基于深度学习LSTM算法生成音乐
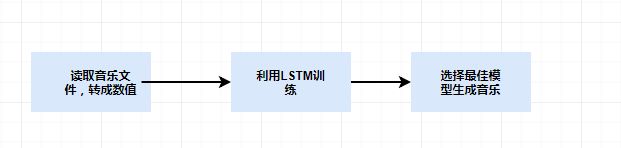
整套架构图
一、背景知识
1.概念 (来自百度百科):
notes(音符):用来记录不同长短的音的进行符号。全音符、二分音符、四分音符、八分音符、十六分音符是最常见的音符。是五线谱中最重要的元素
chord(和弦):和弦是乐理上的一个概念,指的是一定音程关系的一组声音。将三个和三个以上的音,按三度叠置的关系,在纵向上加以结合,就成为和弦
如果无法使用TensorFlow或者配置不够强大,可以使用Colaboratory网址,在线运行,里面已经集成了TensorFlow,pandas等包,很方便使用
二、读取MIDI文件
读取mid里面的音符和和旋信息,我这边使用了70首mid格式的文件作为训练样本,可以网上自己下载。
import tensorflow as tf
import os
from music21 import converter, instrument, note, chord, stream
#读取训练数据的Notes
def get_notes():
filepath='D:/log/music_midi/'
files=os.listdir(filepath)
Notes=[]
for file in files:
try:
stream = converter.parse(filepath+file)
instru = instrument.partitionByInstrument(stream)
if instru: # 如果有乐器部分,取第一个乐器部分
notes = instru.parts[0].recurse()
else: #如果没有乐器部分,直接取note
notes = stream.flat.notes
for element in notes:
# 如果是 Note 类型,取音调
# 如果是 Chord 类型,取音调的序号,存int类型比较容易处理
if isinstance(element, note.Note):
Notes.append(str(element.pitch))
elif isinstance(element, chord.Chord):
Notes.append('.'.join(str(n) for n in element.normalOrder))
except:
pass
with open('Note', 'a+')as f:
f.write(str(Notes))
return Notes先读取第一个文件测试看看,可以看到乐器是piano,C major调,4/4拍,还有Note和Chord的信息
保存之后,大概是这个样子的数据:
三、构建神经网络
本次神经网络使用LSTM网络(Longshort term memory),它基于普通RNN在隐藏层各神经单元中增加记忆单元,从而使时间序列上的记忆信息可控,每次在隐藏层各单元间传递时通过几个可控门(遗忘门、输入门、候选门、输出门),可以控制之前信息和当前信息的记忆和遗忘程度,从而使RNN网络具备了长期记忆功能。
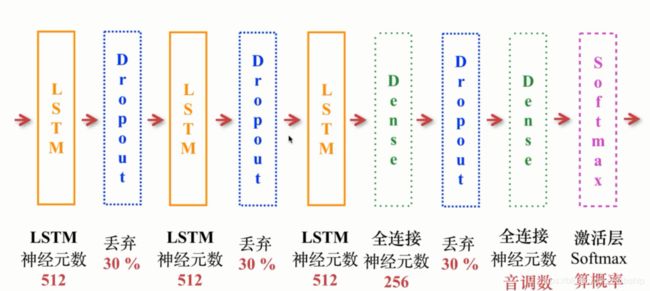
架构图:
def get_model(inputs, notes_len, weights_file=None):
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(512,input_shape=(inputs.shape[1], inputs.shape[2]),return_sequences=True))#512层神经元,return_sequences=True表示返回所有的输出序列
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3)) # 丢弃 30% 神经元,防止过拟合
model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(512, return_sequences=True))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(512)) # return_sequences 是默认的 False,只返回输出序列的最后一个
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(256)) # 256 个神经元的全连接层
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(notes_len)) # 输出的数目等于所有不重复的音调的数目
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop')
if weights_file is not None:
model.load_weights(weights_file)
return model
四、训练数据
def train():
notes=get_notes()
notes_len=len(set(notes))
note_name=sorted(set(i for i in notes))#获得排序的不重复的音符名字
sequence_length = 100 #序列长度
note_dict=dict((j,i) for i,j in enumerate(note_name))#设计一个字典,把音符转换成数字,方便训练
network_input = []#创建输入序列
network_output = []#创建输出序列
for i in range(0, len(notes) - sequence_length):
#输入100个,输出1个
sequence_in = notes[i: i + sequence_length]
sequence_out = notes[i + sequence_length]
network_input.append([note_dict[k] for k in sequence_in])
network_output.append(note_dict[sequence_out])
network_input = np.reshape(network_input, (len(network_input), sequence_length, 1))
network_input = network_input / float(notes_len) #归一化
network_output = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(network_output)#输出布尔矩阵,配合categorical_crossentropy 算法使用
model =get_model(network_input,notes_len)
filepath = "weights-{epoch:02d}-{loss:.2f}.hdf5"
checkpoint = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath,
monitor='loss', # 监控的对象是loss
verbose=0,
save_best_only=True,
mode='min' # 如果监控对象是val_acc则取max,是loss则取min
)
callbacks_list = [checkpoint]
model.fit(network_input, network_output, epochs=100, batch_size=128, callbacks=callbacks_list) #整体迭代100次,每小批128个
我用8G内存的windows电脑在跑,这个等待的时间不仅仅是漫长可以形容的,具体多久呢,跑一个epoch完整大概2小时,我设置跑100次epch,实在等不了了,最终跑了大概50次就暂停了。。。。。。。我现在batch_size是128,如果电脑可以,调高一些,速度会比较快。
五、生成音乐
def generate_notes(model, network_input, note_name, notes_len):
