kube-apiserver v1.11.2 源码分析
本文分析的kubernetes版本
➜ kube-apiserver git:(v1.11.2-custom) ✗ kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"11", GitVersion:"v1.11.2", GitCommit:"bb9ffb1654d4a729bb4cec18ff088eacc153c239", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2018-08-08T16:31:16Z", GoVersion:"go1.10.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"11+", GitVersion:"v1.11.0-168+f47446a730ca03", GitCommit:"f47446a730ca037473fb3bf0c5abeea648c1ac12", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2018-08-25T21:05:52Z", GoVersion:"go1.10.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
分析思路
1.了解架构,用的是什么技术栈,为什么要选择该技术栈
2.理解如何注入各种对象访问的restful url
3.如何GET或者修改etcd数据
了解架构,用的是什么技术栈,为什么要选择该技术栈
技术栈
1.命令行工具包
github.com/spf13/pflag
github.com/spf13/cobra
该包如何使用直接查看github上的README或者查看测试文件
2.go restful框架
go restful是restful 的golang语言的框架,github代码为github.com/emicklei/go-restful
简单例子
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/emicklei/go-restful"
"github.com/emicklei/go-restful-swagger12"
"google.golang.org/appengine"
"google.golang.org/appengine/memcache"
)
// This example is functionally the same as ../restful-user-service.go
// but it`s supposed to run on Goole App Engine (GAE)
//
// contributed by ivanhawkes
type User struct {
Id, Name string
}
type UserService struct {
// normally one would use DAO (data access object)
// but in this example we simple use memcache.
}
func (u UserService) Register() {
ws := new(restful.WebService) //新建一个webserver
ws.
Path("/users").
Consumes(restful.MIME_XML, restful.MIME_JSON).
Produces(restful.MIME_JSON, restful.MIME_XML) // you can specify this per route as well
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{user-id}").To(u.findUser).
// docs
Doc("get a user").
Param(ws.PathParameter("user-id", "identifier of the user").DataType("string")).
Writes(User{})) // on the response
ws.Route(ws.PATCH("").To(u.updateUser).
// docs
Doc("update a user").
Reads(User{})) // from the request
ws.Route(ws.PUT("/{user-id}").To(u.createUser).
// docs
Doc("create a user").
Param(ws.PathParameter("user-id", "identifier of the user").DataType("string")).
Reads(User{})) // from the request
ws.Route(ws.DELETE("/{user-id}").To(u.removeUser).
// docs
Doc("delete a user").
Param(ws.PathParameter("user-id", "identifier of the user").DataType("string")))
restful.Add(ws) // web server 加入container
}
// GET http://localhost:8080/users/1
//
func (u UserService) findUser(request *restful.Request, response *restful.Response) {
c := appengine.NewContext(request.Request)
id := request.PathParameter("user-id")
usr := new(User)
_, err := memcache.Gob.Get(c, id, &usr)
if err != nil || len(usr.Id) == 0 {
response.WriteErrorString(http.StatusNotFound, "User could not be found.")
} else {
response.WriteEntity(usr)
}
}
// PATCH http://localhost:8080/users
// 1 Melissa Raspberry 1 Melissa .appspot.com"
}
}
func init() {
u := UserService{}
u.Register()
// Optionally, you can install the Swagger Service which provides a nice Web UI on your REST API
// You need to download the Swagger HTML5 assets and change the FilePath location in the config below.
// Open .appspot.com/apidocs and enter http://.appspot.com/apidocs.json in the api input field.
config := swagger.Config{
WebServices: restful.RegisteredWebServices(), // you control what services are visible
WebServicesUrl: getGaeURL(),
ApiPath: "/apidocs.json",
// Optionally, specify where the UI is located
SwaggerPath: "/apidocs/",
// GAE support static content which is configured in your app.yaml.
// This example expect the swagger-ui in static/swagger so you should place it there :)
SwaggerFilePath: "static/swagger"}
swagger.InstallSwaggerService(config)
}
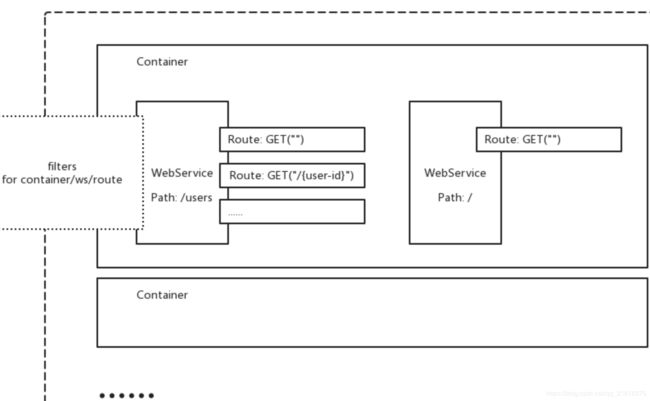
通过简单的例子,可以知道 go-restful就是由 container webserver route三个对象组成的
Route
路由包含两种,一种是RouterJSR311,一种是快速路由CurlyRouter。
CurlyRouter支持正则表达式和动态参数,相比RouterJSR11更加轻量级,k8s使用的是快速路由。
Route包含:http Method,URL Path,输入输出类型(JSON/YAML)以及回调函数restful.RouteFunction,响应内容类型(Accept)等。
官方描述
Configurable router:
(default) Fast routing algorithm that allows static elements, regular expressions and dynamic parameters in the URL path (e.g. /meetings/{id} or /static/{subpath:*}
Routing algorithm after JSR311 that is implemented using (but does not accept) regular expressions
webService
WebService逻辑上是Route的集合,功能上主要是为一组Route统一设置包括root path,请求响应的数据类型等一些通用的属性。WebService必须加入到Container中才能生效。
Container
Container逻辑上是WebService的集合,包括一组restful.WebService和一个http.ServeMux对象,使用RouteSelector进行请求派发。
另外注意一点 webservice必须要添加到container才能生效
3.用的日志包
github.com/golang/glog
4.数据持久化存储技术用的是etcd
https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd
kubernetes之所以要使用etcd作为后端存储技术,主要是因为etcd使用raft算法保证数据的一致性以及它拥有的watch机制
etcdv2版本以及etcdv3版本的Watch,以及过期机制如下两幅图


关于更多etcd的细节请参考官方文档etcd
kubernetes使用到的技术栈很多,上面主要是介绍我认为对分析源码起到重要作用的技术
为什么要用go-restful?
