Android - GET请求,POST请求,数据提交,编码,HttpClient,async-http开源框架,多线程下载,断点续传,xUtils框架
转载请注明出处:https://blog.csdn.net/mythmayor/article/details/72869238
1.GET方式提交数据
new Thread(){
public void run() {
try {
//GET请求方式的特点:在url后面组拼数据
String path = "http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/LoginServlet?qq="+qq+"&pwd="+pwd);
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
int code = conn.getResponseCode();
if(code == 200){
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
String result = StreamTools.readStream(is);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = SUCCESS;
msg.obj = result;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}else{
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};
}.start();
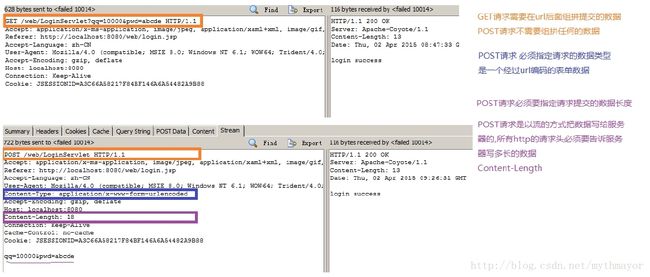
2.GET请求和POST请求的区别
优缺点
* GET请求
优点:使用非常方便,只需要在url后面组拼数据。
缺点:数据在url的后面组拼,不安全。有数据长度限制。
* POST请求
优点:安全,数据不是在url后面组拼而是通过流的方式写给服务器。数据长度不受限制
缺点:编写麻烦。
数据提交
* GET请求
1. 需要在url后面组拼提交的数据
* POST请求
1. 不需要组拼任何的数据
2. 必须指定请求的数据类型,是一个经过url编码的表单数据。Content-Type
3. 以流的方式把数据写给服务器,所以必须指定提交数据的长度。Content-Length
3.POST方式提交数据
new Thread(){
public void run() {
//路径不需要组拼
String path = "http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/LoginServlet";
try {
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
//1.设置请求方式为POST
conn.setRequestMethod("POST"); //注意单词必须大写.
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//2.设置http请求数据的类型为表单类型
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
//3.设置给服务器写的数据的长度
//qq=10000&pwd=abcde
String data = "qq="+qq+"&pwd="+pwd;
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(data.length()));
//4.记得指定要给服务器写数据
conn.setDoOutput(true);
//5.开始向服务器写数据
conn.getOutputStream().write(data.getBytes());
int code = conn.getResponseCode();
if(code == 200){
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
String result = StreamTools.readStream(is);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = SUCCESS;
msg.obj = result;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}else{
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};
}.start();
4.Tomcat默认码表
- Tomcat默认码表iso-8859-1
- Tomcat如果发现字符串不识别,就默认采用本地码表
5.GB2312和GBK
GB2312
1980年发布,标准共收录6763个汉字,其中一级汉字3755个,二级汉字3008个;同时,GB2312收录了包括拉丁字母、希腊字母、日文平假名及片假名字母、俄语西里尔字母在内的682个全角字符。
GB 2312的出现,基本满足了汉字的计算机处理需要,它所收录的汉字已经覆盖中国大陆99.75%的使用频率。
对于人名、古汉语等方面出现的罕用字,GB2312不能处理,这导致了后来GBK及GB18030汉字字符集的出现。
GBK
1995年发布,是在GB2312-80标准基础上的内码扩展规范,共收录了21003个汉字,完全兼容GB2312-80标准。
6.string.getBytes(String charsetName)和new String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName)
- byte[] bytes = string.getBytes(String charsetName)
将字符串按指定的编码转化为byte数组,默认采用本地码表 - new String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName)
将byte数组按指定的编码转化为字符串
注意:出现乱码时不要修改文件,修改后无论怎么切换编码都是错的了
7.提交数据中含有中文的注意事项
客户端
//提交的数据中含有中文时,将字符串qq按照编码UTF-8进行编码
URLEncoder.encode(qq, "UTF-8");
服务端
String qq = request.getParameter("qq");//tomcat采用的编码是iso-8859-1
System.out.println("qq:"+new String(qq.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8"));
8.HttpClient
轻量级的浏览器,将请求和响应都封装成了对象
- 打开浏览器
- 输入地址(数据)
- 敲回车
9.HttpClient的GET和POST请求
GET请求
new Thread(){
public void run() {
try {
String path = "http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/LoginServlet?qq="+URLEncoder.encode(qq, "utf-8")+"&pwd="+URLEncoder.encode(pwd, "utf-8");
//1.打开浏览器
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
//2.输入地址或者数据
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(path);
//3.敲回车
HttpResponse response = client.execute(httpGet);
//获取状态码
