源码学习 | Spring Boot启动流程详解
原文章是基于
Spring Boot 1.3.3版本进行分析的,本文基于原文章在Spring Boot 2.0.2版本进行分析并将原作者没有分析完成的部分继续下去。欢迎大家批评指正。参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/xinzhao/p/5551828.html。
环境介绍
本文基于Spring Boot版本2.0.2, 使用了spring-boot-starter-web。
配置完成后,编写了代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
@RestController
public class RootController {
public static final String PATH_ROOT = "/";
@RequestMapping(PATH_ROOT)
public String welcome() {
return "Welcome!";
}
}
虽然只有几行代码,但是这已经是一个完整的 Web 程序,当访问 url 的 path 部分为 “/” 时,返回字符串 “Welcome!”。
首先是一个非常普通的 java 程序入口,一个符合约定的静态 main 方法。在这个 main 方法中,调用了SpringApplication的静态run方法,并将 DemoApplication 类对象和 main 方法的参数 args 作为参数传递了进去。
然后是一个使用了两个 Spring 注解的 RootController 类,我们在 main 方法中,没有直接使用这个类。
SpringApplication类的静态 run 方法
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
// 参数对应的就是DemoApplication.class以及main方法中的args
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource,
String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
// 最终运行的这个重载方法(它实际上会构造一个SpringApplication 的实例,然后运行它的run方法)
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
在这个静态方法中,创建SpringApplication对象,并调用该对象的run方法。
构造SpringApplication对象
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 为成员变量primarySources赋值
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
构造函数中调用了另一个重载方法,初始化 SpringApplication 对象的成员变量 primarySources,webApplicationType,initializers,listeners,mainApplicationClass。primarySources 的赋值比较简单,就是我们传给 SpringApplication.run方法的参数。剩下的几个,我们依次来看看是怎么做的。
webEnvironment:推断应用类型是 Standard 还是 Web
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
private WebApplicationType webApplicationType;
// 相关常量
private static final String REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet", "org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
...
}
private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
可能会出现三种结果:
- WebApplicationType.REACTIVE:当类路径中存在 REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS 并且不存在 MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS 时
- WebApplicationType.NONE:也就是非 Web 型应用(Standard型),此时类路径中不包含 WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES 中定义的任何一个类时
- WebApplicationType.SERVLET:类路径中包含了 WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES 中定义的所有类型时
在本文的例子中 webApplicationType 的值为 SERVLET。
initializers:设置初始化器
initializers 成员变量,是一个 ApplicationContextInitializer 类型对象的集合。 顾名思义,ApplicationContextInitializer 是一个可以用来初始化 ApplicationContext 的接口。
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
private List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers;
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
...
}
public void setInitializers(
Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) {
this.initializers = new ArrayList<>();
this.initializers.addAll(initializers);
}
可以看到,关键是调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class),来获取ApplicationContextInitializer 类型对象的列表。
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
// 这里的入参type就是ApplicationContextInitializer.class
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 使用Set保存names来避免重复元素
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 根据names来进行实例化
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
// 对实例进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
在该方法中主要做了两件事:
- 首先通过调用
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)来获取所有 Spring Factories 的名字; - 然后调用
createSpringFactoriesInstances方法根据读取到的名字创建对象。最后会将创建好的对象列表排序并返回。
第一件事
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue()));
result.addAll((String) entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames);
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
可以看到,是从一个名字叫 spring.factories的资源文件中,读取 key 为org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的 value。而 spring.factories 的部分内容如下:
以下内容摘自spring-boot-2.0.2.RELEASE.jar中的资源文件META-INF/spring.factories
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
可以看到,最先得到的是ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer这四个类的名字。
第二件事
接下来会调用createSpringFactoriesInstances来创建ApplicationContextInitializer实例。
// 关键参数:
// type: org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer.class
// names: 上一步得到的names集合
// parameterTypes:为一个空的Class集合(new Class[] {})
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
// 加载类
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
// 获取默认的构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass
.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
// 使用默认的构造方法实例化类
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
初始化步骤很直观,没什么好说的,类加载,然后就是得到构造器进行初始化,最后放入到实例列表中。所以在我们的例子中,SpringApplication对象的成员变量 initalizers 就被初始化为,ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer 这四个类的对象组成的 list。
下图画出了加载的ApplicationContextInitializer,并说明了他们的作用。至于何时应用他们,且听后面慢慢分解。

listeners:设置监听器
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
private List<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
// 为成员变量 listeners 赋值
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
...