randindex = np.random.randint(0, len(network_input) - 1)
notedic = dict((i,j) for i, j in enumerate(note_name)) # 把刚才的整数还原成音调
pattern = network_input[randindex]
prediction = []
#随机生成1000个音符
for note_index in range(1000):
prediction_input = np.reshape(pattern, (1, len(pattern), 1))
prediction_input = prediction_input / float(notes_len)#归一化
prediction = model.predict(prediction_input, verbose=0)
index = np.argmax(prediction)
result = notedic[index]
prediction.append(result)
# 往后移动
pattern.append(index)
pattern = pattern[1:len(pattern)]
return prediction
#生成mid音乐
def create_music():
network_input, normal_network_input,notes_len,note_name=train()
#寻找loss最小的weight文件,作为训练参数
files = os.listdir()
minloss = {}
for i in files:
if 'weights' in i:
num = i[11:15]
minloss[num] = i
best_weights = minloss[min(minloss.keys())]
model = get_model(normal_network_input, notes_len,best_weights)
prediction = generate_notes(model, network_input, note_name, notes_len)
offset = 0
output_notes = []
# 生成 Note(音符)或 Chord(和弦)对象
for data in prediction:
if ('.' in data) or data.isdigit():
notes_in_chord = data.split('.')
notes = []
for current_note in notes_in_chord:
new_note = note.Note(int(current_note))
new_note.storedInstrument = instrument.Piano()
notes.append(new_note)
new_chord = chord.Chord(notes)
new_chord.offset = offset
output_notes.append(new_chord)
else:
new_note = note.Note(data)
new_note.offset = offset
new_note.storedInstrument = instrument.Piano()
output_notes.append(new_note)
offset += 1
# 创建音乐流(Stream)
midi_stream = stream.Stream(output_notes)
# 写入 MIDI 文件
midi_stream.write('midi', fp='output1.mid')经过漫长的等待,激动人心的时候到了,终于创造了第一手歌,打开QQ影音播放,听起来还是不错的
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import numpy as np
from music21 import converter, instrument, note, chord, stream
#读取训练数据的Notes
def get_notes():
filepath='D:/log/music_midi/'
files=os.listdir(filepath)
Notes=[]
for file in files:
try:
stream = converter.parse(filepath+file)
instru = instrument.partitionByInstrument(stream)
if instru: # 如果有乐器部分,取第一个乐器部分
notes = instru.parts[0].recurse()
else: #如果没有乐器部分,直接取note
notes = stream.flat.notes
for element in notes:
# 如果是 Note 类型,取音调
# 如果是 Chord 类型,取音调的序号,存int类型比较容易处理
if isinstance(element, note.Note):
Notes.append(str(element.pitch))
elif isinstance(element, chord.Chord):
Notes.append('.'.join(str(n) for n in element.normalOrder))
except:
pass
# with open('Note', 'a+')as f:
# f.write(str(Notes))
return Notes
#构建神经网络模型
def get_model(inputs, notes_len, weights_file=None):
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(512,input_shape=(inputs.shape[1], inputs.shape[2]),return_sequences=True))#512层神经元,return_sequences=True表示返回所有的输出序列
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3)) # 丢弃 30% 神经元,防止过拟合
model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(512, return_sequences=True))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(512)) # return_sequences 是默认的 False,只返回输出序列的最后一个
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(256)) # 256 个神经元的全连接层
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(notes_len)) # 输出的数目等于所有不重复的音调的数目
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop')
if weights_file is not None:
model.load_weights(weights_file)
return model
#训练模型
def train():
notes=get_notes()
notes_len=len(set(notes))
note_name=sorted(set(i for i in notes))#获得排序的不重复的音符名字
sequence_length = 100 #序列长度
note_dict=dict((j,i) for i,j in enumerate(note_name))#设计一个字典,把音符转换成数字,方便训练
network_input = []#创建输入序列
network_output = []#创建输出序列
for i in range(0, len(notes) - sequence_length):