主要是该框架支持restful api,也便于kubernetes kube-apiserver支持多个版本的api
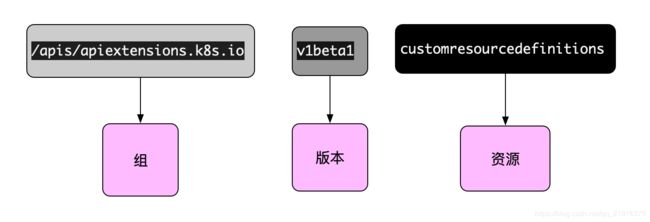
kubernetes 的api接口主要是由三部分构成
1.api组
2.api版本
3.api组下的某个版本的资源(pod deployment PVC daemonset statufulset storageclass,networkpolicy等等)
从代码k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/server/genericapiserver.go
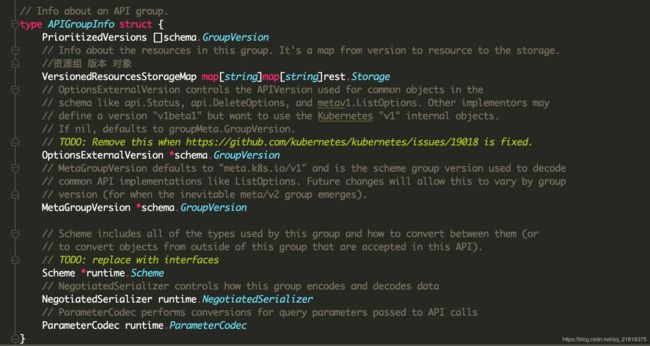
APIGroupInfo的结构体就可以看出kubernetes kube-apiserver都是根据以上三个元素构成api接口
讲完技术栈框架之后,下面就进入正题
首先先上一幅图
这幅图主要说明了kube-apiserver组件是如何使用go-restful框架注册路由,实现rest api的简单显示
下面我们详细地分析kube-apiserver的代码是如何实现的
理解如何注入各种对象访问的restful url
1.如何启动http监听端口
启动kube-apiserver,启动脚本如下
➜ kube-apiserver git:(v1.11.2-custom) ✗ cat run-kube-apiserver.sh
go run apiserver.go \
--enable-admission-plugins=NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger,ServiceAccount,PersistentVolumeLabel,DefaultStorageClass,ResourceQuota \
--anonymous-auth=false \
--advertise-address=0.0.0.0 \
--allow-privileged=true \
--audit-log-maxage=30 \
--audit-log-maxbackup=3 \
--audit-log-maxsize=100 \
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC \
--bind-address=0.0.0.0 \
--secure-port=6443 \
--client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/ca.pem \
--kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/kubernetes.pem \
--kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/kubernetes-key.pem \
--enable-swagger-ui=true \
--etcd-cafile=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/ca.pem \
--etcd-certfile=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/etcd.pem \
--etcd-keyfile=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/etcd-key.pem --etcd-servers="https://etcd-ip:port" \
--kubelet-https=true \
--insecure-bind-address=0.0.0.0 \
--insecure-port=8080 \
--service-account-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/ca-key.pem \
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.254.0.0/18 \
--service-node-port-range=30000-32000 \
--tls-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/kubernetes.pem \
--tls-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/kubernetes-key.pem \
--enable-bootstrap-token-auth \
--storage-media-type=application/json \
--log-dir=/var/log/kuernetes \
--v=2
执行脚本之前需要在目录$GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes执行make generated_files命令
详情请参考这边博客 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21816375/article/details/84929541
然后cd $GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-apiserver 执行启动脚本就可以,当然脚本所需要的启动文件也是必须的,读者可以自行生成
启动http端口的流程图大概是这样子的
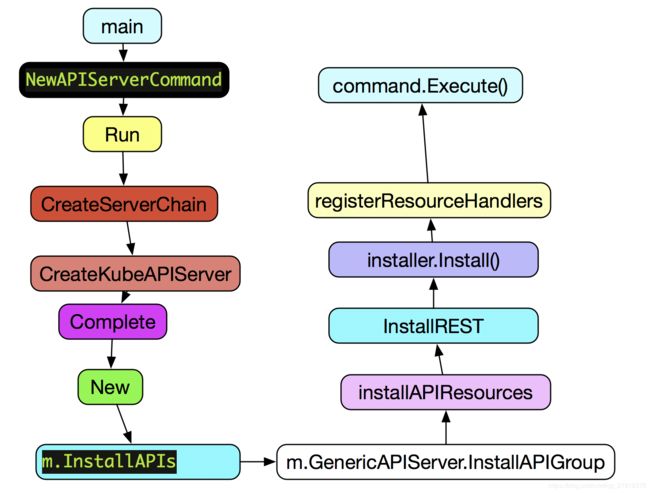
NewAPIServerCommand—>Run—>CreateServerChain—>BuildInsecureHandlerChain—>NonBlockingRun—>serveInsecurely—>RunServer
在函数RunServer下启动一个goroutine启动http端口
具体代码实现如下
CreateServerChain函数细节如下
// CreateServerChain creates the apiservers connected via delegation.
func CreateServerChain(completedOptions completedServerRunOptions, stopCh <-chan struct{}) (*genericapiserver.GenericAPIServer, error) {
nodeTunneler, proxyTransport, err := CreateNodeDialer(completedOptions)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
kubeAPIServerConfig, sharedInformers, versionedInformers, insecureServingOptions, serviceResolver, pluginInitializer, admissionPostStartHook, err := CreateKubeAPIServerConfig(completedOptions, nodeTunneler, proxyTransport)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// If additional API servers are added, they should be gated.
