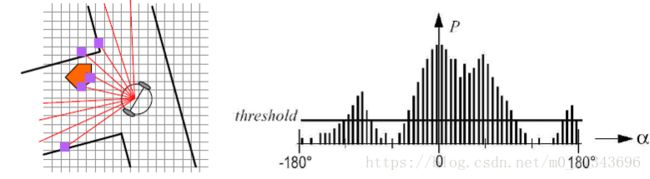
向量场直方图算法(VHF)
矢量场直方图算法(VFH)
环境用网格表示(二维信息)
每个单元赋值表示该单元有障碍的可能性
在每一步环境信息转化为1维直方图
引入代价函数值G,为所有可以通过的方向赋值
选择具有最小代价函数值G的方向
G=a·目标方向+b ·轮转动角度+c ·原运动方向
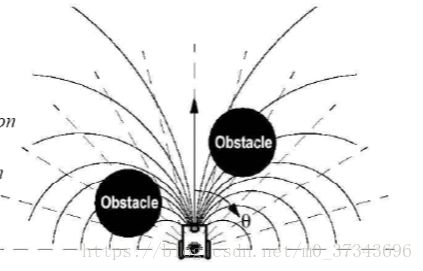
VFH+
用简单形式考虑机器人可行轨迹(动力学约束下)
机器人运动轨迹为弧形
挡住某方向的障碍物,阻止所有通过该方向上的轨迹弧线
VFH+代码
记得这里有个问题就是要先有地图,我忘了传了,不然运行会报错的!!
%%% VFH+算法 考虑机器人宽度
%function h=vfh4(obstacle,startpoint,endpoint)
clc;
clear;
%load obstacle 'obstacle';
%load startpoint 'startpoint';
ob=imread('map3.bmp');
% ob=edge(ob,'sobel');
%imshow(ob);
z=ones(20,20);
ob=imdilate(ob,z);
ob=edge(ob,'sobel');
imshow(ob);
s=ob;
s=double(s);
[row,flow]=size(ob);
n=1;
obstacle=zeros(2000,2);
startpoint=[0,0];
endpoint=[500,500];
for i=1:row
for j=1:flow
if s(i,j)==1
obstacle(n,1:2)=[j row-i+1];
n=n+1;
end
end
end
subplot(2,2,1);
plot(obstacle(:,1),obstacle(:,2),'.k');
% axis([0 500 0 500]);
% set(gca,'XTick',0:10:500);
% set(gca,'YTick',0:10:500);
grid on
hold on
plot(startpoint(1),startpoint(2),'.b');
hold on
plot(endpoint(1),endpoint(2),'.r')
hold on
title('VFH+路径规划算法');
%step=0.1;
step=10;
f=5; %角分辨率,单位:度
%dmax = 2 ; %视野
dmax=200;
smax = 18; %大于18为宽波谷
b=2.5; %常量
a=1+b.*(dmax.^2); %常量,与VFH不同
C=15; %cv值,原始值15
alpha = deg2rad(f); %单位:弧度
n=360/f; %分为72个扇区
threshold=1300; %阈值为150
thresholdlow=400;
%rsafe=0.6; %扩大半径和安全距离0.6
rsafe=20;
robot=startpoint; %机器人位于起始点位置
kb=90/f; %最优的方向
kt=round(caculatebeta(robot,endpoint)/alpha); %定义目标方向
if(kt==0)
kt=n;
end
ffff=zeros(1,72);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 算法:H值>>>安全角>>>机器人下一坐标
while norm(robot-endpoint)~=0 % 机器人不到终点
if(norm(robot-endpoint))>step % 机器人位置和终点位置差距大于0.1时
i=1;mag = zeros(n,1);his=zeros(n,1); %初值
while (i<=length(obstacle))
%%%%%%%%%%% 下面一段程序得到机器人360度范围视野内的障碍物分布值 计算每个扇区极坐标障碍物密度
d = norm(obstacle(i,:) - robot); % 障碍物栅格与机器人之间距离
if (d:)); % 障碍物栅格向量的方向
rangle=asin(rsafe/d); % 扩大的角度
k = round(beta/alpha); % 逆时针数,第k个扇区区域
if(k == 0)
k = n;
end
% 更新后的极坐标直方图的h值
if((5*k>rad2deg(beta)-rad2deg(rangle))&&(5*k1;
else
h(k)=0;
end
% i=i+1;
m = C^2*(a-b*(d.^2)); % 障碍物栅格的幅度值,与VFH算法不同
mag(k)=max(mag(k),m.*h(k)); % mag为zeros(n,1),mag的第k个元素为m
i=i+1;
else
i=i+1;
end
end
his=mag; %现his是一个含72个元素的向量
%%% 下面一段程序计算出目标向量kt,最佳前进方向angle,机器人下一坐标robot
j=1;q=1;
while (q<=n)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 所有合适的方向全部找出来
if(his(q)< threshold)
kr=q; % 找到了波谷的左端
while(q<=n && his(q)< threshold) %这一小段找到了波谷的右端
kl=q;
q=q+1;
end
if(kl-kr > smax) % 宽波谷
c(j) = round(kl - smax/2); % 朝向左侧
c(j+1) = round(kr + smax/2); % 朝向右侧
j=j+2;
if(kt >=kr && kt <= kl)
c(j) = kt; % straight at look ahead
j=j+1;
end
elseif(kl-kr > smax/5) % 窄波谷
c(j) = round((kr+kl)/2);
j=j+1;
end
else
q=q+1; % his(q)不为0,直接下一个
end % 退出if选择,再次进入while条件循环
end % 退出while循环
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 合适的方向都存到c里面了
g=zeros(j-1,1);how=zeros(j-1,1);
for i=1:j-1
g(i)=c(i); % g中不含目标向量
how(i)=5*howmany(g(i),kt)+2*howmany(g(i),kb)+2*howmany(g(i),kb); % how的第i元素为g(i)与kt间的向量数,g中与目标最近的
