kubernetes RBAC认证简介
概述
RBAC是Role-Based Access Control的简称,中文为基于角色的访问控制
RBAC使用“rbac.authorization.k8s.io”API组来驱动授权决策,允许管理员通过Kubernetes API动态配置策略。
从1.8开始,RBAC模式处于稳定版本,并由rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 API提供支持。
要启用RBAC,请使用--authorization-mode = RBAC启动apiserver。
Role and ClusterRole
在RBAC API中,角色包含表示一组权限的规则。 权限纯粹是累加性的(没有“拒绝”规则)。 可以在某个空间指定角色Role或使用ClusterRole在集群范围内定义角色。
Role
Role只能用于授予对单个名称空间内资源的访问权限。 以下是可用于授予对Pod的读取权限的default名称空间中的角色示例:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]ClusterRole
ClusterRole除了拥有Role的权限之外,又因为它是集群内的,所以ClusterRole另外还有其他权限
- 访问集群内的资源如node的资源
- 非资源的endpoints 如
/healthz - 能访问集群内的所有的空间的资源,如
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
# "namespace" omitted since ClusterRoles are not namespaced
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
这个ClusterRole可以访问集群内的所有空间的资源RoleBinding and ClusterRoleBinding
RoleBinding 对应—> Role和ClusterRole
ClusterRoleBinding 对应—>ClusterRole
他们可以是针对某个用户或者某类用户或者是用户组以及service accounts
RoleBinding 对应—> Role
# This role binding allows "jane" to read pods in the "default" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: jane # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
这个表示用户jane可以访问空间default下所有pods的资源信息RoleBinding 对应—> ClusterRole
RoleBinding还可以引用ClusterRole来授予RoleBinding命名空间中ClusterRole中定义的名称空间资源的权限。 这允许管理员为整个群集定义一组通用角色,然后在多个名称空间内重用它们。
# This role binding allows "dave" to read secrets in the "development" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-secrets
namespace: development # This only grants permissions within the "development" namespace.
subjects:
- kind: User
name: dave # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
这个表示用户dave可以访问集群内namespace为development下的所有的secret资源ClusterRoleBinding 对应—>ClusterRole
# This cluster role binding allows anyone in the "manager" group to read secrets in any namespace.
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: manager # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
表示在group manager 中的成员都可以访问所有空间内的secret资源Referring to Resources
大多数资源都以其名称的字符串表示形式表示,如“pods”,就像它出现在相关API的URL中一样。 但是,一些Kubernetes API涉及“子资源”,例如pods的日志。 pods日志的URL是:
GET /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}/log
在这种情况下,“pods”是名称空间资源,“log”是pod的子资源。 要在RBAC角色中表示这种情况,请使用/来分隔资源和子资源。 要允许主题读取Pod和Pod日志,可以这么写:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/log"]//用pods/log实现访问pod的日志的目的
verbs: ["get", "list"]资源也可以通过resourceNames列表的某些请求的名称引用。 指定时,使用“get”,“delete”,“update”和“patch”动词的请求可以限制为资源的单个实例。
例如要限制对configmap只允许“get“,”update”操作权限,可以这么写
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: configmap-updater
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["my-configmap"]
verbs: ["update", "get"]如果设置了 resourceNames 那 verb 就不能是 list, watch, create, deletecollection. 因为资源名resourceNames 不存在list, watch, create, deletecollection请求的URL中
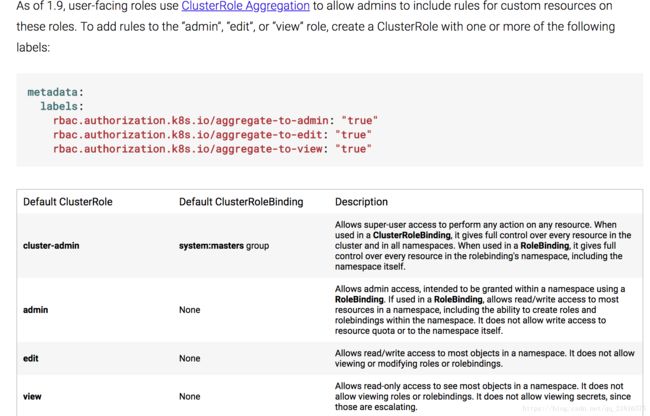
Aggregated ClusterRoles
从kubernetes1.9开始,可以通过使用aggregationRule组合其他ClusterRoles来创建ClusterRoles。 聚集的ClusterRoles的权限由控制器管理,并通过联合与提供的标签选择器匹配的任何ClusterRole的规则来填充。 聚合ClusterRole示例:
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: monitoring
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
rules: [] # Rules are automatically filled in by the controller manager.创建拥有标签rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring:true的ClusterRole
