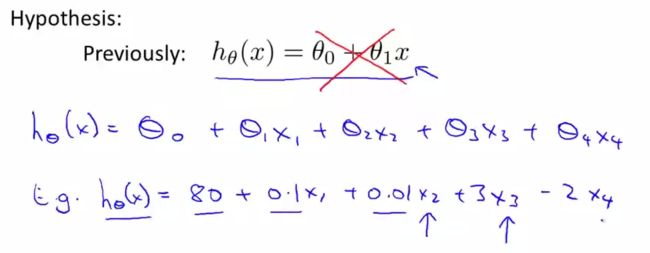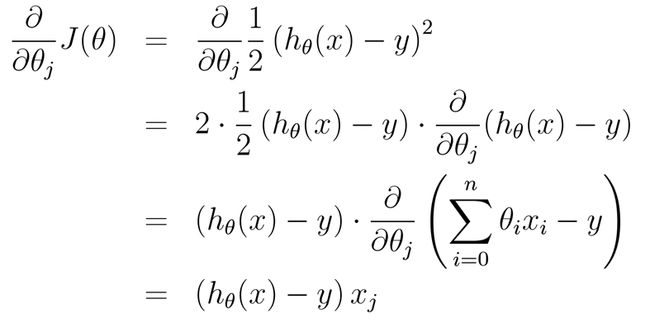梯度下降法 线性回归 多项式回归 python实现
-
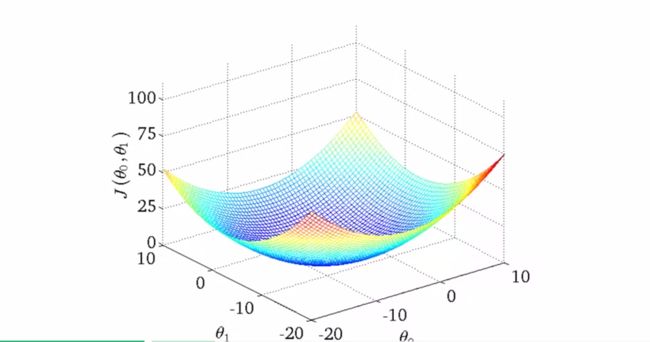
- cost函数 J 代价函数
- 二维的cost函数曲线
- 多个变量时的情景
- 特征缩放
- 平均数归一化
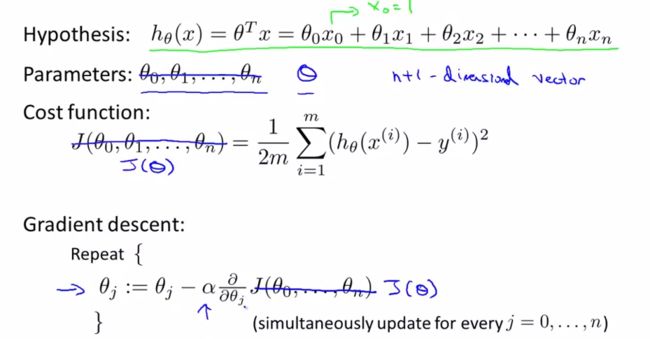
- 梯度下降
- 多项式回归
- Python实现两个变量x0 x1
- 其他问题数组横向纵向拼接
摘自吴恩达老师课程week1-2,为其概括复习版
回归与最优化-广义线性回归
cost函数 J(θ) 代价函数
根据不同的θ取值,cost不同。最小的cost点为最佳拟合系数θ
左图为θ=0时的cost,计算后在右图中标出
二维的cost函数曲线
多个变量时的情景。
x1 x2表示房屋价格,楼层等
如果变量可以合并成新变量,如房屋的长(x1)和宽(x2),则可把他们合并成新变量
特征缩放
如果x1很大而x2很小
则x1改变较小的单位长度(在横轴上的距离)就可使J(θ)有较大变化
而x2的一个单位长度更大
平均数归一化
把各个变量范围分别放缩到-1,1左右
u为均值(期望), s为标准差deviation 或数据集的最大值减最小值. 可视归一化结果而定
梯度下降
首先给定θ0…θn初始值
对每个θ(j), j=0…n 求偏导数。若最终偏导数等于0则θ(j)=θ(j), 即上一次迭代和本次迭代的值相同
认为θ达到要求,为最小值
蓝线框出的即为J(θ)的导数值,便于计算。对于非线性可用diff函数或sage等计算导数(符号计算)对于是否结束迭代,可以画出J(θ)与iterator次数的关系,看J(θ)变化是否趋于稳定
多项式回归
等价于变量替换
需要注意归一化问题。数量及不同,归一更复杂
Python实现(两个变量x0 x1)
引用
# coding=utf-8
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import *
from numpy import *
import random
'''
多项式梯度下降法
http://blog.csdn.net/neuldp/article/details/52063613
'''
# x1, x2, ..xn 个变量为矩阵的横行
# 每个变量的不同取值为列
# 1对于一行的相加 2减去y 3对下一行同样操作并加和
# 参数:当前theta(向量) xset(x的矩阵mxn) yset(y的矩阵mx1)
def sum_J(theta, theta_id, xset, yset):
sum_J_theta_id = 0
for row in xrange(0, len(yset)):
J = 0
for i in xrange(0, len(theta)):
J += theta[i] * xset[row][i]
sum_J_theta_id += (J - yset[row]) * xset[row][theta_id]
print sum_J_theta_id
return sum_J_theta_id
def scaling(read_file_ndarray):
return (read_file_ndarray - read_file_ndarray.mean())/(read_file_ndarray.max() - read_file_ndarray.min())
# degree 最大迭代次数
def grediant(xset, yset, alpha, dgree):
theta = []
if xset[0] is None:
return
# 列的数量
num_theta = len(xset[0])
# for i in range(0, num_theta):
# theta.append(0) #把所有theta初始化成0
# 经多次试验 确定初值 使迭代步骤最少
theta.append(0)
theta.append(0.5)
theta.append(0.5)
# 行数
length = len(yset)
# jtheta = 0
total = 0