int code = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if(code == 200){
InputStream is = response.getEntity().getContent();
String result = StreamTools.readStream(is);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = SUCCESS;
msg.obj = result;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}else{
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};
}.start();
POST请求
new Thread(){
public void run() {
try {
String path = "http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/LoginServlet";
//1.打开浏览器
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
//2.输入地址或者数据
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(path);
List parameters = new ArrayList();
parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("qq", qq));
parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("pwd", pwd));
httpPost.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parameters, "utf-8"));
//3.敲回车
HttpResponse response = client.execute(httpPost);
//获取状态码
int code = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if(code == 200){
InputStream is = response.getEntity().getContent();
String result = StreamTools.readStream(is);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = SUCCESS;
msg.obj = result;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}else{
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ERROR;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};
}.start();
10.async-http开源框架的GET请求
String path = "http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/LoginServlet?qq="+URLEncoder.encode(qq)+"&pwd="+URLEncoder.encode(pwd);
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient();
client.get(path, new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() {
//请求成功的回调
@Override
public void onSuccess(int statusCode, Header[] headers, byte[] responseBody) {
tv_status.setText(new String(responseBody));
}
//请求失败的回调
@Override
public void onFailure(int statusCode, Header[] headers, byte[] responseBody, Throwable error) {
tv_status.setText("http请求失败"+new String(responseBody));
}
});
11.async-http开源框架的POST请求
String path = "http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/LoginServlet";
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient();
RequestParams params = new RequestParams();
params.put("qq", qq);
params.put("pwd", pwd);
client.post(path, params, new AsyncHttpResponseHandler(){
//请求成功的回调
@Override
public void onSuccess(int statusCode, Header[] headers,
byte[] responseBody) {
tv_status.setText("登陆结果:"+new String(responseBody));
}
//请求失败的回调
@Override
public void onFailure(int statusCode, Header[] headers,
byte[] responseBody, Throwable error) {
tv_status.setText("请求失败请检查网络");
}
});
12.async-http开源框架的文件上传
- 文件上传的原理
- 文件上传其实就是一个POST请求
- Content-Type为multipart/form-data
具体代码
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); RequestParams params = new RequestParams(); try { params.put("file", file); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } client.post("http://192.168.1.103:8080/web/UploadServlet", params, new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { @Override public void onSuccess(int statusCode, Header[] headers, byte[] responseBody) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "上传成功", 0).show(); } @Override public void onFailure(int statusCode, Header[] headers, byte[] responseBody, Throwable error) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "上传失败", 0).show(); } });
13.多线程下载
- 多线程并发操作
- 网络请求
14.为什么多线程可以提高下载的速度
- 从服务器上获取的资源变多了,单位时间内下载的速度就变快.
