链表是线性表的一种。线性表是最基本、最简单、也是最常用的一种数据结构。
线性表中数据元素之间的关系是一对一的关系,即除了第一个和最后一个数据元素之外,其它数据元素都是首尾相接的。
线性表有两种存储方式:
- 顺序存储结构
- 链式存储结构
我们常用的数组就是一种典型的顺序存储结构。
在存储一大波数据的时候,我们通常是使用数组来进行存储,但是有的时候数组会显得不够灵活
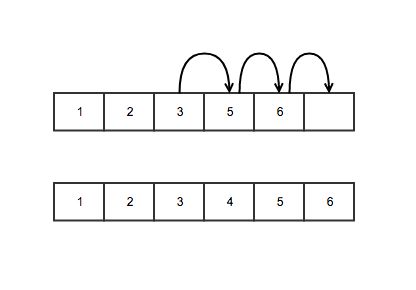
比如,现在有 [1, 2, 3, 5, 6] 这样一个数组,如果要在数字 3 的后面添加一个数字 4, 那就需要将数字 3 后面的所有数字都进行移动才可以插入数字 4,如图
这样操作显然很浪费时间
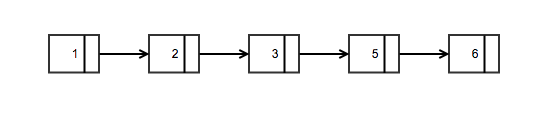
相反,链式存储结构就是两个相邻的元素在内存中可能不是相邻的,每一个元素都有一个指针域,指针域一般是存储着到下一个元素的指针。
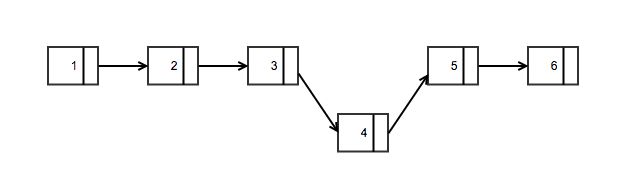
此时如果在数字 3 和数字 5 中间插入一个数字 4,链表的操作如下图所示
链式存储方式的优点是
插入和删除的时间复杂度为 O(1),不会浪费太多内存,添加元素的时候才会申请内存,删除元素会释放内存。
缺点是访问的时间复杂度最坏为 O(n)
顺序表的特性是随机读取,也就是访问一个元素的时间复杂度是O(1)
链式表的特性是插入和删除的时间复杂度为O(1)
链表就是链式存储的线性表。根据指针域的不同,链表分为单向链表、双向链表、循环链表等等。
链表是一种非常基础的数据结构。在链表中的每个节点都包含其数据内容以及一个指向下一个元素的指针。我们可以通过这些指针来遍历链表。
以下代码使用 Kotlin 编写
单链表
单链表顾名思义就是一个链式数据结构,它有一个表头,并且除了最后一个节点外,所有节点都有其后继节点。如下图。
链表节点
首先,我写出链表节点的类。单链表中的每一个节点,都保存其数据域和后驱指针。
class Node (value: T){
val data = value
var next: Node? = null
}
单例表实现
节点出来以后,现将 LinkedList 的基本框架搭建出来,其中包括单链表的初始化函数,单链表的节点访问及修改和单链表的节点插入与删除。
public class LinkedList {
class Node {
T data;
Node next;
Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node header;
public LinkedList(List list) {
}
public int size() {
return 0;
}
public void setData(int index, T data) {
}
public T getData(int index) {
return null;
}
public void insert(int index, T data) {
}
public T delete(int index) {
}
public void clear() {
}
public void isEmpty() {
}
}
框架搭建完成之后,首先是初始化一个链表,传入一个 list 并将其所有元素依次串联成一个链表。 注意,链表对象并不持有所有对象,它只保存了表头。
public LinkedList(List list) {
if (null == list || list.size() == 0) {
return;
}
header = new Node(list.get(0));
Node pointer = header;
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { // index 从 1 开始,因为 0 的 data 已经赋予了 header
pointer.next = new Node(list.get(i));
pointer = pointer.next; // 将指针由 header 移到 next
}
}
想要知道链表有多长,只能是对当前链表进行遍历,时间复杂对为 O(n)
public int size() {
int length = 0;
if (null != header) {
Node pointer = header;
while (null != pointer) {
pointer = pointer.next; // 指针按照链表依次移到
length++;
}
}
return length;
}
如果想要索引链表中的某个元素,还是需要一个个的遍历过去,因为链表只保留了第一个元素的引用。
public void setData(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size() || null == data) {
return;
}
if (index == 0) {
header = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node pointer = header;
int currentIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex < index) {
pointer = pointer.next; // 指针按照链表依次移到
currentIndex++;
}
pointer.data = data;
}
public T getData(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size() || null == header) {
return null;
}
Node pointer = header;
int currentIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex < index) {
pointer = pointer.next;
currentIndex++;
}
return pointer.data;
}
链表中还有两个特别重要的方法,插入和删除。插入需要找到插入的位置,把前一个元素的 next 指针指向被插入的节点,并将被插入节点的 next 指针指向后一个节点,如下图左侧所示。而删除则是把前一个节点的 next 指针指向后一个节点,并返回被删除元素的数据内容,如下图右侧所示。
[图片上传失败...(image-8f71c7-1513179298327)]
public void insert(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size() || null == header || null == data) {
return;
}
if (index == 0) {
header = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node currentPointer = header;
Node prevPointer;
int currentIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex < index) {
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentPointer = currentPointer.next;
currentIndex++;