#输入100个,输出1个
sequence_in = notes[i: i + sequence_length]
sequence_out = notes[i + sequence_length]
network_input.append([note_dict[k] for k in sequence_in])
network_output.append(note_dict[sequence_out])
network_input = np.reshape(network_input, (len(network_input), sequence_length, 1))
normal_network_input = network_input / float(notes_len) #归一化
network_output = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(network_output)#输出布尔矩阵,配合categorical_crossentropy 算法使用
model =get_model(normal_network_input,notes_len)
filepath = "weights-{epoch:02d}-{loss:.2f}.hdf5"
checkpoint = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath,
monitor='loss', # 监控的对象是loss
verbose=0,
save_best_only=True,
mode='min' # 如果监控对象是val_acc则取max,是loss则取min
)
callbacks_list = [checkpoint]
model.fit(normal_network_input, network_output, epochs=100, batch_size=128, callbacks=callbacks_list) #整体迭代100次,每小批128个
return network_input,normal_network_input,notes_len,note_name
#生成音符
def generate_notes(model, network_input, note_name, notes_len):
randindex = np.random.randint(0, len(network_input) - 1)
notedic = dict((i,j) for i, j in enumerate(note_name)) # 把刚才的整数还原成音调
pattern = list(network_input[randindex])#长度为100
predictions = []
#随机生成1000个音符
for note_index in range(1000):
#pattern = list(network_input[np.random.randint(0,500)])
prediction_input = np.reshape(pattern, (1, len(pattern), 1))
prediction_input = prediction_input / float(notes_len)#归一化
prediction = model.predict(prediction_input, verbose=0)#verbose = 0 为不在标准输出流输出日志信息
index = np.argmax(prediction)
#print(index)
result = notedic[index]
predictions.append(result)
# 往后移动
pattern.append(index)
pattern = pattern[1:len(pattern)]
return predictions
#生成mid音乐
def create_music():
notes=get_notes()
notes_len = len(set(notes))
note_name = sorted(set(i for i in notes))
sequence_length = 100 # 序列长度
note_dict = dict((j, i) for i, j in enumerate(note_name)) # 设计一个字典,把音符转换成数字,方便训练
network_input = [] # 创建输入序列
network_output = [] # 创建输出序列
for i in range(0, len(notes) - sequence_length):
# 输入100个,输出1个
sequence_in = notes[i: i + sequence_length]
sequence_out = notes[i + sequence_length]
network_input.append([note_dict[k] for k in sequence_in])
network_output.append(note_dict[sequence_out])
network_input = np.reshape(network_input, (len(network_input), sequence_length, 1))
normal_network_input = network_input / float(notes_len) # 归一化
#print(len(network_input)) #1541019
#network_input, normal_network_input,notes_len,note_name=train()
#寻找loss最小的weight文件,作为训练参数
files = os.listdir()
minloss = {}
for i in files:
if 'weights' in i:
num = i[11:15]
minloss[num] = i
best_weights = minloss[min(minloss.keys())]
print('最佳模型文件为:'+best_weights)
model = get_model(normal_network_input, notes_len,best_weights)
predictions = generate_notes(model, network_input, note_name, notes_len)
offset = 0
output_notes = []
# 生成 Note(音符)或 Chord(和弦)对象
for data in predictions:
if ('.' in data) or data.isdigit():
notes_in_chord = data.split('.')
notes = []
for current_note in notes_in_chord:
new_note = note.Note(int(current_note))
new_note.storedInstrument = instrument.Piano()
notes.append(new_note)
new_chord = chord.Chord(notes)
new_chord.offset = offset
output_notes.append(new_chord)
else:
new_note = note.Note(data)
new_note.offset = offset
new_note.storedInstrument = instrument.Piano()
output_notes.append(new_note)
offset += 1
# 创建音乐流(Stream)
midi_stream = stream.Stream(output_notes)
# 写入 MIDI 文件
midi_stream.write('midi', fp='output1.mid')
if __name__ == '__main__':
#train()#训练的时候执行
create_music()
参考文件:慕课网TensorFlow教程