- 下载速度还受到服务器上传带宽和用户的下载带宽限制
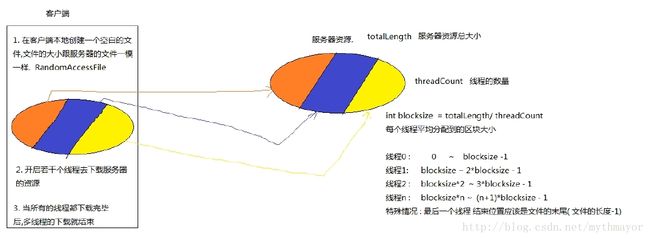
15.多线程下载的步骤
- 在客户端本地创建一个空白文件,文件的大小跟服务器的一模一样。RandomAccessFile
- 开启若干个线程去下载服务器的资源
- 当所有线程都下载完毕,多线程下载就结束了
16.如何划分服务器的资源给不同的线程
int length = conn.getContentLength(); //总长度
int blocksize = length / threadCount; //前(n-1)个线程下载的数据量
for (int threadId = 0; threadId < threadCount; threadId++) {
int startIndex = threadId * blocksize;
int endIndex = (threadId + 1) * blocksize - 1;
if (threadId == (threadCount - 1)) {
endIndex = length - 1;
}
}
17.多线程下载文件
//1.在客户端本地创建一个空白文件,文件的大小跟服务器的一模一样
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(getFileName(path), "rw");
raf.setLength(length);
raf.close();
//2.确定每个线程获取数据的“开始位置”和“结束位置”
int length = conn.getContentLength(); //总长度
int blocksize = length / threadCount; //前(n-1)个线程下载的数据量
for (int threadId = 0; threadId < threadCount; threadId++) {
int startIndex = threadId * blocksize;
int endIndex = (threadId + 1) * blocksize - 1;
if (threadId == (threadCount - 1)) {
endIndex = length - 1;
}
new DownloadThread(threadId, startIndex, endIndex).start();
}
//3.第i个线程只取服务器中的某一段数据
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestProperty("Range", "bytes="+startIndex+"-"+endIndex);
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
//4.第i个线程取回数据后,从某个位置开始写入数据
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(getFileName(path), "rw");
raf.seek(startIndex);//每个线程写文件的开始位置都是不一样的.
18.断点续传的原理
记录每个线程的下载进度,下次再下载的时候从该位置开始下载
19.多线程断点下载的小细节
- 每个下载任务都需要自己的记录进度的文件
- 都下载完后删除记录文件
- 保证同步使用synchronize代码块
- 使用FileOutputStream数据不一定每一次都写到存储设备里,有可能写到硬盘的缓存里,使用RandomAccessFile将模式设置为rwd,可以保证每次都将数据写到磁盘里
20.使用xUtils完成多线程断点下载
HttpUtils http = new HttpUtils();
//第一个参数:服务器地址
//第二个参数:要下载到哪里
//是否断点续传
//下载的一些回调函数
http.download(path, "/mnt/sdcard/xxx.exe", true, new RequestCallBack() {
//下载成功的回调
@Override
public void onSuccess(ResponseInfo arg0) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "下载成功", 0).show();
}
//进度更新的回调
@Override
public void onLoading(long total, long current, boolean isUploading) {
pb0.setMax((int) total);
pb0.setProgress((int) current);
super.onLoading(total, current, isUploading);
}
//下载失败的回调
@Override
public void onFailure(HttpException arg0, String arg1) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "下载失败"+arg1, 0).show();
}
});
21.总结
- 提交数据到服务器
- GET与POST请求方式的区别
- 中文乱码产生的原因、解决方式
- 提交的数据中含有中文的解决方式
- 使用HttpURLConnection进行GET和POST提交
- 使用HttpClient进行GET和POST提交
- 使用开源框架async-http进行GET、POST提交、上传文件
- 多线程断点下载
- 多线程断点下载的原理
- 多线程断点下载的步骤
- 如何获取服务器数据的某一部分
- 如何将获取的数据写入到本地文件的某一部分
- 多线程断点下载的小细节
- 完成的仅为玩具代码,不可在真实项目中使用
- 使用开源项目xUtils实现多线程断点下载