}
public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) {
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>();
this.listeners.addAll(listeners);
}
listeners 成员变量,是一个 ApplicationListener 类型对象的集合。可以看到获取该成员变量内容使用的是跟成员变量initializers 一样的方法,只不过传入的类型从 ApplicationContextInitializer.class 变成了 ApplicationListener.class 。
看一下 spring.factories 中的相关内容:
以下内容摘自spring-boot-2.0.2.RELEASE.jar中的资源文件META-INF/spring.factories
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
也就是说,在我们的例子中,listener 最终会被初始化为ClearCachesApplicationListener,ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,FileEncodingApplicationListener,AnsiOutputApplicationListener,ConfigFileApplicationListener,DelegatingApplicationListener,ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,LoggingApplicationListener,LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener这几个类的对象组成的 list。
下图画出了加载的ApplicationListener,并说明了他们的作用。至于他们何时会被触发,等事件出现时,我们再说明。
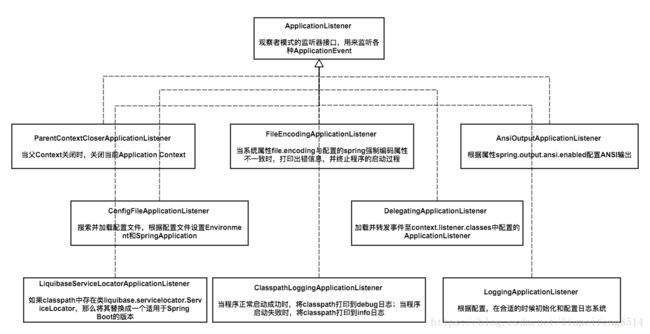
mainApplicationClass:推断应用入口类
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
private Class<?> mainApplicationClass;
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
// 为成员变量mainApplicationClass赋值
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
...
}
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
它通过构造一个运行时异常,通过异常栈中方法名为 main 的栈帧来得到入口类的名字。在我们的例子中mainApplicationClass 即是我们自己编写的 Application 类。
至此,对于 SpringApplication 实例的初始化过程就结束了。
SpringApplication对象的run方法
经过上面的初始化过程,我们已经有了一个 SpringApplication 对象,根据 SpringApplication 类的静态 run 方法一节中的分析,接下来会调用 SpringApplication 对象的 run 方法。我们接下来就分析这个对象的 run 方法。
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 计时工具
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 设置java.awt.headless系统属性为true - 没有图形化界面
configureHeadlessProperty();
// KEY 1 - 获取SpringApplicationRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 发出开始执行的事件
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// KEY 2 - 根据SpringApplicationRunListeners以及参数来准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 准备Banner打印器 - 就是启动Spring Boot的时候打印在console上的ASCII艺术字体
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// KEY 3 - 创建Spring上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
// 准备异常报告器
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// KEY 4 - Spring上下文前置处理
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
// KEY 5 - Spring上下文刷新
refreshContext(context);
// KEY 6 - Spring上下文后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 停止计时器
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 发出结束执行的事件
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
这个 run 方法包含的内容也是有点多的,根据上面列举出的关键步骤逐个进行分析。
SpringApplicationRunListeners
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
...