apiExtensionsConfig, err := createAPIExtensionsConfig(*kubeAPIServerConfig.GenericConfig, versionedInformers, pluginInitializer, completedOptions.ServerRunOptions, completedOptions.MasterCount)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
apiExtensionsServer, err := createAPIExtensionsServer(apiExtensionsConfig, genericapiserver.NewEmptyDelegate())
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
kubeAPIServer, err := CreateKubeAPIServer(kubeAPIServerConfig, apiExtensionsServer.GenericAPIServer, sharedInformers, versionedInformers, admissionPostStartHook)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// otherwise go down the normal path of standing the aggregator up in front of the API server
// this wires up openapi
kubeAPIServer.GenericAPIServer.PrepareRun()
// This will wire up openapi for extension api server
apiExtensionsServer.GenericAPIServer.PrepareRun()
// aggregator comes last in the chain
aggregatorConfig, err := createAggregatorConfig(*kubeAPIServerConfig.GenericConfig, completedOptions.ServerRunOptions, versionedInformers, serviceResolver, proxyTransport, pluginInitializer)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
//生成聚合api
aggregatorServer, err := createAggregatorServer(aggregatorConfig, kubeAPIServer.GenericAPIServer, apiExtensionsServer.Informers)
if err != nil {
// we don't need special handling for innerStopCh because the aggregator server doesn't create any go routines
return nil, err
}
//启用 8080端口
if insecureServingOptions != nil {
insecureHandlerChain := kubeserver.BuildInsecureHandlerChain(aggregatorServer.GenericAPIServer.UnprotectedHandler(), kubeAPIServerConfig.GenericConfig)
if err := kubeserver.NonBlockingRun(insecureServingOptions, insecureHandlerChain, kubeAPIServerConfig.GenericConfig.RequestTimeout, stopCh); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
return aggregatorServer.GenericAPIServer, nil
}
serveInsecurely函数
func serveInsecurely(insecureServingInfo *InsecureServingInfo, insecureHandler http.Handler, shutDownTimeout time.Duration, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
insecureServer := &http.Server{
Addr: insecureServingInfo.BindAddress,
Handler: insecureHandler,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
glog.Infof("Serving insecurely on %s", insecureServingInfo.BindAddress)
ln, _, err := options.CreateListener(insecureServingInfo.BindNetwork, insecureServingInfo.BindAddress)
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = server.RunServer(insecureServer, ln, shutDownTimeout, stopCh)
return err
}
RunServer函数
func RunServer(
server *http.Server,
ln net.Listener,
shutDownTimeout time.Duration,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
) error {
if ln == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("listener must not be nil")
}
// Shutdown server gracefully.
go func() {
<-stopCh
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), shutDownTimeout)
server.Shutdown(ctx)
cancel()
}()
go func() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
var listener net.Listener
listener = tcpKeepAliveListener{ln.(*net.TCPListener)}
if server.TLSConfig != nil {
listener = tls.NewListener(listener, server.TLSConfig)
}
err := server.Serve(listener)
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Stopped listening on %s", ln.Addr().String())
select {
case <-stopCh:
glog.Info(msg)
default:
panic(fmt.Sprintf("%s due to error: %v", msg, err))
}
}()
return nil
}
2.如何启动https监听端口
启动https端口的流程图大概是这样子的
NewAPIServerCommand—>Run—>server.PrepareRun().Run(stopCh)—>s.NonBlockingRun(stopCh)—>s.SecureServingInfo.Serve(s.Handler, s.ShutdownTimeout, internalStopCh)—>RunServer
NonBlockingRun函数
func (s preparedGenericAPIServer) NonBlockingRun(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
// Use an stop channel to allow graceful shutdown without dropping audit events
// after http server shutdown.
auditStopCh := make(chan struct{})
// Start the audit backend before any request comes in. This means we must call Backend.Run
// before http server start serving. Otherwise the Backend.ProcessEvents call might block.
if s.AuditBackend != nil {
if err := s.AuditBackend.Run(auditStopCh); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to run the audit backend: %v", err)
}
}
// Use an internal stop channel to allow cleanup of the listeners on error.
internalStopCh := make(chan struct{})
//启动https安全端口
if s.SecureServingInfo != nil && s.Handler != nil {
if err := s.SecureServingInfo.Serve(s.Handler, s.ShutdownTimeout, internalStopCh); err != nil {
close(internalStopCh)
return err
}
}
// Now that listener have bound successfully, it is the
// responsibility of the caller to close the provided channel to
// ensure cleanup.
go func() {
<-stopCh
close(internalStopCh)
s.HandlerChainWaitGroup.Wait()
close(auditStopCh)
}()
s.RunPostStartHooks(stopCh)
if _, err := systemd.SdNotify(true, "READY=1\n"); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Unable to send systemd daemon successful start message: %v\n", err)
}
return nil
}
Serve函数
func (s *SecureServingInfo) Serve(handler http.Handler, shutdownTimeout time.Duration, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
if s.Listener == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("listener must not be nil")
}
secureServer := &http.Server{
Addr: s.Listener.Addr().String(),
Handler: handler,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
TLSConfig: &tls.Config{
NameToCertificate: s.SNICerts,
// Can't use SSLv3 because of POODLE and BEAST
// Can't use TLSv1.0 because of POODLE and BEAST using CBC cipher
// Can't use TLSv1.1 because of RC4 cipher usage
MinVersion: tls.VersionTLS12,
// enable HTTP2 for go's 1.7 HTTP Server
NextProtos: []string{"h2", "http/1.1"},
},
}
if s.MinTLSVersion > 0 {
secureServer.TLSConfig.MinVersion = s.MinTLSVersion
}
if len(s.CipherSuites) > 0 {
secureServer.TLSConfig.CipherSuites = s.CipherSuites
}
if s.Cert != nil {
secureServer.TLSConfig.Certificates = []tls.Certificate{*s.Cert}
}
// append all named certs. Otherwise, the go tls stack will think no SNI processing
// is necessary because there is only one cert anyway.
