pandas as pd
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
)
|
|
1
2
3
|
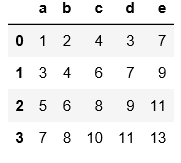
#与上面的例子可以对比一下区别
import
pandas as pd
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
)
|
|
1
2
3
|
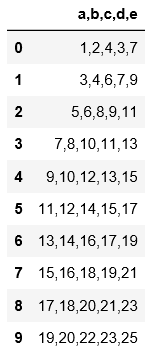
#read_table读取文件时必须要用sep来指定分隔符,否则读出来的数据是原始文件,没有分割开。
import
pandas as pd
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.csv'
)
|
|
1
2
3
|
#read_table读取数据必须指定分隔符
import
pandas as pd
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
)
|
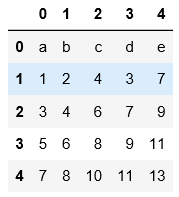
2.读取文本文件时不用header和names指定表头时,默认第一行为表头
|
1
2
|
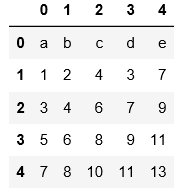
#用header=None表示数据集没有表头,会默认用阿拉伯数字填充表头和索引
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
,header
=
None
)
|
|
1
2
|
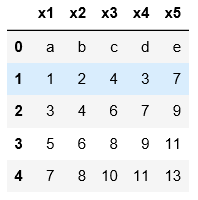
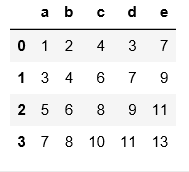
#用names可以自定义表头
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
, names
=
[
'x1'
,
'x2'
,
'x3'
,
'x4'
,
'x5'
])
|
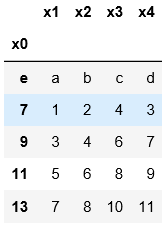
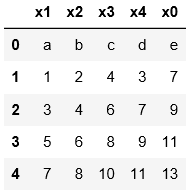
3.默认用阿拉伯数字指定索引;用index_col指定某一列作为索引
|
1
2
3
|
names
=
[
'x1'
,
'x2'
,
'x3'
,
'x4'
,
'x0'
]
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
,
names
=
names,index_col
=
'x0'
)
|
4.以下示例是用skiprows将hello对应的行跳过后读取其他行数据,不管首行是否作为表头,都是将表头作为第0行开始数
可以对比一下三个例子的区别进行理解
|
1
|
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data1.txt'
)
|
|
1
2
3
|
names
=
[
'x1'
,
'x2'
,
'x3'
,
'x4'
,
'x0'
]
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data1.txt'
,names
=
names,
skiprows
=
[
0
,
3
,
6
])
|
|
1
2
|
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data1.txt'
,
skiprows
=
[
0
,
3
,
6
])
|
|
1
2
|
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data1.txt'
,header
=
None
,
skiprows
=
[
0
,
3
,
6
])
|
5.分块读取,data1.txt中总共8行数据,按照每块3行来分,会读3次,第一次3行,第二次3行,第三次1行数据进行读取。
注意这里在分块的时候跟跳行读取不同的是,表头没作为第一行进行分块读取,可通过一下两个例子对比进行理解。
|
1
2
3
4
|
chunker
=
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data1.txt'
,chunksize
=
3
)
for
m
in
chunker:
print
(
len
(m))
print
m
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
chunker
=
pd.read_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data1.txt'
,header
=
None
,
chunksize
=
3
)
for
m
in
chunker:
print
(
len
(m))
print
m
|
(二)将数据写入文本格式用to_csv
以data.txt为例,注意写出文件时,将索引也写入了
|
1
2
|
data
=
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
)
print
data
|
|
1
2
3
|
#可以用index=False禁止索引的写入。
data
=
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
)
data.to_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\outdata.txt'
,sep
=
'!'
,index
=
False
)
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
#可以用columns指定写入的列
data
=
pd.read_table(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\data.txt'
,sep
=
'|'
)
data.to_csv(
'C:\\Users\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\pythonlianxi\\test0424\\outdata2.txt'
,sep
=
','
,index
=
False
,
columns
=
[
'a'
,
'c'
,
'd'
])
|
http://www.dwm8256.cn/
http://www.yhb3879.cn/
http://www.evv5980.cn/
http://www.nat5354.cn/
http://www.nkc4539.cn/
http://www.jal3249.cn/
http://www.ppr6189.cn/
http://www.xnw9449.cn/
http://www.jwv1856.cn/
http://www.ddh4684.cn/
http://www.ymu2666.cn/
http://www.kdz0246.cn/
http://www.sph9900.cn/
http://www.fmh8265.cn/
http://www.igf1400.cn/
http://www.toy2618.cn/
http://www.xjh6427.cn/
http://www.cce2139.cn/
http://www.vzx2078.cn/
http://www.fhw1039.cn/
http://www.dwd9016.cn/
http://www.wqr1047.cn/
http://www.nyc9430.cn/
http://www.bks4017.cn/
http://www.iru8567.cn/
http://www.dyq9159.cn/
http://www.ece1729.cn/
http://www.zpp0623.cn/
http://www.ymg3874.cn/
http://www.jaf1308.cn/
http://www.djz1658.cn/
http://www.jlh2124.cn/
http://www.acj2609.cn/
http://www.per1537.cn/
http://www.jxa6372.cn/
http://www.dja2819.cn/
http://www.sml6389.cn/
http://www.hgh3722.cn/
http://www.ntd5264.cn/
http://www.esn7121.cn/
http://www.oee2689.cn/
http://www.pdh7765.cn/
http://www.qsv0141.cn/
http://www.mar4014.cn/
http://www.rcd9187.cn/
http://www.unw3900.cn/
http://www.tmo9604.cn/
http://www.eko5785.cn/
http://www.eqn5017.cn/
http://www.oek0353.cn/
http://www.hmw0652.cn/
http://www.tub1546.cn/
http://www.taj7240.cn/
http://www.dto7731.cn/
http://www.tox1106.cn/
http://www.pzx0011.cn/
http://www.kdd4058.cn/