Java实现CRC16CCITT算法
最近在搞关于手环的APP,到蓝牙通讯这里是私有协议,用到了CRC校验,APP作为接收端需要实现CRC算法。在网上看了很多大神的文章,我看了感觉不是很清晰,故写此博客。
初次在Java代码中编写算法,有点小激动…
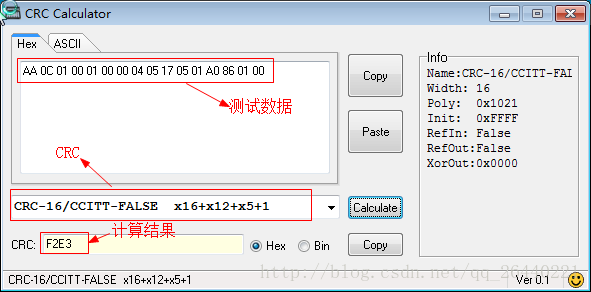
这是在网上找的CRC计算软件,可以用作测试的值是否真确。
CRC校验码计算软件
首先百度了下CRC,这是百度下的内容:
一般的校验方法有:1.奇偶校验2.因特网校验3.循环冗余校验
使用领域:在数据存储、数据通讯领域,CRC无处不在
作用:保证数据完整
定义:Cyclic Redundancy Check循环冗余校验,是基于数据计算一组校验码,用于核对数据传输过程中是否被更改或传输错误。它是利用除法及余数的原理来作错误侦测的。
算法原理:
推荐:可以先看完本文,再去看度娘,讲的很详细,我相信你一定会豁然开朗的。
用Java语言实现的 测试类Crc_16_CCITT_FALSE工具包如下:
测试数据:AA 0C 01 00 01 00 00 04 05 17 05 01 A0 86 01 00
结果为:F2E3
CRC校验码计算软件,在文章开头可以下载。
/**
*
* 测试类
*/
public class Test {
//测试数据
static byte[] data = {(byte)0xAA,0x0C,0x01,0x00,0x01,0x00,0x00,0x04,0x05,0x17,0x05,0x01,(byte)0xA0,(byte)0x86,0x01,0x00};
//AA 0C 01 00 01 00 00 04 05 17 05 01 A0 86 01 00
//结果为:F2E3
public static void main(String[] s){
byte[] crcData = CrcUtil.setParamCRC(data);
if(CrcUtil.isPassCRC(crcData, 2)){
System.out.println("验证通过");
}else{
System.out.println("验证失败");
}
}
}
/**
*
* CRC数组处理工具类及数组合并
*/
public class CrcUtil {
/**
* 为Byte数组最后添加两位CRC校验
*
* @param buf(验证的byte数组)
* @return
*/
public static byte[] setParamCRC(byte[] buf) {
int checkCode = 0;
checkCode = crc_16_CCITT_False(buf, buf.length);
byte[] crcByte = new byte[2];
crcByte[0] = (byte) ((checkCode >> 8) & 0xff);
crcByte[1] = (byte) (checkCode & 0xff);
// 将新生成的byte数组添加到原数据结尾并返回
return concatAll(buf, crcByte);
}
/**
* CRC-16/CCITT-FALSE x16+x12+x5+1 算法
*
* info
* Name:CRC-16/CCITT-FAI
* Width:16
* Poly:0x1021
* Init:0xFFFF
* RefIn:False
* RefOut:False
* XorOut:0x0000
*
* @param bytes
* @param length
* @return
*/
public static int crc_16_CCITT_False(byte[] bytes, int length) {
int crc = 0xffff; // initial value
int polynomial = 0x1021; // poly value
for (int index = 0; index < bytes.length; index++) {
byte b = bytes[index];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
boolean bit = ((b >> (7 - i) & 1) == 1);
boolean c15 = ((crc >> 15 & 1) == 1);
crc <<= 1;
if (c15 ^ bit)
crc ^= polynomial;
}
}
crc &= 0xffff;
//输出String字样的16进制
String strCrc = Integer.toHexString(crc).toUpperCase();
System.out.println(strCrc);
return crc;
}
/***
* CRC校验是否通过
*
* @param srcByte
* @param length(验证码字节长度)
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPassCRC(byte[] srcByte, int length) {
// 取出除crc校验位的其他数组,进行计算,得到CRC校验结果
int calcCRC = calcCRC(srcByte, 0, srcByte.length - length);
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
bytes[0] = (byte) ((calcCRC >> 8) & 0xff);
bytes[1] = (byte) (calcCRC & 0xff);
// 取出CRC校验位,进行计算
int i = srcByte.length;
byte[] b = { srcByte[i - 2] ,srcByte[i - 1] };
// 比较
return bytes[0] == b[0] && bytes[1] == b[1];
}
/**
* 对buf中offset以前crcLen长度的字节作crc校验,返回校验结果
* @param buf
* @param crcLen
*/
private static int calcCRC(byte[] buf, int offset, int crcLen) {
int start = offset;
int end = offset + crcLen;
int crc = 0xffff; // initial value
int polynomial = 0x1021;
for (int index = start; index < end; index++) {
byte b = buf[index];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
boolean bit = ((b >> (7 - i) & 1) == 1);
boolean c15 = ((crc >> 15 & 1) == 1);
crc <<= 1;
if (c15 ^ bit)
crc ^= polynomial;
}
}
crc &= 0xffff;
return crc;
}
/**
* 多个数组合并
*
* @param first
* @param rest
* @return
*/
public static byte[] concatAll(byte[] first, byte[]... rest) {
int totalLength = first.length;
for (byte[] array : rest) {
totalLength += array.length;
}
byte[] result = Arrays.copyOf(first, totalLength);
int offset = first.length;
for (byte[] array : rest) {
System.arraycopy(array, 0, result, offset, array.length);
offset += array.length;
}
return result;
}
}