// Moreover, if ServerCert.CertFile/ServerCert.KeyFile are not set, the first SNI
// cert will become the default cert. That's what we expect anyway.
for _, c := range s.SNICerts {
secureServer.TLSConfig.Certificates = append(secureServer.TLSConfig.Certificates, *c)
}
if s.ClientCA != nil {
// Populate PeerCertificates in requests, but don't reject connections without certificates
// This allows certificates to be validated by authenticators, while still allowing other auth types
secureServer.TLSConfig.ClientAuth = tls.RequestClientCert
// Specify allowed CAs for client certificates
secureServer.TLSConfig.ClientCAs = s.ClientCA
}
if s.HTTP2MaxStreamsPerConnection > 0 {
http2.ConfigureServer(secureServer, &http2.Server{
MaxConcurrentStreams: uint32(s.HTTP2MaxStreamsPerConnection),
})
}
glog.Infof("Serving securely on %s", secureServer.Addr)
return RunServer(secureServer, s.Listener, shutdownTimeout, stopCh)
}
RunServer函数,和启动http端口是同一个函数
func RunServer(
server *http.Server,
ln net.Listener,
shutDownTimeout time.Duration,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
) error {
if ln == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("listener must not be nil")
}
// Shutdown server gracefully.
go func() {
<-stopCh
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), shutDownTimeout)
server.Shutdown(ctx)
cancel()
}()
go func() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
var listener net.Listener
listener = tcpKeepAliveListener{ln.(*net.TCPListener)}
if server.TLSConfig != nil {
listener = tls.NewListener(listener, server.TLSConfig)
}
err := server.Serve(listener)
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Stopped listening on %s", ln.Addr().String())
select {
case <-stopCh:
glog.Info(msg)
default:
panic(fmt.Sprintf("%s due to error: %v", msg, err))
}
}()
return nil
}
3.注入url分析
注入url的基本流程图
NewAPIServerCommand—>Run—>CreateServerChain—>CreateKubeAPIServer—>kubeAPIServerConfig.Complete(versionedInformers).New(delegateAPIServer)—>m.InstallAPIs—>m.GenericAPIServer.InstallAPIGroup(&apiGroupsInfo[i])–>s.installAPIResources(APIGroupPrefix, apiGroupInfo)—>apiGroupVersion.InstallREST(s.Handler.GoRestfulContainer)—>installer.Install()—>a.registerResourceHandlers(path, a.group.Storage[path], ws)
这样就会把每个api group 注入到go-restful里
举个例子
go-restful每注册一个路由就会生成指针类型的RouteBuilder结构体,该结构体的具体属性如下
// RouteBuilder is a helper to construct Routes.
type RouteBuilder struct {
rootPath string
currentPath string
produces []string
consumes []string
httpMethod string // required
function RouteFunction // required
filters []FilterFunction
typeNameHandleFunc TypeNameHandleFunction // required
// documentation
doc string
notes string
operation string
readSample, writeSample interface{}
parameters []*Parameter
errorMap map[int]ResponseError
metadata map[string]interface{}
}
我debug了一个pod
//DELETE POD
{/api/v1 namespaces/{namespace}/pods [application/json application/yaml application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf] [] DELETE 0x1b6a170 [] delete collection of Pod deletecollectionNamespacedPod {{ } { } 0} [0xc420bd0fe0 0xc420bd1038 0xc420bd1040 0xc420bd1050 0xc420bd1098 0xc420bd10a0 0xc420bd10b0 0xc420bd10f8 0xc420bd1100 0xc42034b980] map[200:{200 OK {{ } { } 0} false}] map[x-kubernetes-group-version-kind:{ v1 Pod}]}
//watch POD
{/api/v1 watch/namespaces/{namespace}/pods [application/json application/yaml application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf application/json;stream=watch application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf;stream=watch] [] GET 0x1b6a170 [] watch individual changes to a list of Pod watchNamespacedPodList { {[] }} [0xc420bd1128 0xc420bd1138 0xc420bd1140 0xc420bd1148 0xc420bd1150 0xc420bd1158 0xc420bd1160 0xc420bd1168 0xc420bd1170 0xc42034b980] map[200:{200 OK { {[] }} false}] map[x-kubernetes-group-version-kind:{ v1 Pod}]}
//PUT POD namespace
{/api/v1 namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name} [application/json application/yaml application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf] [] PUT 0x1b6a170 [] replace the specified Pod replaceNamespacedPod {{ } { 0 {{0 0 }} map[] map[] [] [] } {[] [] [] map[] false false false [] [] [] []} { [] [] [] }} {{ } { 0 {{0 0 }} map[] map[] [] [] } {[] [] [] map[] false false false [] [] [] []} { [] [] [] }} [0xc420bd11b8 0xc420bd11c8 0xc42034b980 0xc42034b930] map[200:{200 OK {{ } { 0 {{0 0 }} map[] map[] [] [] } {[] [] [] map[] false false false [] [] [] []} { [] [] [] }} false} 201:{201 Created {{ } { 0 {{0 0 }} map[] map[] [] [] } {[] [] [] map[] false false false [] [] [] []} { [] [] [] }} false}] map[x-kubernetes-group-version-kind:{ v1 Pod}]}
结合结构体RouteBuilder的属性,要访问某个资源的信息,需要用到 rootPath currentPath httpMethod 这三个属性组合而成url,
url=rootPath/currentPath
请求方法httpMethod
GET 协议://ip:port/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}
这样就组合成了url
➜ kube-apiserver git:(v1.11.2-custom) ✗ curl localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/reviews-v3-dd846cc78-mx2v2
{
"kind": "Pod",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "reviews-v3-dd846cc78-mx2v2",
"generateName": "reviews-v3-dd846cc78-",
"namespace": "default",
"selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/reviews-v3-dd846cc78-mx2v2",
"uid": "1f4e2545-d844-11e8-8b84-5254e98192ae",
"resourceVersion": "23157325",
