图像融合方法分类
low level (pixel) mide level (feature) high level (symbolic, image)
- transform fusion
- spatial fusion: fusion rules are directly applied to image pixels or image regions. 空域融合进一步分为:(1)block (2)segmentation based (3) gradient based
according to lishutao 2017
1 multiscale decomposition
2 sparse representation based
3 other transforms like pca ida
4 combination of different transforms
图像融合常见问题
artifact 人工产品,指融合后图像不自然
halo artifact; halo 指光晕 halo artifact near some edges
contras decrease
reduction of sharpness
评价指标 object quality metric
参考文献: zheng liu 等 Objective Assessment of Multiresolution Image Fusion Algorithms for Context Enhancement
in Night Vision: A Comparative Study TPAMI 2012
- information theory based ones
1 Normalized Mutual Information Q
MI
G. Qu, D. Zhang, and P. Yan, “Information Measure for
Performance of Image Fusion,” Electronics Letters, vol. 38, no. 7,
pp. 313-315, 2002.
M. Hossny, S. Nahavandi, and D. Vreighton, “Comments on Information Measure for Performance of Image Fusion’,” Electronics Letters, vol. 44, no. 18, pp. 1066-1067, Aug. 2008.
2 Tsallis Entropy QTE
R. Nava, G. Cristo´ bal, and B. Escalante-Ramı´rez, “Mutual Information Improves Image Fusion Quality Assessments,” SPIE
News Room, http://spie.org/documents/Newsroom/Imported/0824/0824-2007-08-30.pdf, Sept. 2007.
3 Nonlinear Correlation Information Eentropy Q
NCIE
Q. Wang, Y. Shen, and J. Jin, “Performance Evaluation of Image Fusion Techniques,” Image Fusion: Algorithms and Applications,ch. 19, T. Stathaki, ed., pp. 469-492. Elsevier, 2008.
4 Gradient based fusion performance QG [a.k.a, QAB/F]
C.S. Xydeas and V. Petrovic, “Objective Image Fusion Performance Measure,” Electronics Letters, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 308-309, 2000.
5 based on a multiscale frame Q
M
P. Wang and B. Liu, “A Novel Image Fusion Metric Based on Multi-Scale Analysis,” Proc. IEEE Int’l Conf. Signal Processing,
pp. 965-968, 2008.
6 based on Spatial Frenquency QSF
Y. Zheng, E.A. Essock, B.C. Hansen, and A.M. Haun, “A New Metric Based on Extended Spatial Frequency and Its Application
to DWT Based Fusion Algorithms,” Information Fusion, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 177-192, Apr. 2007.
7 based on Phase congruency QP
J. Zhao, R. Laganiere, and Z. Liu, “Performance Assessment of Combinative Pixel-Level Image Fusion Based on an Absolute Feature Measurement,” Int’l J. Innovative Computing, Information and Control, vol. 3, no. 6(A), pp. 1433-1447, Dec. 2007
- image structure similarity based
8 Piella's metric QP
G. Piella and H. Heijmans, “A New Quality Metric for Image Fusion,” Proc. Int’l Conf. Image Processing, 2003.
9 Cvejie's metric QC
N. Cvejic, A. Loza, D. Bul, and N. Canagarajah, “A Similarity Metric for Assessment of Image Fusion Algorithms,” Int’l J. Signal
Processing, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 178-182, 2005.
10 Yang's metric QY
C. Yang, J. Zhang, X. Wang, and X. Liu, “A Novel Similarity BasedQuality Metric for Image Fusion,” Information Fusion, vol. 9,
pp. 156-160, 2008.
11 Chen-Varshney metric QCV
H. Chen and P.K. Varshney, “A Human Perception Inspired Quality Metric for Image Fusion Based on Regional Information,”
Information Fusion, vol. 8, pp. 193-207, 2007.
12 Y.Chen R.S.Blum QCB [a.k.a QHVS]
Y. Chen and R. Blum, “A new automated quality assessment algorithm for image fusion,” Image Vis. Comput., vol. 27, no. 10, pp. 1421–1432,
2009.
该综述性评价文章发表于12年,此后还有别的方法。
13 Visual Information Fidility Fusion metric VIFF
Y. Han, Y. Cai, Y. Cao, and X. Xu, “A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity,” Inf. Fusion, vol. 14, pp. 127–135, 2013.
For most existing fusion methods, either in spatial domain or transform domain, the activity level measurement is essentially implemented by designing local filters to extract high-frequency details. On one hand, for most transform domain fusion methods, the images or image patches are represented using a set of predesigned bases such as wavelet or trained dictionary atoms. From the view of image processing, this is generally equivalent to convolving them with those bases . For example, the implementation of discrete wavelet transform is exactly based on filtering. On the other hand, for spatial domain fusion methods, the situation is even clearer that so many activity level measurements are based on high-pass spatial filtering. Furthermore, the fusion rule, which is usually interpreted as the weight assignment strategy for different source images based on the calculated activity level measures can be transformed into a filtering-based form as well (个人理解: activitity level measurement 或许等同于 image clarity measure, focus measure 常用方法有 energy of laplacian 以及 spatial frequency)
应用领域
数字成像(digital phtotgrapyh),主要包括 multi focus multi exposure
多模态融合(multi modality imaging)主要包括,medical image fusion, visible /infrared image fusion
遥感图像(remote sensing) 例如 MS PAN , MS HS
深度模型
CNN
CSR (convolutional sparse representation)
SAE(stack autoencoder)
概念
CNN 能够 multistage/ hierarchical representation 网络结构 architecture
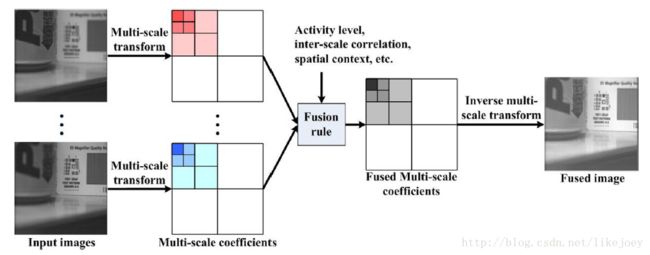
图1 传统模型, 基于多尺度变换的图像融合

图2 传统模型 ,基于稀疏表示的图像融合
以下图标来自 yu liu 等发表于information fusion 的文章:







