内核模块编译时出现的问题解决
第一次把自己编译的驱动模块加载进开发板,就出现问题,还好没花费多长时间,下面列举出现的问题及解决方案
1:出现insmod: error inserting 'hello.ko': -1 Invalid module format
法一(网上的):是因为内核模块生成的环境与运行的环境不一致,用linux-2.6.27内核源代码生成的模块,可能就不能在linux-2.6.32.2内核的linux环境下加载,需要在linux-2.6.27内核的linux环境下加载。
a.执行 uname -r //查看内核版本
b.一般出错信息被记录在文件/var/log/messages中,执行下面命令看错误信息
# cat /var/log/messages |tail
若出现类似下面:
Jun 4 22:07:54 localhost kernel:hello: version magic '2.6.35.6-45.fc14.i686.PAE
KDIR :=/lib/modules/2.6.35.13-92.fc14.i686.PAE/build1 //改成自己内核源码路径
(这里的build1是一个文件链接,链接到/usr/src/kernels/2.6.35.6-45.fc14.i686.PAE和13-92的)
然并卵,我的fedora 14 /usr/src/kernels下并没有2.6.35.13-92.fc14.i686.PAE,只有2.6.35.13-92.fc14.i686,虽然不知道两者有什么区别,但改成2.6.35.13-92.fc14.i686还是不行,照样这个问题,还好后来在看教学视频的到启发
法二:改的还是那个位置
KDIR :=/opt/FriendlyARM/linux-2.6.32.2 //把这里改成你编译生成kernel的那个路径
all:
$ (MAKE) -C $ (KDIR) M = $ (PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- //加这句
2. [70685.298483] hello: module license 'unspecified' taints kernel.
[70685.298673] Disabling lock debugging due to kernel taint
方法:在模块程序中加入: MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
3. rmmod: chdir(2.6.32.2-FriendlyARM): No such file or directory 错误解决
方法:lsmod 可查看模块信息
即无法删除对应的模块。
就是必须在/lib/modules下建立错误提示的对应的目录((2.6.32.2)即可。
|
|
1).创建/lib/modules/2.6.32.2空目录
2).使用如下源码生成rmmod命令,就可以没有任何提示的卸载ko模块了[luther.gliethttp]
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const char *modname = argv[1];
int ret = -1;
int maxtry = 10;
while (maxtry-- > 0) {
ret = delete_module(modname, O_NONBLOCK | O_EXCL);//系统调用sys_delete_module
if (ret < 0 && errno == EAGAIN)
usleep(500000);
else
break;
}
if (ret != 0)
printf("Unable to unload driver module \"%s\": %s\n",
modname, strerror(errno));
}
3).把生成的命令复制到文件系统
# arm-linux-gcc -static -o rmmod rmmod.c
# arm-linux-strip -s rmmod
# cp rmmod /nfs/
cp /nfs/rmmod /sbin
代码如下:
proc.c
#include
#include
#include
#include /* Necessary because we use the proc fs */
#define procfs_name "proctest"
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
struct proc_dir_entry *Our_Proc_File;
int procfile_read(char *buffer,char **buffer_location,off_t offset, int buffer_length, int *eof, void *data)
{ int ret;
ret = sprintf(buffer, "HelloWorld!\n");
return ret;
}
int proc_init()
{ Our_Proc_File = create_proc_entry(procfs_name, 0644, NULL);
if (Our_Proc_File == NULL) {
remove_proc_entry(procfs_name, NULL);
printk(KERN_ALERT "Error: Could not initialize /proc/%s\n",procfs_name);
return -ENOMEM; }
Our_Proc_File->read_proc = procfile_read;//
// Our_Proc_File->owner = THIS_MODULE;
Our_Proc_File->mode = S_IFREG | S_IRUGO;
Our_Proc_File->uid = 0;
Our_Proc_File->gid = 0;
Our_Proc_File->size = 37;
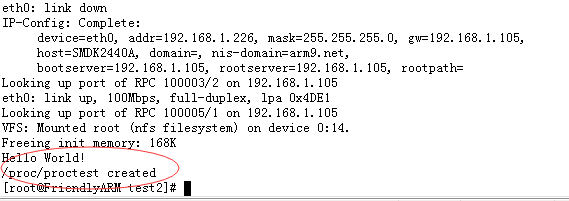
printk("/proc/%s created\n", procfs_name);
return 0;
}
void proc_exit()
{ remove_proc_entry(procfs_name, NULL);
printk(KERN_INFO "/proc/%s removed\n", procfs_name);
}
module_init(proc_init);
module_exit(proc_exit);
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m :=proc.o
else
KDIR :=/opt/FriendlyARM/linux-2.6.32.2
#KDIR :=/lib/modules/2.6.35.13-92.fc14.i686.PAE/build1
PWD :=$(shell pwd)
all:
$(MAKE) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.mod.o *.mod.c *.symvers
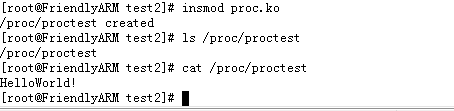
endifmake后生成proc.ko,再在开发板上insmod proc.ko即可

执行 dmesg 就可以看到 产生的内核信息啦