"creationTimestamp": "2018-10-25T10:52:52Z",
"labels": {
"app": "reviews",
"pod-template-hash": "884027734",
"version": "v3"
},
"ownerReferences": [
{
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "ReplicaSet",
"name": "reviews-v3-dd846cc78",
"uid": "1f47bf73-d844-11e8-8b84-5254e98192ae",
"controller": true,
"blockOwnerDeletion": true
}
]
},
"spec": {
"volumes": [
{
"name": "default-token-gwx4c",
"secret": {
"secretName": "default-token-gwx4c",
"defaultMode": 420
}
}
],
"containers": [
{
"name": "reviews",
"image": "istio/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v3:1.8.0",
"ports": [
{
"containerPort": 9080,
"protocol": "TCP"
}
],
"resources": {
},
"volumeMounts": [
{
"name": "default-token-gwx4c",
"readOnly": true,
"mountPath": "/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"
}
],
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
"terminationMessagePolicy": "File",
"imagePullPolicy": "IfNotPresent"
}
],
"restartPolicy": "Always",
"terminationGracePeriodSeconds": 30,
"dnsPolicy": "ClusterFirst",
"serviceAccountName": "default",
"serviceAccount": "default",
"nodeName": "master-47-36",
"securityContext": {
},
"schedulerName": "default-scheduler",
"tolerations": [
{
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/not-ready",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
},
{
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
}
],
"priority": 0
},
"status": {
"phase": "Running",
"conditions": [
{
"type": "Initialized",
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2018-10-25T10:52:53Z"
},
{
"type": "Ready",
"status": "False",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2018-12-04T02:54:54Z",
"reason": "ContainersNotReady",
"message": "containers with unready status: [reviews]"
},
{
"type": "ContainersReady",
"status": "False",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": null,
"reason": "ContainersNotReady",
"message": "containers with unready status: [reviews]"
},
{
"type": "PodScheduled",
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2018-10-25T10:52:52Z"
}
],
"hostIP": "10.39.47.36",
"podIP": "10.253.63.245",
"startTime": "2018-10-25T10:52:53Z",
"containerStatuses": [
{
"name": "reviews",
"state": {
"waiting": {
"reason": "CrashLoopBackOff",
"message": "Back-off 5m0s restarting failed container=reviews pod=reviews-v3-dd846cc78-mx2v2_default(1f4e2545-d844-11e8-8b84-5254e98192ae)"
}
},
"lastState": {
"terminated": {
"exitCode": 128,
"reason": "ContainerCannotRun",
"message": "mkdir /var/run/docker/libcontainerd/edfcef19e160304dc8fbfb5a3b3c5d393cb36206e32d4904a44e73bda4dea73f: no space left on device",
"startedAt": "2018-12-31T08:10:30Z",
"finishedAt": "2018-12-31T08:10:30Z",
"containerID": "docker://edfcef19e160304dc8fbfb5a3b3c5d393cb36206e32d4904a44e73bda4dea73f"
}
},
"ready": false,
"restartCount": 18808,
"image": "docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v3:1.8.0",
"imageID": "docker-pullable://docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v3@sha256:8c0385f0ca799e655d8770b52cb4618ba54e8966a0734ab1aeb6e8b14e171a3b",
"containerID": "docker://edfcef19e160304dc8fbfb5a3b3c5d393cb36206e32d4904a44e73bda4dea73f"
}
],
"qosClass": "BestEffort"
}
}
下面是重要函数的具体实现
InstallAPI函数
func (m *Master) InstallAPIs(apiResourceConfigSource serverstorage.APIResourceConfigSource, restOptionsGetter generic.RESTOptionsGetter, restStorageProviders ...RESTStorageProvider) {
apiGroupsInfo := []genericapiserver.APIGroupInfo{}
for _, restStorageBuilder := range restStorageProviders {
groupName := restStorageBuilder.GroupName()
if !apiResourceConfigSource.AnyVersionForGroupEnabled(groupName) {
glog.V(1).Infof("Skipping disabled API group %q.", groupName)
continue
}
apiGroupInfo, enabled := restStorageBuilder.NewRESTStorage(apiResourceConfigSource, restOptionsGetter)
if !enabled {
glog.Warningf("Problem initializing API group %q, skipping.", groupName)
continue
}
glog.V(1).Infof("Enabling API group %q.", groupName)
if postHookProvider, ok := restStorageBuilder.(genericapiserver.PostStartHookProvider); ok {
name, hook, err := postHookProvider.PostStartHook()
if err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("Error building PostStartHook: %v", err)
}
m.GenericAPIServer.AddPostStartHookOrDie(name, hook)
}
apiGroupsInfo = append(apiGroupsInfo, apiGroupInfo)
}
for i := range apiGroupsInfo {
if err := m.GenericAPIServer.InstallAPIGroup(&apiGroupsInfo[i]); err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("Error in registering group versions: %v", err)
}
}
}
GenericAPIServer 这个结构体非常充要,go-restful所有的WebService都是通过这个ADD到GoRestfulContainer的
$GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/server/genericapiserver.go
type GenericAPIServer struct {
...
// "Outputs"
// Handler holds the handlers being used by this API server
Handler *APIServerHandler
...
}
APIServerHandler函数
type APIServerHandler struct {
// FullHandlerChain is the one that is eventually served with. It should include the full filter
// chain and then call the Director.
FullHandlerChain http.Handler
// The registered APIs. InstallAPIs uses this. Other servers probably shouldn't access this directly.
GoRestfulContainer *restful.Container
// NonGoRestfulMux is the final HTTP handler in the chain.
// It comes after all filters and the API handling
// This is where other servers can attach handler to various parts of the chain.
