spring boot实战(第六篇)加载application资源文件源码分析
前言
在上一篇中了解了spring配置资源的加载过程,本篇在此基础上学习spring boot如何默认加载application.xml等文件信息的。
ConfigFileApplicationListener
在 spring boot实战(第三篇)事件监听源码分析中可知在构造SpringApplication时加载相关的监听器,其中存在一个监听器ConfigFileApplicationListener,其定义如下:public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements
ApplicationListener, Ordered {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event);
}
}
} 监听 ApplicationEvent 事件,在触发所有其子类以及本身事件时会执行其onApplicationEvent方法。在执行
for (SpringApplicationRunListener runListener : runListeners) {
runListener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
Environment environment = event.getEnvironment();
if (environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment,
event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
在上一篇中可以知道enviroment为StandardServletEnvironment实例,因此执行
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
方法
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
bindToSpringApplication(environment, application);
}protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
try {
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to load configuration files", ex);
}
}
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment)
将随机方法放入到PropertySources中
public static void addToEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
environment.getPropertySources().addAfter(
StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new RandomValuePropertySource("random"));
logger.trace("RandomValuePropertySource add to Environment");
}如何从Random中获取值是需要看getProperty方法:
public Object getProperty(String name) {
if (!name.startsWith("random.")) {
return null;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Generating random property for '" + name + "'");
}
if (name.endsWith("int")) {
return getSource().nextInt();
}
if (name.startsWith("random.long")) {
return getSource().nextLong();
}
if (name.startsWith("random.int") && name.length() > "random.int".length() + 1) {
String range = name.substring("random.int".length() + 1);
range = range.substring(0, range.length() - 1);
return getNextInRange(range);
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[32];
getSource().nextBytes(bytes);
return DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(bytes);
}其中的getSource()表示Random类。
接下来看
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load()
看load方法
public void load() throws IOException {
...//处理profiles信息
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
String profile = this.profiles.poll();
for (String location : getSearchLocations()) {
if (!location.endsWith("/")) {
// location is a filename already, so don't search for more
// filenames
load(location, null, profile);
}
else {
for (String name : getSearchNames()) {
load(location, name, profile);
}
}
}
}
addConfigurationProperties(this.propertiesLoader.getPropertySources());
}看getSearchLocations()方法
private Set getSearchLocations() {
Set locations = new LinkedHashSet();
// User-configured settings take precedence, so we do them first
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY)) {
for (String path : asResolvedSet(
this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY), null)) {
if (!path.contains("$")) {
if (!path.contains(":")) {
path = "file:" + path;
}
path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
}
locations.add(path);
}
}
locations.addAll(asResolvedSet(
ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.searchLocations,
DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS));
return locations;
} 首先看CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY(spring.config.location)是否存在配置,无则走默认配置路径DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS(classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/)
继续来看
getSearchNames()
方法
private Set getSearchNames() {
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY)) {
return asResolvedSet(this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY),
null);
}
return asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.names, DEFAULT_NAMES);
}
解析完路径和配置文件名以后,将开始判断路径+名称组合是否存在 执行load(...)方法
private void load(String location, String name, String profile)
throws IOException {
String group = "profile=" + (profile == null ? "" : profile);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
// Try to load directly from the location
loadIntoGroup(group, location, profile);
}
else {
// Search for a file with the given name
for (String ext : this.propertiesLoader.getAllFileExtensions()) {
if (profile != null) {
// Try the profile specific file
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-" + profile + "." + ext,
null);
// Sometimes people put "spring.profiles: dev" in
// application-dev.yml (gh-340). Arguably we should try and error
// out on that, but we can be kind and load it anyway.
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-" + profile + "." + ext,
profile);
}
// Also try the profile specific section (if any) of the normal file
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "." + ext, profile);
}
}
}public Set getAllFileExtensions() {
Set fileExtensions = new HashSet();
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.loaders) {
fileExtensions.addAll(Arrays.asList(loader.getFileExtensions()));
}
return fileExtensions;
} loader.getFileExtensions() 获取所有支持的文件后缀,其中loader在执行load方法时实例化
public void load() throws IOException {
this.propertiesLoader = new PropertySourcesLoader();
...} public PropertySourcesLoader(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
Assert.notNull(propertySources, "PropertySources must not be null");
this.propertySources = propertySources;
this.loaders = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(PropertySourceLoader.class,
null);
}
可以看出
this.loaders是由
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(PropertySourceLoader.class,
null)
得到
public static List loadFactories(Class factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryClass, "'factoryClass' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
List factoryNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryClass, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryClass.getName() + "] names: " + factoryNames);
}
List result = new ArrayList(factoryNames.size());
for (String factoryName : factoryNames) {
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryName, factoryClass, classLoaderToUse));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
} 加载META-INF/spring.factories文件下对应内容
# PropertySource Loaders
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader- PropertiesPropertySourceLoader 支持文件后缀格式 "properties","xml"
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return new String[] { "properties", "xml" };
}- YamlPropertySourceLoader 支持文件后缀格式 "yml","yaml"
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return new String[] { "yml", "yaml" };
}两者覆写的load方法实现如何处理资源为PropertySource对象。
获取完文件后缀后调用loadIntoGroup方法将资源信息转化为PropertySource,其实质为调用PropertySourcesLoader中load方法
private PropertySource loadIntoGroup(String identifier, String location,
String profile) throws IOException {
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
PropertySource propertySource = null;
if (resource != null) {
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + location + "]";
String group = "applicationConfig: [" + identifier + "]";
propertySource = this.propertiesLoader.load(resource, group, name,
profile);
if (propertySource != null) {
maybeActivateProfiles(propertySource
.getProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY));
addIncludeProfiles(propertySource
.getProperty(INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY));
}
}
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
msg.append(propertySource == null ? "Skipped " : "Loaded ");
msg.append("config file ");
msg.append("'").append(location).append("'");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(profile)) {
msg.append(" for profile" + profile);
}
if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) {
msg.append(" resource not found");
}
this.debug.add(msg);
return propertySource;
}最后调用addConfigurationProperties( this. propertiesLoader.getPropertySources())方法将解析过后的资源信息放置进Enviroment中propertySources属性集合中
private void addConfigurationProperties(MutablePropertySources sources) {
List> reorderedSources = new ArrayList>();
for (PropertySource item : sources) {
reorderedSources.add(item);
}
// Maybe we should add before the DEFAULT_PROPERTIES if it exists?
this.environment.getPropertySources().addLast(
new ConfigurationPropertySources(reorderedSources));
} 至此 application.xml等文件的加载分析结束。
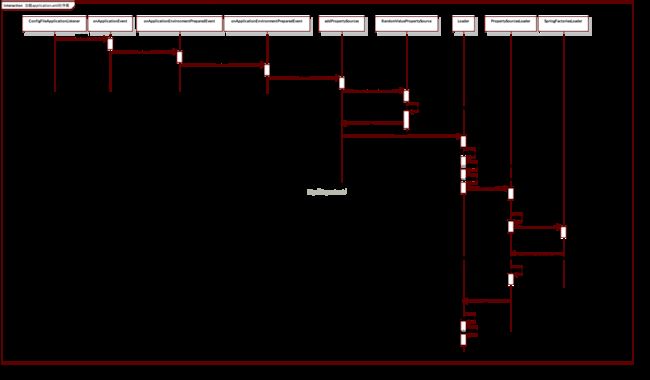
时序图
简单的画了一下时序图,可能和实际调用存在出入,仅作参考使用
转载请注明
http://blog.csdn.net/liaokailin/article/details/48186331
http://blog.csdn.net/liaokailin/article/details/48186331