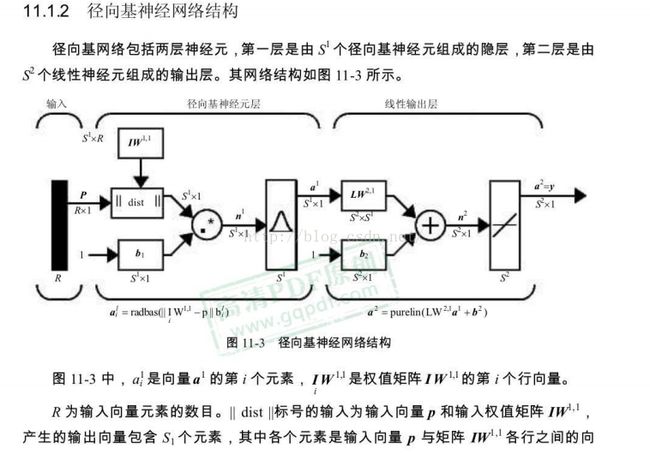
径向基神经网络(实例故障分类)
径向神经网络的创建:
调用格式:
net=newrbe(p,t,spread) -------------------p t分别为输入和输出样本,spread 为径向神经网络的散布常数
或者更高效的神经网络
net=newrb(p,t,goal,spread);
概率神经网络的创建:
P = [0 0;1 1;0 3;1 4;3 1;4 1;4 3]',
Tc = [1 1 2 2 3 3 3],
T = ind2vec(Tc); %吧分类标签转换成向量的形式
net = newpnn(P,T); %创建概率神经网络
Y = sim(net,P); %生成概率神经网络计算的值
Yc = vec2ind(Y) %将向量标签改换成位置标签
P2 = [1 4;0 1;5 2]',
Y = sim(net,P2);
Yc = vec2ind(Y)
newgrnn(p,t)
P = [4 5 6];
T = [1.5 3.6 6.7];
net = newgrnn(P,T);
P = 4.5;
v = sim(net,P),
径向神经网络的设计实例:
径向基网络函数的逼近:
P = -1:.1:1;
T = [-.9602 -.5770 -.0729 .3771 .6405 .6600 .4609 ...
.1336 -.2013 -.4344 -.5000 -.3930 -.1647 .0988 ...
.3072 .3960 .3449 .1816 -.0312 -.2189 -.3201];
plot(P,T,'+');
title('训练样本(Training Vectors)');
xlabel('输入样本向量(Input Vector P)');
ylabel('目标向量(Target Vector T)');
p = -3:.1:3;
a = radbas(p); %隐含层和输出层之间的径向传递函数
plot(p,a)
title('径向基传递函数');
xlabel('输入 p');
ylabel('输出 a');
a2 = radbas(p-1.5);
a3 = radbas(p+2);
a4 = a + a2*1 + a3*0.5;
plot(p,a,'b-',p,a2,'b-',p,a3,'b-',p,a4,'m--')
title('径向基传递函数加权和');
xlabel('输入 p');
ylabel('输出 a');
eg = 0.02; % 期望均方误差
sc = 1; % 杂散常数
net = newrb(P,T,eg,sc); %生成径向基神经网络,并且进行训练
plot(P,T,'+');
xlabel('Input');
X = -1:.01:1;
Y = sim(net,X); %生成预测的值
hold on;
plot(X,Y);
hold off;
legend({'目标向量','网络输出'})
下面是散布常数选择不当时的场景。
P = -1:.1:1;
T = [-.9602 -.5770 -.0729 .3771 .6405 .6600 .4609 ...
.1336 -.2013 -.4344 -.5000 -.3930 -.1647 .0988 ...
.3072 .3960 .3449 .1816 -.0312 -.2189 -.3201];
plot(P,T,'+');
title('训练样本(Training Vectors)');
xlabel('输入样本向量(Input Vector P)');
ylabel('目标向量(Target Vector T)');
eg = 0.02; % 期望均方误差
sc = .01; % 散布常数
net = newrb(P,T,eg,sc);
X=-1:.01:1;
Y=sim(net,X);
hold on;
plot(X,Y);
hold off;
P = -1:.1:1;
T = [-.9602 -.5770 -.0729 .3771 .6405 .6600 .4609 ...
.1336 -.2013 -.4344 -.5000 -.3930 -.1647 .0988 ...
