k8s ingress and egress
上次面试被问到Ingress 一脸懵逼 -_-||,这回学习记录一下。
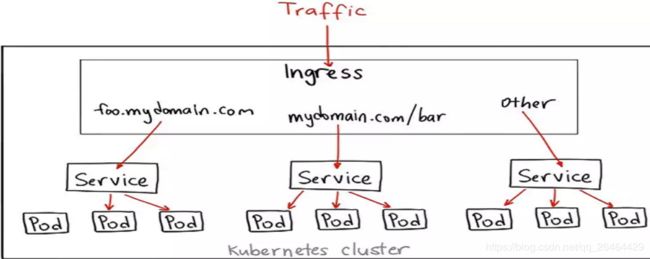
simple architecture of ingress in k8s:
create ingress controller
To create the ingress controller, use Helm to install nginx-ingress. For added redundancy, two replicas of the NGINX ingress controllers are deployed with the --set controller.replicaCount parameter. To fully benefit from running replicas of the ingress controller, make sure there’s more than one node in your AKS cluster.
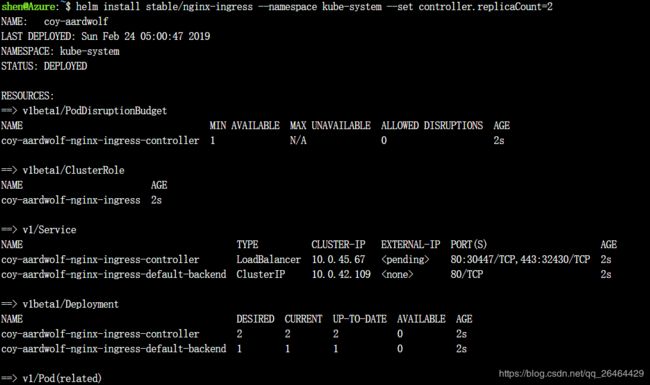
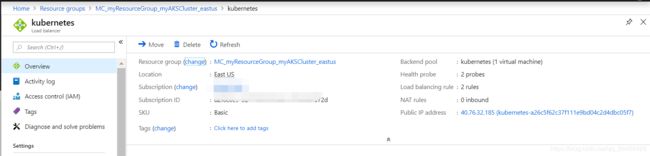
When the Kubernetes load balancer service is created for the NGINX ingress controller, a dynamic public IP address is assigned, as shown in the following example output:
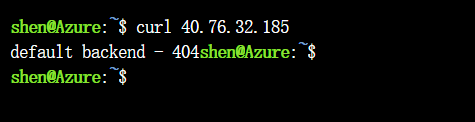
No ingress rules have been created yet, so the NGINX ingress controller’s default 404 page is displayed if you browse to the internal IP address.
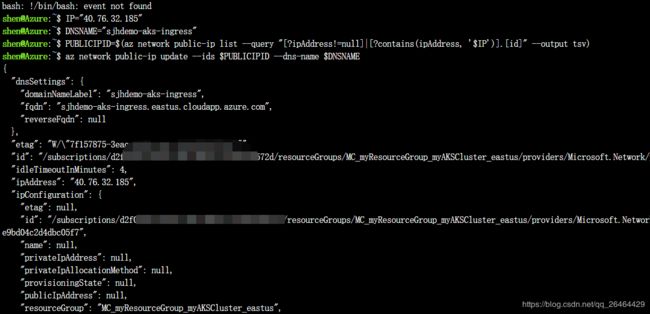
config DNS:
For the HTTPS certificates to work correctly, configure an FQDN for the ingress controller IP address.
install cert-manager which provides automatic Lets Encrypt certificate generation and management functionality.:
kubectl label namespace kube-system certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=true
kubectl apply
-f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jetstack/cert-manager/release-0.6/deploy/manifests/00-crds.yaml
helm install stable/cert-manager
–namespace kube-system
–set ingressShim.defaultIssuerName=letsencrypt-staging
–set ingressShim.defaultIssuerKind=ClusterIssuer
–set rbac.create=false
–set serviceAccount.create=false
–version v0.6.0
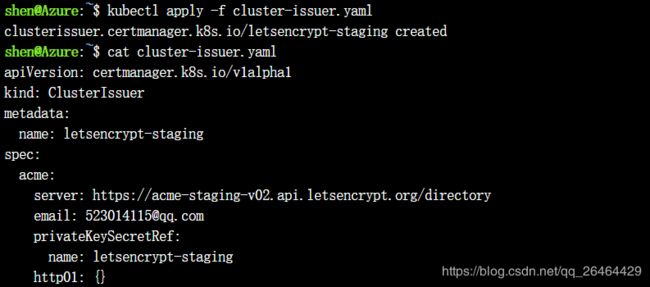
create a CA cluster issuer:
create demo app:
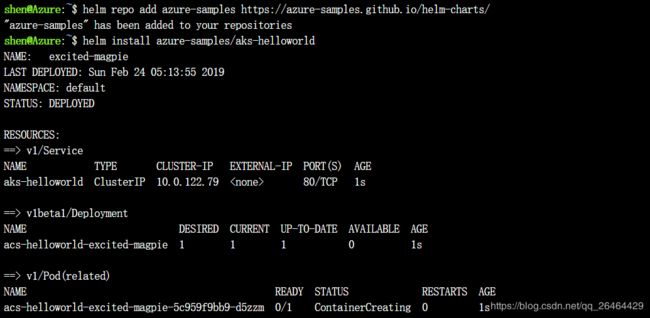
add the Azure samples repository to your Helm environment
Create the first demo application from a Helm chart
Now install a second instance of the demo application. For the second instance, you specify a new title so that the two applications are visually distinct. You also specify a unique service name