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: monitoring-endpoints
labels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
# These rules will be added to the "monitoring" role.
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
Resources: ["services", "endpoints", "pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]Aggregated ClusterRoles例子,该例子表示 aggregate-cron-tabs-edit对crontabs拥有”get”, “list”, “watch”, “create”, “update”, “patch”, “delete”权限,而aggregate-cron-tabs-view只有”get”, “list”, “watch”操作权限
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: aggregate-cron-tabs-edit
labels:
# Add these permissions to the "admin" and "edit" default roles.
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
rules:
- apiGroups: ["stable.example.com"]
resources: ["crontabs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: aggregate-cron-tabs-view
labels:
# Add these permissions to the "view" default role.
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
rules:
- apiGroups: ["stable.example.com"]
resources: ["crontabs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]Role Examples
只允许读的权限
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]允许读写的权限(对deployments的extensions或者apps的api)
rules:
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]允许读pods,允许读写jobs
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]允许读名字为my-config的ConfigMap(必须与RoleBinding绑定,以限制单个命名空间中的单个ConfigMap)
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["my-config"]
verbs: ["get"]允许读node上的资源(因为节点是集群范围的,所以必须在ClusterRole中绑定一个ClusterRoleBinding才能生效)
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]允许post get操作的例子
rules:
- nonResourceURLs: ["/healthz", "/healthz/*"] # '*' in a nonResourceURL is a suffix glob match
verbs: ["get", "post"]Referring to Subjects
RoleBinding 和 ClusterRoleBinding帮定某个具体的subjects,subjects可以是 groups, users或者 service accounts,例如可以是名字test或者邮箱,还有某类前缀等等,但是有些前缀是系统的保留的如system:就不能使用
Service Accounts 拥有 system:serviceaccount:前缀的用户属于拥有system:serviceaccounts:的groups.
例子
用户名为[email protected]的用户
subjects:
- kind: User
name: "[email protected]"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io组名为frontend-admins
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: "frontend-admins"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io名字为default空间是kube-system的service
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: kube-systemservice accounts 为qa
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:qa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io任何服务service accounts都生效
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io所有经过认账的用户(kubernetes 1.5+)
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io未认证的用户(kubernetes 1.5+)
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io所有用户(kubernetes 1.5+)
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iodefault Roles and Role Bindings
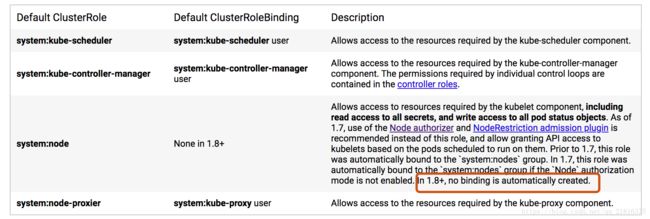
API服务器创建一组默认的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding对象。 其中很多是system:前缀,表示该资源由基础设施“拥有”。 对这些资源的修改可能会影响集群的功能。
例如 system:节点ClusterRole。 该角色定义了kubelets的权限。 如果角色被修改,它将会影响kubelets的正常运行。
默认的Roles and Role Bindings 都带有这个labelkubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults
禁用Auto-reconciliation功能
在annotation 添加 rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate:false就可以实现,不自动更新权限
Discovery Roles
User-facing Roles(本人能力有限)直接引用官方的
Controller Roles
控制器角色的前缀为system:controller:,如果启用--use-service-account-credentials,将会在各自的权限下管理 否则必须授予所有的访问权限
system:controller:attachdetach-controller
system:controller:certificate-controller
system:controller:cronjob-controller
system:controller:daemon-set-controller