.3072 .3960 .3449 .1816 -.0312 -.2189 -.3201];
plot(P,T,'+');
title('训练样本(Training Vectors)');
xlabel('输入样本向量(Input Vector P)');
ylabel('目标向量(Target Vector T)');
eg = 0.02; % 期望均方误差
sc =100; % 散布常数
net = newrb(P,T,eg,sc);
X=-1:.01:1;
Y=sim(net,X);
hold on;
plot(X,Y);
hold off;
P = [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8];
T = [0 1 2 3 2 1 2 1];
plot(P,T,'.','markersize',30)
axis([0 9 -1 4])
title('输入输出样本')
xlabel('P')
ylabel('T')
%%
spread = 0.7;
net = newgrnn(P,T,spread);
A = sim(net,P);
hold on
outputline = plot(P,A,'o','markersize',10,'color',[1 0 0]);
title('网络输出与样本比较')
xlabel('P')
ylabel('T and A')
%%
p = 3.5;
a = sim(net,p);
plot(p,a,'+','markersize',10,'color',[1 0 0]);
title('新输入值')
xlabel('P and p')
ylabel('T and a')
%%
P2 = 0:.1:9;
A2 = sim(net,P2);
plot(P2,A2,'linewidth',4,'color',[1 0 0])
title('网络拟合的函数曲线')
xlabel('P and P2')
ylabel('T and A2')
概率神经网络的分类问题:
P = [1 2; 2 2; 1 1]';
Tc = [1 2 3];
plot(P(1,:),P(2,:),'.','markersize',30)
for i=1:3, text(P(1,i)+0.1,P(2,i),sprintf('class %g',Tc(i))), end
axis([0 3 0 3])
title('3个样本向量')
xlabel('P(1,:)')
ylabel('P(2,:)')
%%
T = ind2vec(Tc);
spread = 1;
net = newpnn(P,T,spread);
A = sim(net,P);
Ac = vec2ind(A);
plot(P(1,:),P(2,:),'o','markersize',10)
axis([0 3 0 3])
for i=1:3,text(P(1,i)+0.1,P(2,i),sprintf('class %g',Ac(i))),end
title('网络仿真测试结果')
xlabel('P(1,:)')
ylabel('P(2,:)')
%%
p = [2; 1.5];
a = sim(net,p);
ac = vec2ind(a);
hold on
plot(p(1),p(2),'.','markersize',30,'color',[1 0 0])
text(p(1)+0.1,p(2),sprintf('class %g',ac))
hold off
title('新输入样本的分类仿真结果')
xlabel('P(1,:) and p(1)')
ylabel('P(2,:) and p(2)')
%%
p1 = 0:.05:3;
p2 = p1;
[P1,P2] = meshgrid(p1,p2);
pp = [P1(:) P2(:)]';
aa = sim(net,pp);
aa = full(aa);
m = mesh(P1,P2,reshape(aa(1,:),length(p1),length(p2)));
%%
set(m,'facecolor',[0 0.5 1],'linestyle','none');
hold on
m = mesh(P1,P2,reshape(aa(2,:),length(p1),length(p2)));
set(m,'facecolor',[0 1.0 0.5],'linestyle','none');
m = mesh(P1,P2,reshape(aa(3,:),length(p1),length(p2)));
set(m,'facecolor',[0.5 0 1],'linestyle','none');
plot3(P(1,:),P(2,:),[1 1 1]+0.1,'.','markersize',30)
%%
plot3(p(1),p(2),1.1,'.','markersize',30,'color',[1 0 0])
hold off
view(2)
title('3类划分区域')
xlabel('P(1,:) and p(1)')
ylabel('P(2,:) and p(2)')
[filename, pathname] = uigetfile('16_5_P.xls');
file=[pathname filename];
x=xlsread(file);
p=x;
p=p';
t1=[0.9 0.1 0.1]'
t2=[0.1 0.9 0.1]'
t3=[0.1 0.1 0.9]'
t = [t1 t1 t1 t1 t1 t2 t2 t2 t2 t2 t3 t3 t3 t3 t3];
spread = 0.6;
net = newrbe(p,t,spread);
[filename, pathname] = uigetfile('16_5_Ptest.xls');
file=[pathname filename];
xtest=xlsread(file);
ptest=xtest;
ptest=ptest';
ans = sim(net, ptest),