if (currentIndex == index) {
// 把前一个元素的 next 指针指向被插入的节点,并将被插入节点的 next 指针指向后一个节点
Node insertNode = new Node(data);
prevPointer.next = insertNode;
insertNode.next = currentPointer;
}
}
}
public T delete(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size() || null == header) {
return null;
}
if (index == 0) {
T result = header.data;
header = header.next;
return result;
}
Node currentPointer = header;
Node prevPointer;
int currentIndex = 0;
T data = null;
while (currentIndex < index) {
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentPointer = currentPointer.next;
currentIndex++;
if (currentIndex == index) {
// 把前一个节点的 next 指针指向后一个节点,并返回被删除元素的数据内容
data = currentPointer.data;
prevPointer.next = currentPointer.next;
}
}
return data;
}
以上就是单链表数据结构的简单实现
注意: 链表对象并不持有所有元素,它只保存了表头。
双向链表
双向链表和单链表不同之处在于,链表中的每一个节点,都保存其数据域和前/后驱指针。这就意味着如果你想删除链表的最后一个元素,你不需要从表头开始遍历到最后一个元素了。你可以直接从表尾开始直接删除这个元素。显然,双向链表在效率上要高于单链表,不过其数据结构更复杂,占用了更多的空间。
[图片上传失败...(image-a0a60c-1513179298327)]
还是先来定义节点类。包含数据以及 prev & next 两个指针
class Node {
T data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
整个双链表的整体框架如下所示
public class RoundLinkedList {
class Node {
T data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public RoundLinkedList(List list) {
}
public int size() {
return 0;
}
public T getData(int index) {
return null;
}
public void setData(int index, T data) {
}
public void insert(int index, T data) {
}
public T delete(int index) {
return null;
}
}
我们写出初始化函数,我们可以读入一个数组并将其生成一个链表,注意双端链表要从头到尾从尾到头都可以查找。
public RoundLinkedList(List list) {
if (null == list) {
return;
}
int size = list.size();
if (size == 1) {
head = new Node(list.get(0));
tail = head;
return;
}
// 初始化首&末节点
head = new Node(list.get(0));
tail = new Node(list.get(size - 1));
Node pointer = head;
for (int i = 1; i < size - 1; i++) { // 排除 index 为 0 和 size - 1 的情况
Node node = new Node(list.get(0));
pointer.next = node; // 当前节点指向下个节点
node.prev = pointer; // 下一个节点指回上一个节点
pointer = node; // 移动指针从当前节点到下一个节点
}
// 连接末节点
pointer.next = tail;
tail.prev = pointer;
}
主要需要注意的是插入和删除,我们需要判断插入位置是靠近头还是尾。 如果靠近头,我们就从头开始遍历找到操作位置,否则就从尾部开始遍历
public void insert(int index, T data) {
if (null == data) {
return;
}
Node node = null;
if (null == head && index == 0) {
node = new Node(data);
head = node;
tail = head;
return;
}
// 在头部插入
if (index == 0) {
node = new Node(data);
head.prev = node;
head = node;
return;
}
// 在尾部出入
if (index == size()) {
node = new Node(data);
tail.next = node;
node.prev = tail;
tail = node;
return;
}
Node currentPointer;
Node prevPointer;
int currentIndex = 0;
// 靠近头部,从头开始
if (index <= size() / 2) {
currentPointer = head;
prevPointer = currentPointer;
while (currentIndex < index) {
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentPointer = currentPointer.next;
currentIndex++;
}
node = new Node(data);
prevPointer.next = node;
node.prev = prevPointer;
node.next = currentPointer;
currentPointer.prev = node;
return;
}
// 靠近尾部,从尾开始
if (index > size() / 2) {
currentPointer = tail;
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentIndex = size();
while (index < currentIndex) {
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentPointer = currentPointer.prev;
currentIndex--;
}
node = new Node(data);
currentPointer.next = node;
node.prev = currentPointer;
node.next = prevPointer;
prevPointer.prev = node;
}
}