}
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
run 方法中,加载了一系列 SpringApplicationRunListener 对象。可以看到,加载 SpringApplicationRunListener 时,使用的是跟加载 ApplicationContextInitializer 和 ApplicationListener 时一样的方法。那么加载了什么,就可以从spring.factories文件中看到了:
以下内容摘自spring-boot-2.0.2.RELEASE.jar中的资源文件META-INF/spring.factories
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
可以看到,在我们的例子中加载的是 org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener。我们看一看这个 SpringApplicationRunListener 究竟做了点什么工作了?
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(
new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
this.application, this.args, environment));
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
...
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(
new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
@Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(
new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
......
......
}
EventPublishingRunListener 在对象初始化时,将 SpringApplication 对象的成员变量 listeners 全都保存下来,然后在自己的 public 方法被调用时,发布相应的事件,或执行相应的操作。可以说这个 RunListener 是在 SpringApplication 对象的 run 方法执行到不同的阶段时,发布相应的 event 给 SpringApplication 对象的成员变量 listeners 中记录的事件监听器。
下图画出了 SpringApplicationRunListeners 相关的类结构,虽然我们的例子中只有一个 SpringApplicationRunListener ,但在这样的设计下,想要扩展是非常容易的!

接下来,我们看一下在调用 listeners 的 starting 方法。在我们的例子中,也就是发布了 ApplicationStartingEvent 时,我们已经加载的事件监听器都做了什么操作。至于其它事件的发布,我们按照代码执行的顺序在后面的章节在介绍。
以下是监听 ApplicationStartingEvent 事件的监听器类:
- LoggingApplicationListener
- BackgroundPreinitializer:实现了ApplicationListener接口
- LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener:会检查classpath中是否有liquibase.servicelocator.ServiceLocator并做相应操作;
LoggingApplicationListener
监听ApplicationStartingEvent ,会根据 classpath 中的类情况创建相应的日志系统对象,并执行一些初始化之前的操作。
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent) {
onApplicationStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event);
}
...
}
private void onApplicationStartingEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
this.loggingSystem = LoggingSystem
.get(event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
this.loggingSystem.beforeInitialize();
}
我们的例子中,创建的是 org.springframework.boot.logging.logback.LogbackLoggingSystem 类的对象,Logback是 SpringBoot 默认采用的日志系统。下图画出了 SpringBoot 中的日志系统体系:
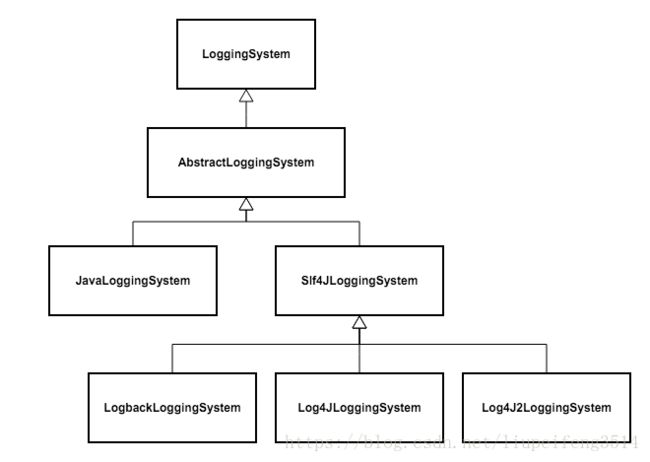
BackgroundPreinitializer:实现了ApplicationListener接口
监听ApplicationStartingEvent ,会启动一个后台线程完成一些耗时的初始化。
以下代码摘自:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(SpringApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent
&& preinitializationStarted.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
performPreinitialization();
}
...
}
private void performPreinitialization() {
try {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
runSafely(new ConversionServiceInitializer());
runSafely(new ValidationInitializer());
runSafely(new MessageConverterInitializer());
runSafely(new MBeanFactoryInitializer());
runSafely(new JacksonInitializer());
runSafely(new CharsetInitializer());
preinitializationComplete.countDown();
}
public void runSafely(Runnable runnable) {
try {
runnable.run();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
}, "background-preinit");
thread.start();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
...
}
}