用tensorflow实现VGG网络,训练mnist数据集
VGG作为流行的几个模型之一,训练图形数据效果不错,在mnist数据集是常用的入门集数据,VGG层数非常多,如果严格按照规范来实现,并用来训练mnist数据集,会出现各种问题,如,经过16层卷积后,28*28*1的图片几乎无法进行。
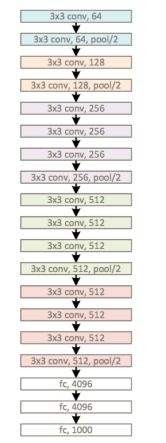
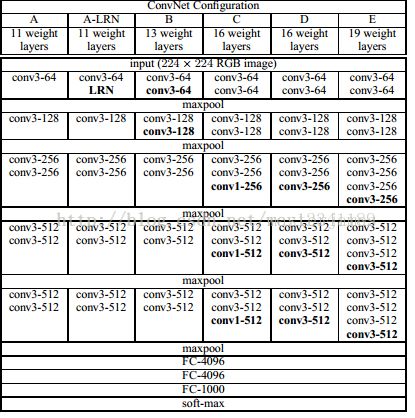
先介绍下VGG
ILSVRC 2014的第二名是Karen Simonyan和 Andrew Zisserman实现的卷积神经网络,现在称其为 VGGNet
。它主要的贡献是展示出网络的深度是算法优良性能的关键部分。
他们最好的网络包含了16个卷积/全连接层。网络的结构非常一致,从头到尾全部使用的是3x3的卷积和2x2的汇聚。他们的 预训练模型
是可以在网络上获得并在Caffe中使用的。
VGGNet不好的一点是它耗费更多计算资源,并且使用了更多的参数,导致更多的内存占用(140M)。其中绝大多数的参数都是来自于第一个全连接层。
本文在实现时候,尽量保存VGG原来模型结构,核心代码如下:
weights ={
'wc1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,1,64])),
'wc2':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,64,64])),
'wc3':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,64,128])),
'wc4':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,128,128])),
'wc5':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,128,256])),
'wc6':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,256,256])),
'wc7':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,256,256])),
'wc8':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,256,256])),
'wc9':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,256,512])),
'wc10':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,512])),
'wc11':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,512])),
'wc12':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,512])),
'wc13':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,512])),
'wc14':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,512])),
'wc15':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,512])),
'wc16':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,3,512,256])),
'wd1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096,4096])),
'wd2':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096,4096])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096,nn_classes])),
}
biases ={
'bc1':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([64])),
'bc2':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([64])),
'bc3':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128])),
'bc4':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128])),
'bc5':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])),
'bc6':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])),
'bc7':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])),
'bc8':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])),
'bc9':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc10':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc11':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc12':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc13':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc14':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc15':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])),
'bc16':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])),
'bd1':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([4096])),
'bd2':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([4096])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.zeros([nn_classes])),
}卷积实现:
def convLevel(i,input,type):
num = i
out = conv2D('conv'+str(num),input,weights['wc'+str(num)],biases['bc'+str(num)])
if type=='p':
out = maxPool2D('pool'+str(num),out, k=2)
out = norm('norm'+str(num),out, lsize=4)
return out
def VGG(x,weights,biases,dropout):
x = tf.reshape(x,shape=[-1,28,28,1])
input = x
for i in range(16):
i += 1
if(i==2) or (i==4) or (i==12) : # 根据模型定义还需要更多的POOL化,但mnist图片大小不允许。
input = convLevel(i,input,'p')
else:
input = convLevel(i,input,'c')训练:
pred = VGG(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred,labels=y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1))
accuracy_ = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
step = 1
while step*batch_size < train_iters:
batch_x,batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(optimizer,feed_dict={x:batch_x,y:batch_y,keep_prob:dropout})
print(step*batch_size)
if step % display_step == 0 :
#loss,acc = sess.run([cost,accuracy],feed_dict={x:batch_x,y:batch_y,keep_prob=1.0})
acc = sess.run(accuracy_, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.})
# 计算损失值
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.})
print("iter: "+str(step*batch_size)+"mini batch Loss="+"{:.6f}".format(loss)+",acc="+"{:6f}".format(acc))
step += 1
print("training end!") 最终效果:
训练10000次后:结果如下:
iter: 12288 mini batch Loss=5088409.500000,acc=0.578125
iter: 12800 mini batch Loss=4514274.000000,acc=0.601562
iter: 13312 mini batch Loss=4483454.500000,acc=0.648438
这种深度的模型可以考虑循环10万次以上。目前效果还不错,本人没有GPU,心痛笔记本的CPU,100%的CPU利用率,听到风扇响就不忍心再训练,本文也借鉴了alex网络实现,当然我也实现了这个网络模型。在MNIST数据上,ALEX由于层数较少,收敛更快,当然MNIST,用CNN足够了。