shell编程(2)
紧接着上一篇的shell编程(1)
一、条件测试
格式:
1) test 测试条件 测试内容
2) [ 测试条件 测试内容 ]
1、测试文件类型
a)test -e 文件名 测试文件是否存在,存在为真
[ -e 文件名 ] 注意:[]中必须有空格,即在-e前面和文件名后面各加一个空格
步骤如下:
(方法一)
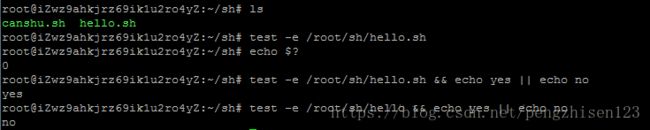
1、进入到目录/root/sh/下,查看该目录下的文件:ls
2、测试该目录下文件hello.sh是否存在:test -e /root/sh/hello.sh
3、通过预定义变量&?判断上一步命令的返回值,如果存在,就返回0,不存在,返回一个非0的随机数:echo $?
4、测试发现返回值为0,说明hello.sh文件存在。
(方法二)
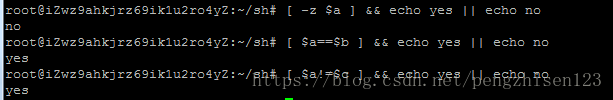
1、通过多命令执行来进行判断即 命令1&&命令2 || 命令3,表示命令1正确时执行命令2,命令1错误时执行命令3,运行:test -e /root/sh/hello.sh && echo yes || echo no
2、可以看出运行结果为:yes
3、运行一个不存在的文件:test -e /root/sh/hello && echo yes || echo no
4、可以看出运行结果为:no
(方法三)
![]()
1、使用:[ -e /root/sh/hello.sh ] && echo yes || echo no
2、可以看出运行结果也为:yes
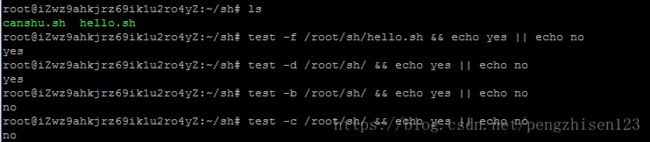
b) test -f 文件名 判断是否是普通文件
c)test -d 文件名 判断是否为目录
d)test -b 文件名 判断是否为块设备文件
e)test -C 文件名 字符设备文件
2、测试文件权限
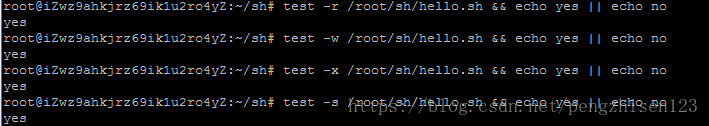
test -r 文件名 判断是否有可读权限
test -w 文件名 判断是否有可写权限
test -x 文件名 判断是否有执行权限
test -s 文件名 判断是否为非空白,有内容为真
3、两个文档比较
[ file1 -nt file2 ] file1是否比file2新
[ file1 -ot file2 ] file1是否比file2旧
[ file1 -ef file2 ] file1与file2是否是链接文件(也即是判断两者是不是快捷方式)
4、两个数值之间判断
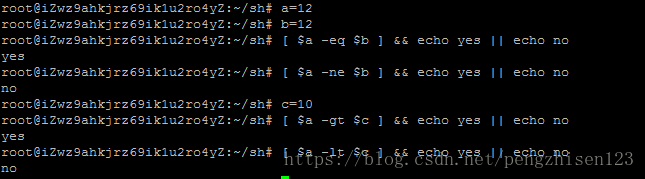
[ n1 -eq n2 ] n1和n2是否相等
[ n1 -ne n2 ] n1和n2是否不等
[ n1 -gt n2 ] n1大于n2
[ n1 -lt n2 ] n1小于n2
[ n1 -ge n2 ] n1大于等于n2
[ n1 -le n2 ] n1小于等于n2
5、判断字符串
[ -z 字符串] 判断字符串是否为空
[ 字符串1 == 字符串2 ] 判断字符串1是否与字符串2相等
例: [ $a==$b ] && echo 1 || echo 2
[ 字符串1 != 字符串2] 判断字符串是否不等
6、多重判断
-a 逻辑与
[ -z $file -a -e $file] (既要文件内容不为空,也要文件存在)
-o 逻辑或
! 逻辑非
例子:判断输入的文件类型和文件权限
#!/bin/bash
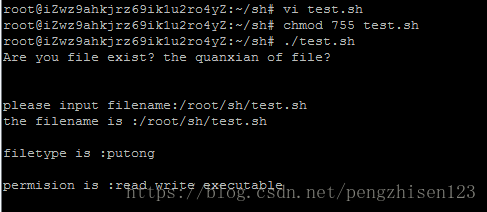
echo -e "Are you file exist? the quanxian of file?\n\n"
