前面的内容请参见Android应用自动化测试-提纲。 这篇我们将介绍在Android SDK中一个非常关键的工具,ADB。可以说ADB是Android开发、自动化测试的基础。
ADB即Android Debug Bridge,android调试桥,是开发设备(PC)和android设备之间的连接通道,通过它,开发者可以在PC端实现对设备的连接、控制和一些基本操作。
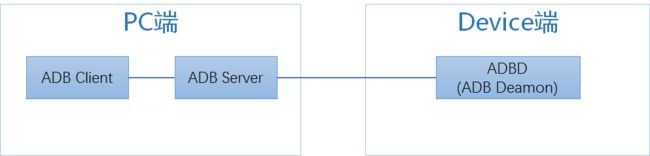
ADB的组成如图
在PC端:
ADB由Client和Server两部分组成,client即我们运行ADB的命令行程序,用于接收我们的操作指定,并和server端通过5037端口进行通信,server端启动后和5037端口绑定,与client端交互并建立和设备端的adbd通信,一般设备端是5555端口,PC端则使用5554端口。多个不同设备会成对分配(5556:5557...)
在Device端:
则运行了adbd,即adb在设备上的守护进程,随时接收来自PC端的指令。模拟器是默认开启的,真机在我们开启了开发者的调试模式以后,也就是启动了adbd进程。
ADB工具的作用非常多,在命令行中运行adb help可以得到以下输出,列出了adb支持的使用命令清单。
c:>adb help
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.36
Revision 0e9850346394-android
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL environment variable.
-p - simple product name like 'sooner', or a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.If -p is not specified, the
ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT environment variable is used, which mustbe an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect [:] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [[:]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push ...
- copy files/dirs to device
adb pull [-a] ...
- copy files/dirs from device
(-a preserves file timestamp and mode)
adb sync [ ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
adb shell [-e escape] [-n] [-Tt] [-x] [command]
- run remote shell command (interactive shell if no command given)
(-e: choose escape character, or "none"; default '~')
(-n: don't read from stdin)
(-T: disable PTY allocation)
(-t: force PTY allocation)
(-x: disable remote exit codes and stdout/stderr separation)
adb emu - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
" " " " "\n"
adb forward - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:
localabstract:
localreserved:
localfilesystem:
dev:
jdwp: (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind
- same as 'adb forward ' but fails
if is already forwarded
adb forward --remove - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb reverse --list - list all reverse socket connections from device
adb reverse - reverse socket connections
reverse specs are one of:
tcp:
localabstract:
localreserved:
localfilesystem:
adb reverse --no-rebind
- same as 'adb reverse ' but fails
if is already reversed.
adb reverse --remove
- remove a specific reversed socket connection
adb reverse --remove-all - remove all reversed socket connections from device
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-lrtsdg]
- push this package file to the device and install it
(-l: forward lock application)
(-r: replace existing application)
(-t: allow test packages)
(-s: install application on sdcard)
(-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only))
(-g: grant all runtime permissions)
adb install-multiple [-lrtsdpg]
- push this package file to the device and install it
(-l: forward lock application)
(-r: replace existing application)
(-t: allow test packages)
(-s: install application on sdcard)
(-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only))
(-p: partial application install)
(-g: grant all runtime permissions)
adb uninstall [-k] - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport [] - return all information from the device that should be included in a zipped bug report.
If is a file, the bug report will be saved as that file.
If is a directory, the bug report will be saved in that directory with the name provided by the device.
If is omitted, the bug report will be saved in the current directory with the name provided by the device.
NOTE: if the device does not support zipped bug reports, the bug report will be output on stdout.
adb backup [-f ] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] []
- write an archive of the device's data to .
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
( is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore - restore device contents from the backup archive
adb disable-verity - disable dm-verity checking on USERDEBUG builds
adb enable-verity - re-enable dm-verity checking on USERDEBUG builds
adb keygen - generate adb public/private key. The private key is stored in ,
and the public key is stored in .pub. Any existing files
are overwritten.