NonGoRestfulMux *mux.PathRecorderMux
// Director is here so that we can properly handle fall through and proxy cases.
// This looks a bit bonkers, but here's what's happening. We need to have /apis handling registered in gorestful in order to have
// swagger generated for compatibility. Doing that with `/apis` as a webservice, means that it forcibly 404s (no defaulting allowed)
// all requests which are not /apis or /apis/. We need those calls to fall through behind goresful for proper delegation. Trying to
// register for a pattern which includes everything behind it doesn't work because gorestful negotiates for verbs and content encoding
// and all those things go crazy when gorestful really just needs to pass through. In addition, openapi enforces unique verb constraints
// which we don't fit into and it still muddies up swagger. Trying to switch the webservices into a route doesn't work because the
// containing webservice faces all the same problems listed above.
// This leads to the crazy thing done here. Our mux does what we need, so we'll place it in front of gorestful. It will introspect to
// decide if the route is likely to be handled by goresful and route there if needed. Otherwise, it goes to PostGoRestful mux in
// order to handle "normal" paths and delegation. Hopefully no API consumers will ever have to deal with this level of detail. I think
// we should consider completely removing gorestful.
// Other servers should only use this opaquely to delegate to an API server.
Director http.Handler
}
installAPIResources
// installAPIResources is a private method for installing the REST storage backing each api groupversionresource
func (s *GenericAPIServer) installAPIResources(apiPrefix string, apiGroupInfo *APIGroupInfo) error {
for _, groupVersion := range apiGroupInfo.PrioritizedVersions {
if len(apiGroupInfo.VersionedResourcesStorageMap[groupVersion.Version]) == 0 {
glog.Warningf("Skipping API %v because it has no resources.", groupVersion)
continue
}
apiGroupVersion := s.getAPIGroupVersion(apiGroupInfo, groupVersion, apiPrefix)
if apiGroupInfo.OptionsExternalVersion != nil {
apiGroupVersion.OptionsExternalVersion = apiGroupInfo.OptionsExternalVersion
}
if err := apiGroupVersion.InstallREST(s.Handler.GoRestfulContainer); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to setup API %v: %v", apiGroupInfo, err)
}
}
return nil
}
InstallREST
func (g *APIGroupVersion) InstallREST(container *restful.Container) error {
prefix := path.Join(g.Root, g.GroupVersion.Group, g.GroupVersion.Version)
installer := &APIInstaller{
group: g,
prefix: prefix,
minRequestTimeout: g.MinRequestTimeout,
enableAPIResponseCompression: g.EnableAPIResponseCompression,
}
apiResources, ws, registrationErrors := installer.Install()
versionDiscoveryHandler := discovery.NewAPIVersionHandler(g.Serializer, g.GroupVersion, staticLister{apiResources})
versionDiscoveryHandler.AddToWebService(ws)
container.Add(ws)
return utilerrors.NewAggregate(registrationErrors)
}
installer.Install()
// Install handlers for API resources.
func (a *APIInstaller) Install() ([]metav1.APIResource, *restful.WebService, []error) {
var apiResources []metav1.APIResource
var errors []error
ws := a.newWebService()
glog.Infof("a.group.Storage===== : %s \n", a.group.Storage)
// Register the paths in a deterministic (sorted) order to get a deterministic swagger spec.
paths := make([]string, len(a.group.Storage))
var i int = 0
for path := range a.group.Storage {
paths[i] = path
glog.Infof("a.group.Storage[%s]=%s \n", path,a.group.Storage[path])
i++
}
sort.Strings(paths)
for _, path := range paths {
apiResource, err := a.registerResourceHandlers(path, a.group.Storage[path], ws)
if err != nil {
errors = append(errors, fmt.Errorf("error in registering resource: %s, %v", path, err))
}
if apiResource != nil {
apiResources = append(apiResources, *apiResource)
}
}
return apiResources, ws, errors
}
registerResourceHandlers 由于代码量太多,这里就不粘贴了,具体代码在$GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/endpoints/installer.go文件
4.如何GET或者修改etcd数据
先看操作etcd的源代码
从文件 $GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/storagebackend/factory/factory.go
可以看出etcd实现了接口storage.Interface
实现文件如下
package factory
import (
"fmt"
"k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage"
"k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/storagebackend"
)
// DestroyFunc is to destroy any resources used by the storage returned in Create() together.
type DestroyFunc func()
// Create creates a storage backend based on given config.
func Create(c storagebackend.Config) (storage.Interface, DestroyFunc, error) {
switch c.Type {
case storagebackend.StorageTypeETCD2:
return newETCD2Storage(c)
case storagebackend.StorageTypeUnset, storagebackend.StorageTypeETCD3:
// TODO: We have the following features to implement:
// - Support secure connection by using key, cert, and CA files.
// - Honor "https" scheme to support secure connection in gRPC.
// - Support non-quorum read.
return newETCD3Storage(c)
default:
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown storage type: %s", c.Type)
}
}
k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/interfaces.go
//etcd实现该接口 各个接口也要实现
// Interface offers a common interface for object marshaling/unmarshaling operations and
// hides all the storage-related operations behind it.
type Interface interface {
// Returns Versioner associated with this interface.
Versioner() Versioner
// Create adds a new object at a key unless it already exists. 'ttl' is time-to-live
// in seconds (0 means forever). If no error is returned and out is not nil, out will be
// set to the read value from database.
Create(ctx context.Context, key string, obj, out runtime.Object, ttl uint64) error
// Delete removes the specified key and returns the value that existed at that spot.
// If key didn't exist, it will return NotFound storage error.
Delete(ctx context.Context, key string, out runtime.Object, preconditions *Preconditions) error
// Watch begins watching the specified key. Events are decoded into API objects,
// and any items selected by 'p' are sent down to returned watch.Interface.
// resourceVersion may be used to specify what version to begin watching,
// which should be the current resourceVersion, and no longer rv+1
// (e.g. reconnecting without missing any updates).