public T delete(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
return null;
}
T data = null;
// 删除链表头
if (index == 0) {
data = head.data;
head = head.next;
}
// 删除链表尾
if (index == size() - 1) {
data = tail.data;
tail = tail.prev;
}
Node currentPointer;
Node prevPointer;
int currentIndex = 0;
// 删除靠近头部的元素
if (index <= size() / 2) {
currentPointer = head;
prevPointer = currentPointer;
while (currentIndex < index) {
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentPointer = currentPointer.next;
currentIndex++;
}
data = currentPointer.data;
prevPointer.next = currentPointer.next;
currentPointer.next.prev = prevPointer;
}
// 删除靠近尾部的元素
if (index > size() / 2) {
currentPointer = tail;
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentIndex = size() - 1;
while (index < currentIndex) {
prevPointer = currentPointer;
currentPointer = currentPointer.prev;
currentIndex--;
}
data = currentPointer.data;
prevPointer.prev = currentPointer.prev;
currentPointer.prev.next = prevPointer;
}
return data;
}
LeetCode 实战
检查链表中是否有环
题目来源
题目分析: 我们可以用两个指针从表头开始,一快一慢的遍历链表,快的一次走两步,慢的一次走一步。如果单链表有环,则不存在表尾(所有节点都有后继节点),当指针进入环后,将在环里面一直转,两个指针由于一快一慢,快的指针必然会在某一个时刻”追上”慢的指针,两个指针达到同一个点。如下图中,快慢两个指针将在 5-10 这几个节点形成的环中进行追击,直到相遇。所以,如果两个指针在出发后可以到达同一节点,我们就可以判断这个链表有环。
[图片上传失败...(image-9a916d-1513179298327)]
假设该链表中存在环,并且设慢指针走过的路程为 K, 环的长度为 R, 则可以得出公式 2K - K = nR, K = nR (n 为走过的环的圈数), 现在设链表的头节点到环开始节点之间的距离为 X, 而链表头节点到快慢两指针第一次相遇节点之间的距离,也就是慢指针所走过的距离为 K, 设快慢两指针第一次相遇节点到环开始节点的距离为 M, 则可以得出等式 X = K - (R - M) = nR - R + M = (n - 1)R + M, 取 n = 1, 则链表头节点到环开始节点的距离等于快慢两指针第一次相遇节点到环开始节点的距离。
以下为相关代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (null == head || null == head.next) {
return null;
}
boolean isCycle = false;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && slow != null) {
fast = fast.next; // fast 领先走一步
if (null == fast) { // 链表走到了头,说明不存在环
return null;
}
// fast 和 slow 各自走一步,但 fast 每次比 slow 多一步
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) { // fast 最终与 slow 相遇说明存在环
isCycle = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isCycle) {
return null;
}
// 链表头节点到环开始节点的距离等于快慢两指针第一次相遇节点到环开始节点的距离
while (head != slow) {
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return head;
}
}
删除当前节点
题目来源
题目分析: 从前面的小节中我们已经得知,想要删除一个节点,需要把这个节点前驱节点的 next 指针知道其后面的节点。但是如下图,我们要删除 "hello" 节点,却不知道它的前驱节点的。笨办法是从链表头开始遍历找到待删除的节点。好的办法是,我们把当前节点的后继节点的数据域复制到当前节点,然后删掉后继节点。还是以下图为例,我们把第二个节点的数据域复制到第一个节点,然后删除第二个节点。
[图片上传失败...(image-438de7-1513179298327)]
以下是相关代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val; // 将下一个节点的值赋予此节点
node.next = node.next.next; // 将此节点连向下一个节点的下一个节点
}
}
删除从尾部数起第 N 个节点
题目来源
题目分析: 我们没有办法从尾部开始遍历单链表,而且我们也不知道单链表的长度(除非我们遍历一次)。一个比较取巧的方法是用两个指针指向表头,一个先走 n 步,然后两个指针一起出发,当前面那个指针到达表尾的时候,后面那个指针正好处在待删除节点的前驱节点。下面就很简单啦。
以下图为例,我们想删除链表的倒数第二个节点。首先在表头设定两个指针 p1,p2,并让 p2 先走两步,然后两个指针一同出发直到 p2 到达表尾。然后删除p1的后继节点(就是倒数第二个节点)。
[图片上传失败...(image-aaa72b-1513179298327)]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if (null == head) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
int index = 0;
while (index < n) { // fast 与 slow 间隔 n 步
fast = fast.next;
index++;
}
if (null == fast) {
return head.next;
}
// 当前面那个指针到达表尾的时候,后面那个指针正好处在待删除节点的前驱节点
while (null != fast.next) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
}
}
参考
- 链表
- [数据结构与算法/leetcode/lintcode题解](https://www.kancloud.cn/kancloud/data-structure-and-algorithm-note