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for[-]-
- wait for device to be in the given state:
device, recovery, sideload, or bootloader
Transport is: usb, local or any [default=any]
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints:
adb get-devpath - prints:
adb remount - remounts the /system, /vendor (if present) and /oem (if present) partitions on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery]
- reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program.
adb reboot sideload - reboots the device into the sideload mode in recovery program (adb root required).
adb reboot sideload-auto-reboot
- reboots into the sideload mode, then reboots automatically after the sideload regardless of the result.
adb sideload - sideloads the given package
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb unroot - restarts the adbd daemon without root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns》
adb sync notes: adb sync [ ]
can be interpreted in several ways:
- If is not specified, /system, /vendor (if present), /oem (if present) and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system", "vendor", "oem" or "data", only the corresponding partition is updated.
internal debugging:
adb reconnect Kick current connection from host side and make it reconnect.
adb reconnect device Kick current connection from device side and make it reconnect.
environment variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.
其中有一些我们经常需要使用的命令,在此重点说明一下:
adb devices
adb devices用于列出当前连接到adb server的所有设备清单。
c:\>adb devices
List of devices attached
emulator-5554 device
其中 emulator-5554是DeviceID,device则是设备状态。
一般有以下状态:
offline — 实例未连接到 adb server或不响应。
device — 实例现在已连接到 adb server。
no device — 未连接模拟器/设备。
当连接了多个设备时,我们可以使用-s参数来指定需要操作的设备,-s所带参数即deviceid。另外如果多个连接的设备中只有一个通过USB连接的真机,可以使用-d参数,如果只有一个模拟器,可以使用-e参数(无需带deviceid)
adb install/uninstall
adb可以方便地向设备上进行应用的安装和卸载操作。
adb install [apkpath] 给定apk文件的路径,执行即可
adb uninstall packagename uninstall操作需要给出应用的包名
packagename如何获得? 一般可以通过adb shell pm list packages列出确定。
通过adb shell进入/data/data目录,也可以看到所有的包
adb push/pull
adb push/pull则是文件操作
adb push [pc file path] [device file path]-- 将PC端文件上载到设备端
adb pull [device file path] [pc file path]--将设备端文件下载到PC端
adb forword
adb forward用于端口转发。可以使用 forward 命令设置将对特定主机端口的请求转发到模拟器/设备实例上的其他端口。
adb forward tcp:6100 tcp:7100
表示将PC端的6100端口的通信转发到设备端的7100端口上
adb kill-server/start-server
当adb server进程出现异常时,我们可以会用adb kill-server 命令来停止adb server进程。
adb start-server则用来启动adb server进程。但其实执行任何adb命令,在server没有运行时,都会启动adb server
adb connect/disconnect
当我们的设备在无线wifi环境下时,我们可以通过adb connect命令来连接指定ip的设备。默认设备端口是5555
adb disconnect则用于断开已经建立的连接
比如genymotion模拟器,就是默认模拟的这种连接方式
adb logcat
adb logcat用于将logcat日志信息输出到屏幕。logcat的作用我们在后文再详细说明
adb shell
adb shell则是可以直接进入设备并执行大量的系统指令。进入adb shell后,即可执行很多类linux的系统指令,如:
操作Activity manager的am命令,可以直接从命令行启动一个应用的Activity。
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW
利用包管理器pm来卸载应用
adb shell pm uninstall com.example.MyApp
进行屏幕截图
adb shell screencap /sdcard/screen.png
录制操作视频
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/demo.mp4
更多用法可参考: 官网说明
关于android自动化测试的更多实战操作可以参见慕课网实战课程 Android自动化测试实战 工具 框架 脚本
欢迎保留作者信息和出处进行转载,欢迎关注微信公众号:秋草说测试。 测试干货资源池