spring security 4 filter UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(一)
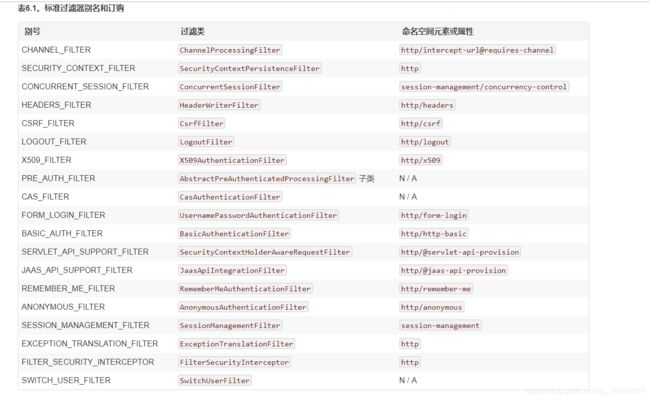
spring security 就是由一系列filter组成的一个安全认证框架,熟悉其中一些重要的filter是对熟悉spring security本身就是一种方式。首先我将先附上spring security官网上几个默认的filter
然后我会重点讲几个,今天我们先说UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter这个过滤器,从官网上的截图可以看到左边的别名是“FORM_LOGIN_FILTER”,最右边的是其namespace element(命名空间)以及 attribute(配置属性),可以看到这个filter显示的是http/form-login。那这filter主要做什么,其实我们从别名和属性可以看主要处理form-login,form表单登录请求处理的filter。这个就体现出其重要性了,毕竟是登录这一块。
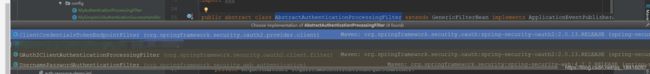
我们先来看一下源码,我们先看一下UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
protected ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
protected AuthenticationDetailsSource authenticationDetailsSource = new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource();
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
private RememberMeServices rememberMeServices = new NullRememberMeServices();
private RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher;
private boolean continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication = false;
private SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionStrategy = new NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy();
private boolean allowSessionCreation = true;
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler = new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler();
private AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler = new SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler();
protected AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter(String defaultFilterProcessesUrl) {
this.setFilterProcessesUrl(defaultFilterProcessesUrl);
}
protected AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter(RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher) {
Assert.notNull(requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher, "requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher cannot be null");
this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher = requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
Assert.notNull(this.authenticationManager, "authenticationManager must be specified");
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
// 判断访问是否需要过滤
// 默认过滤 /login post方式
if (!this.requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
authResult = this.attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
return;
}
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var8) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", var8);
this.unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var8);
return;
} catch (AuthenticationException var9) {
this.unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var9);
return;
}
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
this.successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
}
protected boolean requiresAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
return this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher.matches(request);
}
public abstract Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2) throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException;
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: " + authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass()));
}
this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed.toString(), failed);
this.logger.debug("Updated SecurityContextHolder to contain null Authentication");
this.logger.debug("Delegating to authentication failure handler " + this.failureHandler);
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
this.failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}
protected AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() {
return this.authenticationManager;
}
public void setAuthenticationManager(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
}
public void setFilterProcessesUrl(String filterProcessesUrl) {
this.setRequiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher(filterProcessesUrl));
}
public final void setRequiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher(RequestMatcher requestMatcher) {
Assert.notNull(requestMatcher, "requestMatcher cannot be null");
this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher = requestMatcher;
}
public RememberMeServices getRememberMeServices() {
return this.rememberMeServices;
}
public void setRememberMeServices(RememberMeServices rememberMeServices) {
Assert.notNull(rememberMeServices, "rememberMeServices cannot be null");
this.rememberMeServices = rememberMeServices;
}
public void setContinueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication(boolean continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication = continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication;
}
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher) {
this.eventPublisher = eventPublisher;
}
public void setAuthenticationDetailsSource(AuthenticationDetailsSource authenticationDetailsSource) {
Assert.notNull(authenticationDetailsSource, "AuthenticationDetailsSource required");
this.authenticationDetailsSource = authenticationDetailsSource;
}
public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messages = new MessageSourceAccessor(messageSource);
}
protected boolean getAllowSessionCreation() {
return this.allowSessionCreation;
}
public void setAllowSessionCreation(boolean allowSessionCreation) {
this.allowSessionCreation = allowSessionCreation;
}
public void setSessionAuthenticationStrategy(SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionStrategy) {
this.sessionStrategy = sessionStrategy;
}