system:controller:deployment-controller
system:controller:disruption-controller
system:controller:endpoint-controller
system:controller:generic-garbage-collector
system:controller:horizontal-pod-autoscaler
system:controller:job-controller
system:controller:namespace-controller
system:controller:node-controller
system:controller:persistent-volume-binder
system:controller:pod-garbage-collector
system:controller:pv-protection-controller
system:controller:pvc-protection-controller
system:controller:replicaset-controller
system:controller:replication-controller
system:controller:resourcequota-controller
system:controller:route-controller
system:controller:service-account-controller
system:controller:service-controller
system:controller:statefulset-controller
system:controller:ttl-controller
权限升级
例如:授予用户user-1在user-1-namespace下admin, edit,以及 view的权限
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: role-grantor
rules:
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["rolebindings"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["clusterroles"]
verbs: ["bind"]
resourceNames: ["admin","edit","view"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: role-grantor-binding
namespace: user-1-namespace
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: role-grantor
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: User
name: user-1使用命令行授予命名空间或整个集群内的角色。
kubectl create rolebinding
授予指定空间 Role 或者 ClusterRole 角色权限 :
授予用户为bob在空间acme下 admin ClusterRole 权限:
kubectl create rolebinding bob-admin-binding --clusterrole=admin --user=bob --namespace=acme授予service account为myapp空间为acme的 view ClusterRole 权限:
kubectl create rolebinding myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=acme:myapp --namespace=acmekubectl create clusterrolebinding
授予用户root cluster-admin ClusterRole 集群权限:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding root-cluster-admin-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=root授予用户kubelet system:node ClusterRole 集群权限:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubelet-node-binding --clusterrole=system:node --user=kubelet授予 service account 为myapp空间为acme view ClusterRole 集群权限:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=acme:myappService Account Permissions
kubernetes RBAC默认不授权给除了空间名为kube-system之外的Service Account权限,留给用户自主管理,这样就让用户自己管理好解决,更好地掌握权限的粒度
为特定于应用程序的服务帐户授予角色(最佳做法):
前提: pod spec指定serviceAccountName且创建了对应的serviceaccount
授予service account 为my-sa 在空间my-namespace下 read-only 权限
kubectl create rolebinding my-sa-view \
--clusterrole=view \
--serviceaccount=my-namespace:my-sa \
--namespace=my-namespace授予 service account 为default 在空间my-namespace下的read-only权限
注意k8s默认就生成了一个name为default的service account
kubectl create rolebinding default-view \
--clusterrole=view \
--serviceaccount=my-namespace:default \
--namespace=my-namespace许多插件都是在service account为default 空间为kube-system下,因此要赋予插件以super-user的权限就必须授予service account为default 空间为kube-system下cluster-admin的权限
kubectl create clusterrolebinding add-on-cluster-admin \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--serviceaccount=kube-system:default授权my-namespace空间下所有service accounts的read-only权限
kubectl create rolebinding serviceaccounts-view \
--clusterrole=view \
--group=system:serviceaccounts:my-namespace \
--namespace=my-namespace授予所有空间下所有service accounts的 read-only权限
kubectl create clusterrolebinding serviceaccounts-view \
--clusterrole=view \
--group=system:serviceaccounts授予所有service accounts super-user 权限
kubectl create clusterrolebinding serviceaccounts-cluster-admin \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--group=system:serviceaccounts参考
rbac