// If resource version is "0", this interface will get current object at given key
// and send it in an "ADDED" event, before watch starts.
Watch(ctx context.Context, key string, resourceVersion string, p SelectionPredicate) (watch.Interface, error)
// WatchList begins watching the specified key's items. Items are decoded into API
// objects and any item selected by 'p' are sent down to returned watch.Interface.
// resourceVersion may be used to specify what version to begin watching,
// which should be the current resourceVersion, and no longer rv+1
// (e.g. reconnecting without missing any updates).
// If resource version is "0", this interface will list current objects directory defined by key
// and send them in "ADDED" events, before watch starts.
WatchList(ctx context.Context, key string, resourceVersion string, p SelectionPredicate) (watch.Interface, error)
// Get unmarshals json found at key into objPtr. On a not found error, will either
// return a zero object of the requested type, or an error, depending on ignoreNotFound.
// Treats empty responses and nil response nodes exactly like a not found error.
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// be have at least 'resourceVersion'.
Get(ctx context.Context, key string, resourceVersion string, objPtr runtime.Object, ignoreNotFound bool) error
// GetToList unmarshals json found at key and opaque it into *List api object
// (an object that satisfies the runtime.IsList definition).
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// be have at least 'resourceVersion'.
GetToList(ctx context.Context, key string, resourceVersion string, p SelectionPredicate, listObj runtime.Object) error
// List unmarshalls jsons found at directory defined by key and opaque them
// into *List api object (an object that satisfies runtime.IsList definition).
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// be have at least 'resourceVersion'.
List(ctx context.Context, key string, resourceVersion string, p SelectionPredicate, listObj runtime.Object) error
// GuaranteedUpdate keeps calling 'tryUpdate()' to update key 'key' (of type 'ptrToType')
// retrying the update until success if there is index conflict.
// Note that object passed to tryUpdate may change across invocations of tryUpdate() if
// other writers are simultaneously updating it, so tryUpdate() needs to take into account
// the current contents of the object when deciding how the update object should look.
// If the key doesn't exist, it will return NotFound storage error if ignoreNotFound=false
// or zero value in 'ptrToType' parameter otherwise.
// If the object to update has the same value as previous, it won't do any update
// but will return the object in 'ptrToType' parameter.
// If 'suggestion' can contain zero or one element - in such case this can be used as
// a suggestion about the current version of the object to avoid read operation from
// storage to get it.
//
// Example:
//
// s := /* implementation of Interface */
// err := s.GuaranteedUpdate(
// "myKey", &MyType{}, true,
// func(input runtime.Object, res ResponseMeta) (runtime.Object, *uint64, error) {
// // Before each incovation of the user defined function, "input" is reset to
// // current contents for "myKey" in database.
// curr := input.(*MyType) // Guaranteed to succeed.
//
// // Make the modification
// curr.Counter++
//
// // Return the modified object - return an error to stop iterating. Return
// // a uint64 to alter the TTL on the object, or nil to keep it the same value.
// return cur, nil, nil
// }
// })
GuaranteedUpdate(
ctx context.Context, key string, ptrToType runtime.Object, ignoreNotFound bool,
precondtions *Preconditions, tryUpdate UpdateFunc, suggestion ...runtime.Object) error
// Count returns number of different entries under the key (generally being path prefix).
Count(key string) (int64, error)
}
接下来k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go中的Store结构体
type Store struct {
// NewFunc returns a new instance of the type this registry returns for a
// GET of a single object, e.g.:
//
// curl GET /apis/group/version/namespaces/my-ns/myresource/name-of-object
NewFunc func() runtime.Object
// NewListFunc returns a new list of the type this registry; it is the
// type returned when the resource is listed, e.g.:
//
// curl GET /apis/group/version/namespaces/my-ns/myresource
NewListFunc func() runtime.Object
// DefaultQualifiedResource is the pluralized name of the resource.
// This field is used if there is no request info present in the context.
// See qualifiedResourceFromContext for details.
DefaultQualifiedResource schema.GroupResource
// KeyRootFunc returns the root etcd key for this resource; should not
// include trailing "/". This is used for operations that work on the
// entire collection (listing and watching).
//
// KeyRootFunc and KeyFunc must be supplied together or not at all.
KeyRootFunc func(ctx context.Context) string
// KeyFunc returns the key for a specific object in the collection.
// KeyFunc is called for Create/Update/Get/Delete. Note that 'namespace'
// can be gotten from ctx.
//
// KeyFunc and KeyRootFunc must be supplied together or not at all.
KeyFunc func(ctx context.Context, name string) (string, error)
// ObjectNameFunc returns the name of an object or an error.
ObjectNameFunc func(obj runtime.Object) (string, error)
// TTLFunc returns the TTL (time to live) that objects should be persisted
// with. The existing parameter is the current TTL or the default for this
// operation. The update parameter indicates whether this is an operation
// against an existing object.
//
// Objects that are persisted with a TTL are evicted once the TTL expires.
TTLFunc func(obj runtime.Object, existing uint64, update bool) (uint64, error)
// PredicateFunc returns a matcher corresponding to the provided labels
// and fields. The SelectionPredicate returned should return true if the
// object matches the given field and label selectors.
PredicateFunc func(label labels.Selector, field fields.Selector) storage.SelectionPredicate
// EnableGarbageCollection affects the handling of Update and Delete
// requests. Enabling garbage collection allows finalizers to do work to
// finalize this object before the store deletes it.
//
// If any store has garbage collection enabled, it must also be enabled in
// the kube-controller-manager.
EnableGarbageCollection bool
// DeleteCollectionWorkers is the maximum number of workers in a single
// DeleteCollection call. Delete requests for the items in a collection
// are issued in parallel.
DeleteCollectionWorkers int
// Decorator is an optional exit hook on an object returned from the
// underlying storage. The returned object could be an individual object
// (e.g. Pod) or a list type (e.g. PodList). Decorator is intended for
// integrations that are above storage and should only be used for
// specific cases where storage of the value is not appropriate, since
// they cannot be watched.