public void setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler) {
Assert.notNull(successHandler, "successHandler cannot be null");
this.successHandler = successHandler;
}
public void setAuthenticationFailureHandler(AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler) {
Assert.notNull(failureHandler, "failureHandler cannot be null");
this.failureHandler = failureHandler;
}
protected AuthenticationSuccessHandler getSuccessHandler() {
return this.successHandler;
}
protected AuthenticationFailureHandler getFailureHandler() {
return this.failureHandler;
}
}
我们先看一下其属性,有很多我们熟悉的比方:AuthenticationSuccessHandler,AuthenticationFailureHandler,SessionAuthenticationStrategy,AuthenticationManager这些可以试试可以在我们在配置spring security 的时候看到这些类,这些类都有默认的实现类,也可以被自定义类set进去。
然后我们看一下filter类中最重要的doFilter方法
if (!this.requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} 这个方法是控制只拦截请求为“/login”,请求方式为“post”的,如果符合条件就进入该拦截器的业务处理,不是就进入下面的filter。
然后满足条件的就即将进入下面的业务处理
try {
// 进行认证操作,获取认证信息的主要方法
authResult = this.attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
return;
}
//判断session是否过期、把当前用户放入session
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var8) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", var8);
this.unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var8);
return;
} catch (AuthenticationException var9) {
this.unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var9);
return;
}我们看到在 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter这个类中的attemptAuthentication这个方法是一个抽象方法,具体实现由它的子类去实现。现在我们来看看它的子类有哪些。
我们可以看到子类有三个UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter,ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter
我们先讲一下跟登录,账号,密码有关UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter。我们先说一下这个类在什么情况下会加载到容器里面。
首先我们看真假配置的securityConfiguration类
//defaultSuccessUrl :成功登录过程后,用户将被重定向到页面 - 默认情况下,该页面是Web应用程序的根目录。
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/w/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin()我们点到formLogin()方法
public FormLoginConfigurer formLogin() throws Exception {
return (FormLoginConfigurer)this.getOrApply(new FormLoginConfigurer());
} 这个代码是的springsecurity启动了FormLoginConfigurer,所以只要你谢了formLogin方法就应该可以启动这个过滤器了。然后我们继续往下看看,我们可以看到FormLoginConfigurer类的这个方法
public FormLoginConfigurer() {
super(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(), (String)null);
this.usernameParameter("username");
this.passwordParameter("password");
}super方法会去执行父类的AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer的如下方法
protected AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer(F authenticationFilter, String defaultLoginProcessingUrl) {
this.authFilter = authenticationFilter;
this.setLoginPage("/login");
if (defaultLoginProcessingUrl != null) {
this.loginProcessingUrl(defaultLoginProcessingUrl);
}
}这样我们的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器就开始起作用了。
继续回到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter类来,看一下attemptAuthentication方法
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
// 将账号,密码封装到相应的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 中
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}重点我们看一下如下这一段认证的核心代码
this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);这就是AuthenticationManager接口调用authenticate方法,AuthenticationManager接口的实现类是ProviderManager.现在我们来看一下ProviderManager中的authenticate方法
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
Iterator var6 = this.getProviders().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
AuthenticationProvider provider = (AuthenticationProvider)var6.next();
if (provider.supports(toTest)) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using " + provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
this.copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
} catch (AccountStatusException var11) {
this.prepareException(var11, authentication);
throw var11;
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var12) {
this.prepareException(var12, authentication);
throw var12;
} catch (AuthenticationException var13) {
lastException = var13;
}
}
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
try {
result = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
} catch (ProviderNotFoundException var9) {
;
} catch (AuthenticationException var10) {
lastException = var10;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && result instanceof CredentialsContainer) {
((CredentialsContainer)result).eraseCredentials();
}
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
} else {
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound", new Object[]{toTest.getName()}, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
this.prepareException((AuthenticationException)lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
}这个方法的作用就是将所有AuthenticationProvider都循环一遍,满足条件的AuthenticationProvider调用其authenticate方法。AuthenticationProvider类的其中一个跟jdbc有关的最常用的实现类DaoAuthenticationProvider
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
UserDetails loadedUser;
try {
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException var6) {
if (authentication.getCredentials() != null) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
this.passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(this.userNotFoundEncodedPassword, presentedPassword, (Object)null);
}
throw var6;
} catch (Exception var7) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(var7.getMessage(), var7);
}
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
} else {
return loadedUser;
}
}里面就有这么一个核心方法,这个核心方法里面就有一段核心代码
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);看到这里大家可能就清楚了,因为我们再配置自定义userDetailService的时候就可以自定义loadUserByname方法。loadUserByname方法得到一个user对象,然后在封装一下变成Authentication,最后放在session里面