read -p "please input filename:" -t 30 filename
test -z $filename && echo"please input filename!!" && exit 1
# -z变量 判断字符串是否为空,为空时为真
test ! -e $filename && echo "file isnot exist!" && exit 2
# -e变量 判断文件是否存在,存在为真 !逻辑非
test -f $filename && filetype=putong
# -f 是否为普通文件
test -d $filename && filetype=mulu
# -d 是否为目录
test -r $filename && perm="read"
# -r 是否有可读权限
test -w $filename && perm="$perm write"
# -w 是否可写
test -x $filename && perm="$perm executable"
# -x 是否可执行
echo -e "the filename is :$filename \n"
# 打印文件名
echo -e "filetype is :$filetype \n"
#打印文件类型
echo -e "permision is :$perm \n"
#打印文件权限
具体步骤:
1、创建一个test.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi test.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 test.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./test.sh
4、通过键盘输入文件名:/root/sh/test.sh
5、运行后会看到运行结果如上。
二、流程控制
1、if 语句
1)if条件语句 ------单分支。当“条件成立”时执行相应的操作。
格式:
if 条件测试命令
then 命令序列
fi例子:如果/run/lock分区的空间使用超过80%,则输出警告(脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
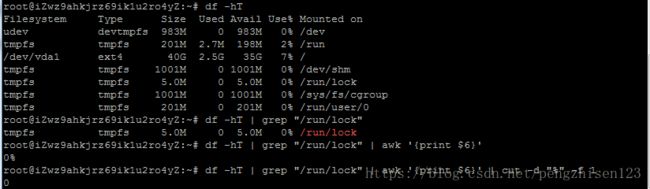
RATE=`df -hT | grep "/run/lock" | awk '{print $6}' | cut -d "%" -f1`
if [ $RATE -gt 80 ]
then
echo "Warning,/boot DISK is full!"
fi命令`df -hT | grep "/run/lock" | awk '{print $6}' | cut -d "%" f 1`的意思如下图所示
2)if 条件语句 ------双分支语句。当“条件成立”、“条件不成立”时执行不同操作
格式:
if 条件测试命令
then 命令序列1
else 命令序列2
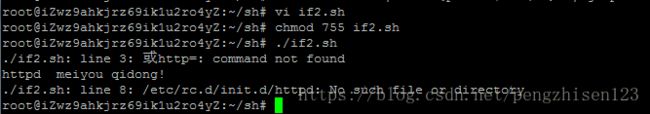
fi例子:判断httpd 服务是否启动,如果没有启动则启动
#!/bin/bash
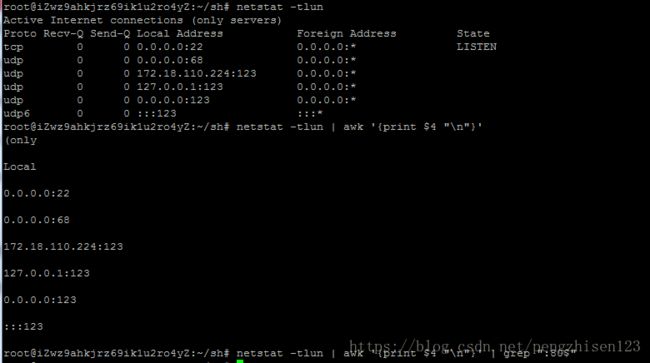
http=`netstat -tlun | awk '{print $4 "\n"}' | grep ":80$"`
(或http=$( ps aux | grep httpd | grep -v grep))
if [ -z "$http" ]
then
echo "httpd meiyou qidong!"