Decorator ObjectFunc
// CreateStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during creation.
CreateStrategy rest.RESTCreateStrategy
// AfterCreate implements a further operation to run after a resource is
// created and before it is decorated, optional.
AfterCreate ObjectFunc
// UpdateStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during updates.
UpdateStrategy rest.RESTUpdateStrategy
// AfterUpdate implements a further operation to run after a resource is
// updated and before it is decorated, optional.
AfterUpdate ObjectFunc
// DeleteStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during deletion.
DeleteStrategy rest.RESTDeleteStrategy
// AfterDelete implements a further operation to run after a resource is
// deleted and before it is decorated, optional.
AfterDelete ObjectFunc
// ReturnDeletedObject determines whether the Store returns the object
// that was deleted. Otherwise, return a generic success status response.
ReturnDeletedObject bool
// ExportStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during export,
// optional. Exported objects are not decorated.
ExportStrategy rest.RESTExportStrategy
// TableConvertor is an optional interface for transforming items or lists
// of items into tabular output. If unset, the default will be used.
TableConvertor rest.TableConvertor
// Storage is the interface for the underlying storage for the resource.
Storage storage.Interface
// Called to cleanup clients used by the underlying Storage; optional.
DestroyFunc func()
}
实现了如下接口
var _ rest.StandardStorage = &Store{}
var _ rest.Exporter = &Store{}
var _ rest.TableConvertor = &Store{}
var _ GenericStore = &Store{}
从$GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/registry这个包查看,各个kubernetes 资源对象都继承了*genericregistry.Store结构体所有的属性以及方法
总体来看从$GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/registry这个kubernetes 资源包实现了 $GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/rest的接口,所以每个runtime.Object都有一下方法
// what verbs are supported by the storage, used to know what verbs we support per path
creater, isCreater := storage.(rest.Creater)
namedCreater, isNamedCreater := storage.(rest.NamedCreater)
lister, isLister := storage.(rest.Lister)
getter, isGetter := storage.(rest.Getter)
getterWithOptions, isGetterWithOptions := storage.(rest.GetterWithOptions)
gracefulDeleter, isGracefulDeleter := storage.(rest.GracefulDeleter)
collectionDeleter, isCollectionDeleter := storage.(rest.CollectionDeleter)
updater, isUpdater := storage.(rest.Updater)
patcher, isPatcher := storage.(rest.Patcher)
watcher, isWatcher := storage.(rest.Watcher)
connecter, isConnecter := storage.(rest.Connecter)
storageMeta, isMetadata := storage.(rest.StorageMetadata)
if !isMetadata {
storageMeta = defaultStorageMetadata{}
}
exporter, isExporter := storage.(rest.Exporter)
if !isExporter {
exporter = nil
}
通过这个方法来操作存储在etcd里的对象
看Install() 函数的 debug 日志
从日志可以看出,每个资源对象都继承了k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go中的Store结构体的属性以及方法
举个例子
GET PUT DELETE POST 等所有的操作都是从$GOPATH/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/endpoints/installer.go文件进行

获取资源时是从header函数获取的,我们来分析handler = restfulGetResource(getter, exporter, reqScope)这个的具体流程


这里就是获取kubernetes 资源对象的代码,也就是调用对象的方法了
接下来再分析kube-apiserver如何连接etcd,大概流程图如下
Run—>CreateServerChain—>CreateKubeAPIServer—>Complete—>cfg.createEndpointReconciler()—>c.createLeaseReconciler()—>storagefactory.Create(*config)
storagefactory.Create(*config)的代码如下
// Create creates a storage backend based on given config.
func Create(c storagebackend.Config) (storage.Interface, DestroyFunc, error) {
switch c.Type {
case storagebackend.StorageTypeETCD2:
return newETCD2Storage(c)
case storagebackend.StorageTypeUnset, storagebackend.StorageTypeETCD3:
// TODO: We have the following features to implement:
// - Support secure connection by using key, cert, and CA files.
// - Honor "https" scheme to support secure connection in gRPC.
// - Support non-quorum read.
return newETCD3Storage(c)
default:
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown storage type: %s", c.Type)
}
}
接下来每个kubernetes 资源对象都可以操作etcd的数据了
声明,由于本人的能力有限,还有很多具体的细节没有分析到,需要读者自己去看源码,才能更好地理解kube-apiserver的源码
简单分析
/apis/apps组
{
"kind": "APIGroup",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"name": "apps",
"versions": [
{
"groupVersion": "apps/v1",
"version": "v1"
},
{
"groupVersion": "apps/v1beta2",
"version": "v1beta2"
},
{
"groupVersion": "apps/v1beta1",
"version": "v1beta1"
}
],
"preferredVersion": {
"groupVersion": "apps/v1",
"version": "v1"
}
}
/apis/apps/v1版本有的资源对象以及能进行的操作
{
"kind": "APIResourceList",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"groupVersion": "apps/v1",
"resources": [
{
"name": "controllerrevisions",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ControllerRevision",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
]
},
{
"name": "daemonsets",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "DaemonSet",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"ds"
],
"categories": [
"all"
]
},
{
"name": "daemonsets/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "DaemonSet",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "deployments",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Deployment",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"deploy"
],
"categories": [
"all"
]
},
{
"name": "deployments/scale",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"group": "autoscaling",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "Scale",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "deployments/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Deployment",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "replicasets",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ReplicaSet",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"rs"
],
"categories": [
"all"
]
},
{
"name": "replicasets/scale",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"group": "autoscaling",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "Scale",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "replicasets/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ReplicaSet",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "statefulsets",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "StatefulSet",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"sts"
],
"categories": [
"all"
]
},
{
"name": "statefulsets/scale",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"group": "autoscaling",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "Scale",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "statefulsets/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "StatefulSet",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
}
]
}
END