SLAM文献阅读(不定期更新)
SLAM文献阅读
- [1] Comparison of Optimization Techniques for 3D Graph-based SLAM
- [2] AEKF-SLAM: A New Algorithm for Robotic Underwater Navigation
- [3] A SLAM-based Approach for Underwater Mapping using AUVs with Poor Inertial Information
- [4] Map Building Fusing Acoustic and Visual Information using Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
[1] Comparison of Optimization Techniques for 3D Graph-based SLAM
综述性论文,针对Graph SLAM的总体框架、前端、后端分别进行描述。
- 前端分类为map to map (构建submap), image to map(通过点特征确定相机相对于map的位姿), image to image (相机图像匹配,simplest);
- 后端中主要使用了三种工具:G2O(General (Hyper) Graph Optimization)、GTSAM(Georgia Tech Smoothing and Mapping)和HOG-Man(Hierarchical Optimization on Manifolds)
G2O: It is a C++ framework for performing the optimization of nonlinear least squares problems that can be embedded as a graph or in an hyper-graph. (工程常用)
GTSAM: It is a C++ library based on factor graphs. A factor graph consists of factors connected to variables. The factors represent probabilistic information on the unknown random variables in the estimation problem. (代码具有优秀的编程规范,适合学习, iSAM 求解器)
HOG-Man: It applies Gauss Newton with sparse Cholesky factorization that considers a manifold representation of the state space to better deal with the camera rotations. (划分submap,多层图结构)
[2] AEKF-SLAM: A New Algorithm for Robotic Underwater Navigation
-
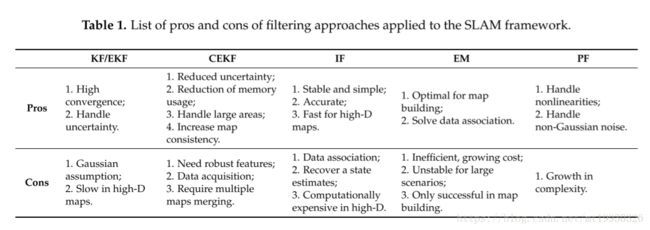
sensors的论文感觉都挺长啊,这篇论文里综述部分整理的很有条理,表格如下
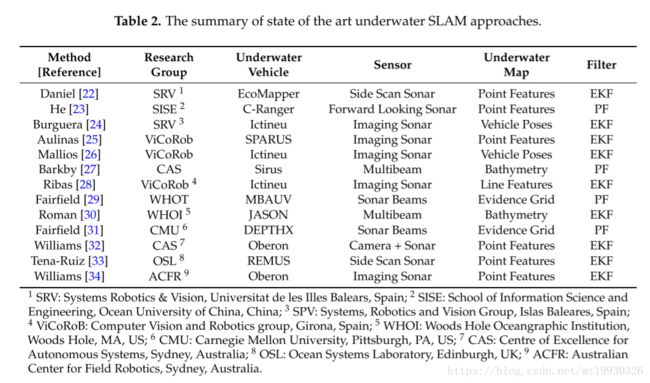
[23]. He, B.; Liang, Y.; Feng, X.; Nian, R.; Yan, T.H.; Li, M.H.; Zhang, S.J. AUV SLAM and experiments using a mechanical scanning forward-looking sonar. Sensors 2012, 12, 9386–9410.
[24]. Burguera, A.; Gonzalez, Y.; Oliver, G. Underwater SLAM with robocentric trajectory using a mechanically scanned imaging sonar. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 3577–3582.
[25]. Aulinas, J.; Carreras, M.; Llado, X.; Salvi, J.; Garcia, R.; Petillot, Y.R. Feature extraction for underwater visual SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Oceans, Santander, Spain, 6–9 June 2011; pp. 1–7.
[26]. Mallios, A.; Ridao, P.; Hernàndez, E.; Ribas, D.; Maurelli, F.; Petillot, Y.R. Pose-based SLAM with probabilistic scan matching algorithm using a mechanical scanned imaging sonar. In Proceedings of the 2009 Europe Oceans, Bremen, Germany, 11–14 May 2009; pp. 1–6.
[27]. Barkby, S.; Williams, S.B.; Pizarro, O.; Jakuba, M. Incorporating prior bathymetric maps with distributed particle bathymetric SLAM for improved AUV navigation and mapping. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE Oceans Conference and Exhibition, Biloxi, MS, USA, 26–29 October 2009; Volume 2, pp. 1–7.
[28]. Ribas, D.; Ridao, P.; Tardós, J.D. Underwater SLAM in man made structured environments. J. Field Robot. 2008, 25, 898–921. [CrossRef]
[29]. Fairfield, N.; Wettergreen, D. Active localization on the ocean floor with multibeam sonar. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Quebec City, Canada, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–10.
[30]. Roman, C.N.; Singh, H. A self-consistent bathymetric mapping algorithm. J. Field Robot. 2007, 24, 23–50.
[31]. Fairfield, N.; Kantor, G.; Wettergreen, D. Real-time slam with octree evidence grids for exploration in underwater tunnels. J. Field Robot. 2007, 24, 3–21.