end % how为差距向量
ft=find(how==min(how));
fk=ft(1);
kb=g(fk); %前进向量
%%%% 跟踪位置避障
% if(norm(robot-endpoint))>100
% target=robot+[100*cos(kb*alpha),100*sin(kb*alpha)];
% scatter(target(1),target(2),'*r');
% drawnow;
% else
% target=endpoint;
% end
%
% while(norm(robot-target))>step
% robot=robot+[step*cos(kb*alpha),step*sin(kb*alpha)];
% scatter(robot(1),robot(2),'.b');
% drawnow;
% end
%%%% 跟踪速度避障
robot=robot+[step*cos(kb*alpha),step*sin(kb*alpha)];
scatter(robot(1),robot(2),'.b');
drawnow;
kt=round(caculatebeta(robot,endpoint)/alpha);
if(kt==0)
kt=n;
end
%%%%%%%%% 画极坐标直方图
plotHistogram(his,kt,kb,threshold,thresholdlow);
nn=plotBinHistogram(his,kt,kb,threshold,thresholdlow,ffff);
ffff=nn;
else
break
end
pause(0.1)
end
function lic = actxlicense(progid)
if strcmpi(progid, 'air.airctrl.1')
lic = 'Copyright (c) 1996 ';
return;
end
%计算角度
function beta = caculatebeta(s,e)
dy = e(2) - s(2);
dx = e(1) - s(1);
if dx==0
beta=pi/2;
else
beta = atan(dy/dx);
if(dx < 0)
if(dy > 0)
beta = pi - abs(beta);
else
beta = pi + abs(beta);
end
else
if(dy < 0)
beta = 2*pi- abs(beta);
end
end
end
%计算角度
function rangle = caculaterangle(s,e)
dy = e(2) - s(2);
dx = e(1) - s(1);
if dx==0
rangle=pi/2;
else
rangle = asin(dy/dx);
if(dx < 0)
if(dy > 0)
rangle = pi - abs(rangle);
else
rangle = pi + abs(rangle);
end
else
if(dy < 0)
rangle = 2*pi- abs(rangle);
end
end
end
function drawpoint
global obstacle;
load obstacle;
axis([0 10 0 10]);
grid on;
%plot(obstale(:,1),obstale(:,2),'.k')
%for i=1:length(ob)
% plot(ob(i,1),ob(i,2),'.k');
% hold on
end
function nn=plotBinHistogram(his,kt,kb,threshold,thresholdlow,nn)
mm=zeros(1,72);
n=length(his);
x1 = 1:n;
k1 = kt; k2=kb;
hh=his;
for i=1:n
if (hh(i)>=threshold)
mm(i)=1;
elseif (hh(n)<=thresholdlow)
mm(i)=0;
else
mm(i)=nn(i);
end
end
subplot(2,2,3)
hold off
bar(x1,mm); %%%%%%%%没有加实际线
axis([0 80 0 3]);
hold on
ylabel('H值');
xlabel('扇区');
title('二值极坐标直方图');
line([k1,k1],[0,2],'LineStyle','-.', 'color','r');%line([X1 X2],[Y1 Y2],S);
line([k2,k2],[0,2],'LineStyle','--', 'color','g');
legend('危险程度','目标方向','避障方向','阈值')
nn=mm;
subplot(2,2,1);
%%画极坐标直方图
function plotHistogram(his,kt,kb,threshold,thresholdlow)
%global his kt kb
n=length(his);
x1 = [1:n];
k1 = kt; k2=kb;
y = [0:max(his)];
if(max(his) <=1)
y=[0:0.01:1]; %to get a smoother line
end
subplot(2,2,2);
hold off
bar(x1,his); %%%%%%%%没有加实际线
hold on
ylabel('H值');
xlabel('扇区');
title('主极坐标直方图');
line([k1,k1],[0,max(his)],'LineStyle','-.', 'color','r');%line([X1 X2],[Y1 Y2],S);
line([k2,k2],[0,max(his)],'LineStyle','--', 'color','g');
line([0,n],[threshold,threshold],'LineStyle','-', 'color','k');
line([0,n],[thresholdlow,thresholdlow],'LineStyle','-', 'color','y');
legend('危险程度','目标方向','避障方向','高阈值','低阈值')
%%直方图和避障图交替进行
subplot(2,2,3);
function dif=howmany(c1,c2)
n = 72; % 扇区数目
dif = min([abs(c1-c2), abs(c1-c2-n), abs(c1-c2+n)]);