create ingress route:
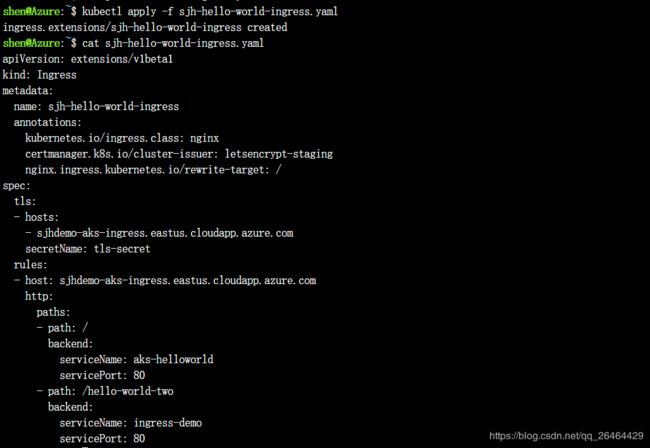
Both applications are now running on your Kubernetes cluster. To route traffic to each application, create a Kubernetes ingress resource. The ingress resource configures the rules that route traffic to one of the two applications.
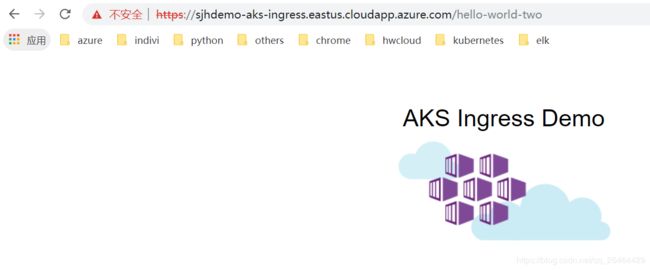
https://sjhdemo-aks-ingress.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com/ is routed to the service named aks-helloworld. Traffic to the address https://sjhdemo-aks-ingress.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com/hello-world-two is routed to the ingress-demo service.
create a certificate object:
The certificate resource defines the desired X.509 certificate.
Cert-manager has likely automatically created a certificate object for you using ingress-shim, which is automatically deployed with cert-manager since v0.2.2.
kubectl describe certificate tls-secret

otherwise you can create your own certificate
test ingress configuration
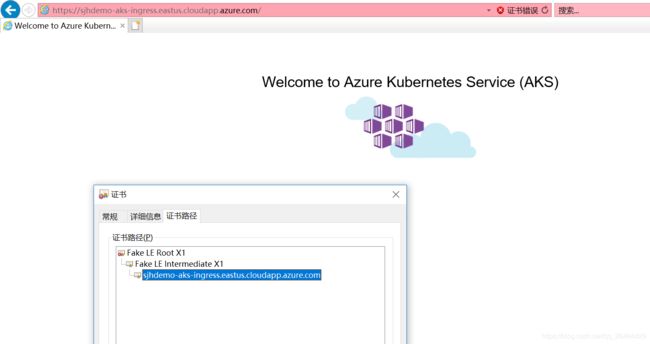
Open a web browser to the FQDN of your Kubernetes ingress controller
As these examples use letsencrypt-staging, the issued SSL certificate is not trusted by the browser. Accept the warning prompt to continue to your application. The certificate information shows this Fake LE Intermediate X1 certificate is issued by Let’s Encrypt. This fake certificate indicates cert-manager processed the request correctly and received a certificate from the provider:
then browse https://sjhdemo-aks-ingress.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com/hello-world-two.
Egress
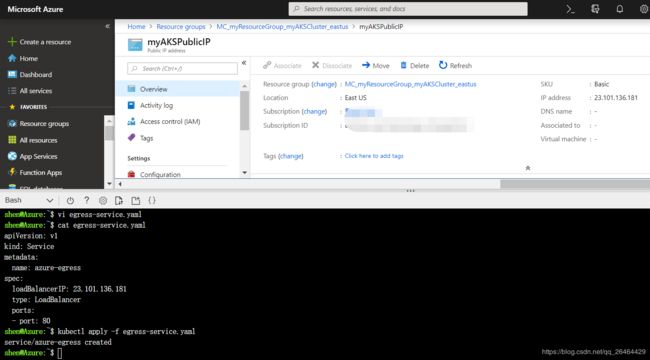
when you app need to be whistlisted and loadbalancer of Serivce 's lifecycle is following app of Service,a static IP with Service and Egress:
This service configures a new frontend IP on the Azure Load Balancer.
check ip by :
curl -s checkip.dyndns.org