[32]. Williams, S.; Mahon, I. Simultaneous localisation and mapping on the Great Barrier Reef. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1771–1776.
[33]. Tena-Ruiz, I.; Raucourt, S.; Petillot, Y.; Lane, D.M. Concurrent mapping and localization using side-scan sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 442–456.
[34]. Williams, S.B. Efficient Solutions to Autonomous Mapping and Navigation Problems. Ph.D thesis, Australian Center for Field Robotics, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2001. -
Hector SLAM and GMapping :常用的两种laser SLAM方法,有ROS工具包
Hector SLAM:基于Gauss-Newton法,单独使用scan matching估计位置
http://wiki.ros.org/hector_slam (ROS package)
Gmapping:Rao-Blackwellized particle filter,使用里程计估计位置
http://wiki.ros.org/gmapping/ (ROS package) -
Augmented Extended Kalman Filter (AEKF)
相较于EKF,其改进在于认为系统噪声均值不为0(仍满足高斯分布),在每一步对过程噪声和测量噪声的均值和方差进行修正(在update过程中)。 -
本文以考虑机器人x,y和首向角三自由度运动距离,测量信息为测距,公式说明极其细致,适合EKF SLAM的入门学习。
-
European Smart and Networking Underwater Robots in Cooperation Meshes (SWARMs) project:该项目中有水下机器人SLAM的部分,网址为
http://www.swarms.eu/index.html
[3] A SLAM-based Approach for Underwater Mapping using AUVs with Poor Inertial Information
- 这篇论文里很有趣的部分在于将bathymetric SLAM 认为是一种feature SLAM方法,通过一些方法在点云数据中提取特征,并且匹配算法还对错误的匹配据有鲁棒性。
“In the past few years there has been great interest and progress made in the development of 3D point cloud feature extraction among the terrestrial robotics community. Many of these algorithms are closely related to 2D image features. This is not surprising, as many of the image feature algorithms treat images as if they were terrain maps, where the image intensity of a given pixel can be thought of as terrain height. Some well-known algorithms that use this idea are Harris Corners [16], SIFT [17], and SURF [18]. The general approach with all of these algorithms is that by considering not only a single point or pixel, but a small neighborhood of points and pixels, stable features can be identified and statistics extracted such that the feature can be identified and matched by later observations. Methods vary in their computational complexity, robustness to noise, invariance under various combinations of transformation, rotation, lighting, etc.” - 本文主要是在点云中提取具有较高曲率的点作为特征,使用面地形中的点云进行特征提取,理论依据主要是“ over short time scales, the effects of this warping are small, and can be ignored. Using these submaps built from data collected over short intervals, features can be extracted.”
[4] Map Building Fusing Acoustic and Visual Information using Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
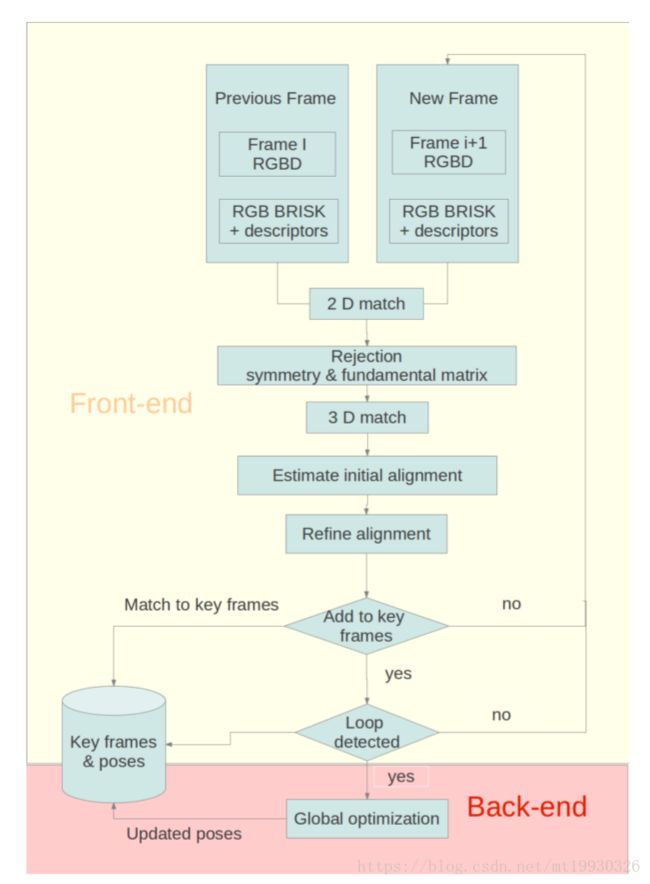
一篇很长的论文,让我一度以为这是硕士的毕业论文。论文主要讲述的是使用视觉和声学(主要是多波束声纳)的混合SLAM方法,没怎么细看框架,但是论文使用的应该是图优化方法,同时在视觉上使用了BA。这篇论文说明了视觉/声学SLAM具备可行性。
但是,根据该篇论文显示,两种传感器的混合并没有显著提高建图精度,其目的主要是丰富测绘得到的信息从而保证算法在信息贫瘠的区域能够运行。