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd start
else
echo "httpd runing"
fi运行该脚本的步骤:
1、创建一个test.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi if2.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 if2.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./if2.sh
4、运行后会看到运行结果如上。
3)if 条件语句 ------多分支
格式:
if 条件测试命令1 ; then
命令序列1
elif 条件测试命令2 ; then
命令序列2
elif ...
else
命令序列n
fi例子:判断输入的字符
#!/bin/bash
echo "if you want to beijing ,please input 1"
echo "if you want to shanghai ,please input 2"
echo "if you want to chengdu ,please input 3"
read -p "please input a num: " -t 30 num
if [ "$num" == "1" ]
then
echo "beijing!!!"
elif [ "$num" == "2" ]
then
echo "shanghai!!!!"
elif [ "$num" == "3" ]
then
echo "chengdu!!!"
else
echo "error,please input 1 or 2 or 3."
fi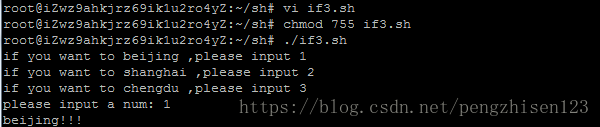
运行步骤如下:
1、创建一个if3.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi if3.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 if3.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./if3.sh
4、通过键盘输入数字:1
5、运行后会看到运行结果如上。
2、for 语句
1)使用 in 关键字循环
根据变量的不同取值,重复执行一组命令操作
格式:
for 变量名 in 取值列表
do
命令序列
done
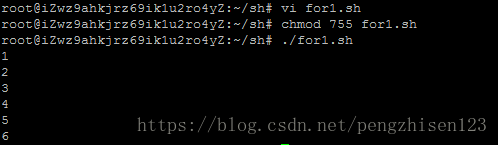
例子1:循环(脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
for i in 1 2 3 4 5 6
do
echo $i
done运行步骤如下:
1、创建一个for1.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi for1.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 for1.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./for1.sh
4、运行后会看到运行结果如上。
例子2:输出目录/root/sh下的所有文件名 (脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
a=$(ls /root/sh)
for i in $a
do
echo $i
done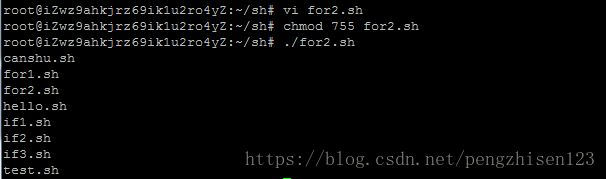
运行步骤如下:
1、创建一个for2.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi for2.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 for2.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./for2.sh
4、运行后会看到运行结果如上。
例子3:输入目录名,显示目录下所有内容 (脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
read -p "please input a filename!" -t 30 filename
if [ -z $filename ];then
echo "please input!!!!!!"
exit 1
fi
#如果字符串为空,报错跳出
if [ ! -e $filename ]
then
echo "$filename not cunzai!!"