sum_total = 0
e = 1000 # 误差 初始值可以很大
iter_num = 0
# while e >= 1e-2 or iter_num <= dgree:
# for对每一个theta迭代操作
while iter_num < dgree:
print theta
total = 0
for j in range(0, num_theta):
# 全部theta数组, theta下标, x, y, 行号
total = sum_J(theta, j, xset, yset)
# 更新所有theta
theta[j] = theta[j] - (alpha/length)*(total)
if e > (alpha/length)*(total):
e = (alpha/length)*(total)
iter_num += 1
return theta
#X=[1.5,2,1.5,2,3,3,3.5,3.5,4,4,5,5]
#Y=[3,3.2,4,4.5,4,5,4.2,4.5,5,5.5,4.8,6.5]
# x0 == 1
# m x n : m组数据 n列
X = [[1, 2104, 3],
[1, 1600, 3],
[1, 2400, 3],
[1, 1416, 2],
[1, 3000, 4]
]
Y = [400, 330, 369, 232, 540]
# 函数入口
#a = grediant(X,Y,0.0005,10)
#print a
read_file = genfromtxt("ex1data2.txt" , delimiter=',')
print read_file.shape
X = []
for i in xrange(0,len(read_file)):
theta1 = scaling(read_file[:, 0])
theta0 = ones(theta1.shape)
theta2 = scaling(read_file[:, 1])
X = column_stack(( theta0, theta1, theta2 ))
print X
Y = scaling(read_file[:, 2])
print Y
# print read_file[:, 1].mean()
# print read_file[:, 0].mean()
# print read_file[:, 0].max()
a = grediant(X, Y, 0.1, 60)
print a其他问题:数组横向,纵向拼接
a = np.array((0, 1))
b = np.array((2, 1))
c = np.array((-1, -1))
np.hstack((a, b, c))
# array([ 0, 1, 2, 1, -1, -1]) ## Noooooo
np.reshape(np.hstack((a, b, c)), (2, 3))
# array([[ 0, 1, 2], [ 1, -1, -1]]) ## Reshaping won't help
一种可能(但也就是
np.hstack((a[:, np.newaxis], b[:, np.newaxis], c[:, np.newaxis]))
# array([[ 0, 2, -1], [ 1, 1, -1]]) ##
有没有更好的方法?
本文地址 :CodeGo.net/550614/
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. numpy.column_stack 例如:
>>> a = np.array((0, 1))
>>> b = np.array((2, 1))
>>> c = np.array((-1, -1))
>>> numpy.column_stack((a,b,c))
array([[ 0, 2, -1],
[ 1, 1, -1]])
它基本上等于
>>> numpy.vstack((a,b,c)).T
2. 我尝试了以下内容
>>> np.vstack((a,b,c))
array([[ 0, 1],
[ 2, 1],
[-1, -1]])
>>> np.vstack((a,b,c)).T
array([[ 0, 2, -1],
[ 1, 1, -1]])