exit 2
fi
#如果文件不存在,报错跳出
if [ ! -d $filename ]
then
echo "$filename is not driectory"
exit 3
fi
#如果不是目录,报错跳出
file=`ls $filename`
for test in $file
do
echo $test
done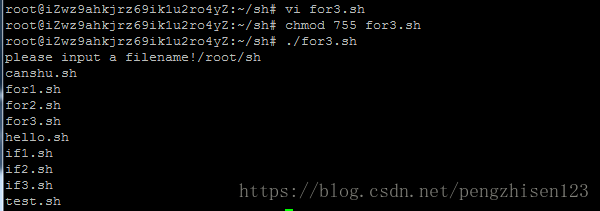
运行步骤如下:
1、创建一个for3.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi for3.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 for3.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./for3.sh
4、运行后会看到运行结果如上。
例4:从1加到100 (脚本如下)
#/bin/bash
s=0
for ((i=1;i<=100;i=i+1))
do
s=$(($s+$i))
done
echo $s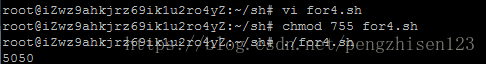
3、while循环语句
重复测试指定的条件,只有条件成立则反复执行对应的命令操作
格式:
while 命令或表达式
do
命令列表
done例1:批量添加用户(脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
i=1
while [ $i -le 20 ]
do
useradd stu$i
echo "123456" | passwd --stdin stu$i &> /dev/null
i=`expr $i + 1`
done
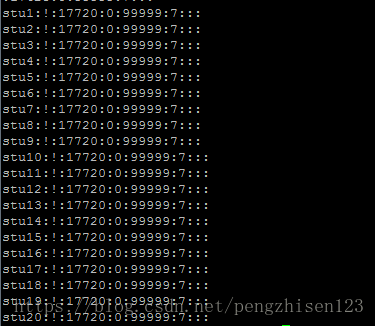
运行步骤如下:
1、创建一个while1.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi while1.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 while1.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./while1.sh
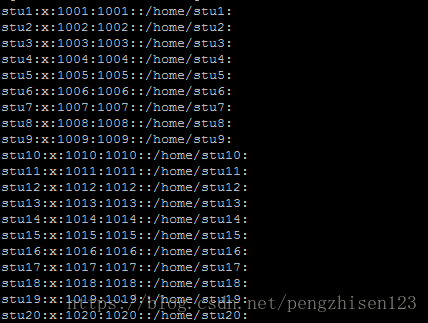
4、查看运行用户:cat /etc/passwd
5、查看运行密码:cat /etc/shadow
例2:批量删除用户(脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
aa=`cat /etc/passwd | grep "/bin/bash"|grep -v "root"|cut -d ":" -f 1`
for i in $aa
do
userdel -r $i
done例3:使用for 批量添加用户(脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
aa=10
for ((i=1;i<=$aa;i=i+1))
do
useradd stu$i
echo "123456" | passwd --stdin stu$i &> /dev/null
echo $i
done4、case 多重分支语句
根据变量的不同取值,分别执行不同的命令操作
例1:打印选择列表,输出选择 (脚本内容如下)
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "shanghai: 1\n"
echo -e "beijing: 2\n"
echo -e "chengdu: 3\n"
read -p "input your choice:" -t 30 choi
case $choi in
"1")
echo "shanghai!!!"
;;
"2")
echo "beijing!!!"
;;
"3")
echo "chengdu!!!"
;;
*)
echo "qing chongxin shuru!"
;;
esac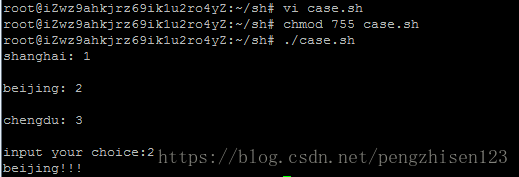
运行步骤如下:
1、创建一个case.sh的shell脚本并编辑上述内容:vi case.sh
2、修改该脚本文件的权限:chmod 755 case.sh
3、通过相对路径执行该脚本文件:./case.sh
4、从键盘输入一个数字:2
5、运行结果如上图
三、apache启动脚本分析
启动Apache命令:/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd start
其脚本内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
#
# httpd Startup script for the Apache HTTP Server
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
#自启动设定 -代表自启动级别,85(S85)代表启动序号,15(K15)代表关闭序号。
# description: The Apache HTTP Server is an efficient and extensible \
# server implementing the current HTTP standards.
#服务描述。以上两行用于apache自启动。
# processname: httpd
# config: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/httpd
# pidfile: /var/run/httpd/httpd.pid
#
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: httpd
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network
# Should-Start: distcache
# Short-Description: start and stop Apache HTTP Server
# Description: The Apache HTTP Server is an extensible server
# implementing the current HTTP standards.
### END INIT INFO
#以上都是注释。
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
#"."其实就是source,就是调用functions文件。
if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/httpd ]; then
. /etc/sysconfig/httpd
fi
#判断httpd如果是文件,则调用httpd文件。
# Start httpd in the C locale by default.
HTTPD_LANG=${HTTPD_LANG-"C"}
#定义变量HTTPD_LANG的值。并追加变量的值为C,即英文。
# This will prevent initlog from swallowing up a pass-phrase prompt if
# mod_ssl needs a pass-phrase from the user.
INITLOG_ARGS=""
# Set HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker in /etc/sysconfig/httpd to use a server
# with the thread-based "worker" MPM; BE WARNED that some modules may not
# work correctly with a thread-based MPM; notably PHP will refuse to start.
# Path to the apachectl script, server binary, and short-form for messages.
apachectl=/usr/sbin/apachectl
httpd=${HTTPD-/usr/sbin/httpd}
prog=httpd
pidfile=${PIDFILE-/var/run/httpd/httpd.pid}
lockfile=${LOCKFILE-/var/lock/subsys/httpd}
#定义一系列变量,用于后面的执行。
RETVAL=0
#定义全局命令返回变量。
STOP_TIMEOUT=${STOP_TIMEOUT-10}
# The semantics of these two functions differ from the way apachectl does
# things -- attempting to start while running is a failure, and shutdown
# when not running is also a failure. So we just do it the way init scripts
# are expected to behave here.
start() {
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
LANG=$HTTPD_LANG daemon --pidfile=${pidfile} $httpd $OPTIONS
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && touch ${lockfile}
return $RETVAL
}
#定义start函数,用于apache的启动。
#如果守护进程/usr/sbin/httpd 启动成功($RETVAL = 0),就建立/var/lock/subsys/httpd文件(touch #${lockfile})。通过$httpd变量执行/usr/sbin/httpd命令启动apache。通过$pidfile变量调用apache
#的PID。通过变量$OPTIONS定义命令执行时的初始化环境配置,依赖/etc/sysconfig/httpd文件。
# When stopping httpd, a delay (of default 10 second) is required
# before SIGKILLing the httpd parent; this gives enough time for the
# httpd parent to SIGKILL any errant children.
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc -p ${pidfile} -d ${STOP_TIMEOUT} $httpd
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f ${lockfile} ${pidfile}
}
#定义stop函数,用来关闭apache服务,关闭服务之后会删除pid文件。
reload() {
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
if ! LANG=$HTTPD_LANG $httpd $OPTIONS -t >&/dev/null; then
RETVAL=6
echo $"not reloading due to configuration syntax error"
failure $"not reloading $httpd due to configuration syntax error"
else
# Force LSB behaviour from killproc
LSB=1 killproc -p ${pidfile} $httpd -HUP
RETVAL=$?
if [ $RETVAL -eq 7 ]; then
failure $"httpd shutdown"
fi
fi
echo
}
#定义reload函数,用于apache的重新加载。
#通过/usr/sbin/httpd –t命令判断apache的配置文件。如果配置文件报错,则输出错误提示。如果配
#置文件正确,则重新加载apache。
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
#判断执行脚本后的第一个参数的值,$1表示执行脚本时的第一个参数。
start)
start
;;
;;
#如果参数值为start,则调用start函数。
stop)
stop
;;
#如果参数值为stop,则调用stop函数。
status)
status -p ${pidfile} $httpd
RETVAL=$?
;;
#如果参数值为status,则执行status –p $httpd命令测试apache状态。
restart)
stop
start
;;
#如果参数值为restart,则先调用stop函数,再调用start函数
condrestart|try-restart)
if status -p ${pidfile} $httpd >&/dev/null; then
stop
start
fi
;;
#如果参数值为condrestart或try-restart,则只有apache服务是已经运行时才先调用stop函数,再调
#用start函数,重启apache。如果apache服务没有运行,则不重启apache。
force-reload|reload)
reload
;;
#如果参数值为force-reload或reload,则调用reload函数。
graceful|help|configtest|fullstatus)
$apachectl $@
RETVAL=$?
;;
#如果参数是graceful或help或configtest或fullstatus,则执行/usr/sbin/apachectl命令,并把参
#数作为命令的参数传入apachectl命令。
*)
echo $"Usage: $prog {start|stop|restart|condrestart|try-restart|force-reload|reload|status|fullstatus|graceful|help|configtest}"
RETVAL=2
#如果输出的参数不是以上任何参数,则输出错误信息
esac
exit $RETVAL