Service 服务详解 及自定义服务模板
文章目录
- 1、服务简介
- 2、服务的生命周期
- 1) Service 的 启动 停止
- 2)、服务的生命周期的方法
- 3、使用startService 启动后服务的生命周期
- 1)、文件结构
- 2) activity_main.xml 文件
- 3)、myService 自定义服务文件
- 4)、MainActivity 文件
- 5)、AndroidManifest.xml 文件
- 6)、打印的相关log
- 5、使用bindService 启动后服务的生命周期
- 1) 文件结构
- 2) MyService 文件
- 3、ManiActivity 文件
- 4、log 打印
1、服务简介
在Android 中,服务时很重要的组件,它运行在系统之中,是不可见的,但它在系统的后台运行,为系统运行提供支持。
例如,一个服务可以在用户做其他事情的时候在后台播放音乐,或者是从网略上下载数据,把结果传递给其他组件使用。
2、服务的生命周期
Service 运行于应用程序进程的主线程里,因此它不会阻塞其他组件和用户界面。Service 有自己的生命周期,但Service 是不能够自己启动的。
1) Service 的 启动 停止
Services 启动或停止有一下三种方法:
1)调用 context.startService() 启动,调用 context.stopService() 结束
2)调用service.stopSelf() 或 service.stopSelfResult()来自己停止
3)调用 context.bindService()方法建立,调用 context.unbindService()关闭
每种启动和结束 是 配对的,不能交叉使用:
1)使用 startService()启动,就要使用 stopService() 结束
2)可以自己控制自己结束
3)start Service bindService 的区别:
(1) startService 调用者和服务没有关联,即使调用者结束了,服务仍然可以运行。
(2)bindService 调用者和服务绑在一起,调用者一但退出,服务也就终止。
(3)无论调用了多少次 startService()方法,但是只要有一次调用stopService()方法,服务就会停止。
(4)多个客户端可以绑定一个服务,如果此时服务还没有加载,bindService() 会先加载它。
(5)start Service bindService 并不是完全分离的,用户使用starService 里也可以使用bindService
2)、服务的生命周期的方法
(1) void onCreate() //当Service 创建时执行,不能直接调用
(2)void onStart(Intent intent) //当onCreate()之后,开始启动Servcie
(3)void onBind(Intent intent) //在onCreate 之后,绑定服务到组件
(4)void onUnbind(Intent intent) //在onDestory()之前,先解除绑定,再退出
(5)void onDestroy() //service 被销毁的时候执行
3、使用startService 启动后服务的生命周期
定义了两个按钮,一个是开启服务,一个是关闭服务
1)、文件结构
2) activity_main.xml 文件
3)、myService 自定义服务文件
package com.example.lum.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* Created by lum on 2018/11/25.
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
private String TAG = "MyService: ";
public void onCreate() {
//创建服务
Log.i(TAG,"创建服务 onCreate ");
super.onCreate();
}
public void onStart(Intent intent,int startId) {
//服务启动
Log.i(TAG,"服务启动 onStart ");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
//服务绑定
Log.i(TAG,"服务绑定 onBind ");
return null;
}
public void onDestroy() {
//服务销毁
Log.i(TAG,"服务启动 onDestroy ");
super.onDestroy();
}
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
//解除服务
Log.i(TAG,"服务解绑 onUnbind ");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
}
4)、MainActivity 文件
开启 关闭服务
package com.example.lum.myservice;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private String TAG = "MainActivity: ";
private Button buttonStart,buttonStop;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startService_id);
buttonStop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stopService_id);
buttonStart.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonStop.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent myService = new Intent(this,MyService.class);
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.startService_id:
Log.i(TAG,"开启服务");
myService.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK);// 设置新的TASK 方式
//以startService 方法启动该服务
startService(myService);
break;
case R.id.stopService_id:
Log.i(TAG,"关闭服务");
//以stop Service 方法 关闭服务
stopService(myService);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
5)、AndroidManifest.xml 文件
对自己服务进行注册
6)、打印的相关log
5、使用bindService 启动后服务的生命周期
再 MyService 中重载 onBind(Intent intent) 和 onUnbind(Intent intent) 方法,打印日志,定义内部类MyBind(Binder 为进程间通信的一种实现方式),在onBind(Intent intent) 方法中返回MyBinder 类的实例。
1) 文件结构
其中 AndroidManifest.xml Activity_main.xml 文件 同上
差异化再 MyService 和 ManiAc’ti’vi’t’y 文件
2) MyService 文件
package com.example.lum.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* Created by lum on 2018/11/25.
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
private String TAG = "MyService: ";
private int count; //计数
private boolean flag; //线程循环编辑
private final IBinder binder = new MyBinder();
//Binder类,如果希望对象能被其他进程访问,必须实现 IBinder接口
/*
* 因为是用绑定的方式开启的服务,所以在服务被创建后,
* 执行与调用者之间的关系,
* 关闭时先解除绑定,再销毁服务,
* 定义的Binder是Activity 与 Service 之间的通信接口
* */
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
//获取当前计数
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public void onCreate() {
//创建服务
Log.i(TAG,"创建服务 onCreate ");
//线程计数器累加
flag = true;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count ++ ; //累计计数
Log.i(TAG,"count: " + count);
}
}
}).start();
super.onCreate();
}
public void onStart(Intent intent,int startId) {
//服务启动
Log.i(TAG,"服务启动 onStart ");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
//服务绑定
Log.i(TAG,"服务绑定 onBind ");
return binder;
}
public void onDestroy() {
//服务销毁
Log.i(TAG,"服务关闭 onDestroy ");
flag = false; //控制线程的计数器累计
super.onDestroy();
}
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
//解除服务
Log.i(TAG,"服务解绑 onUnbind ");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
}
3、ManiActivity 文件
package com.example.lum.myservice;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private String TAG = "MainActivity: ";
private Button buttonStart,buttonStop;
//服务链接接口,链接Service 与 Activity
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//链接
Log.i(TAG,"onServiceConnected");
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
//断开链接
Log.i(TAG,"onServiceDisconnected");
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startService_id);
buttonStop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stopService_id);
buttonStart.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonStop.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent myService = new Intent(this,MyService.class);
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.startService_id:
Log.i(TAG,"绑定服务");
myService.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK);// 设置新的TASK 方式
//以bindService 方法启动该服务
boolean f = bindService(myService,serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
if (f) {
Log.i(TAG,"服务已经启动");
}else {
Log.i(TAG,"服务启动失败");
}
break;
case R.id.stopService_id:
Log.i(TAG,"解绑服务");
//以unbind Service 方法 关闭服务
unbindService(serviceConnection);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
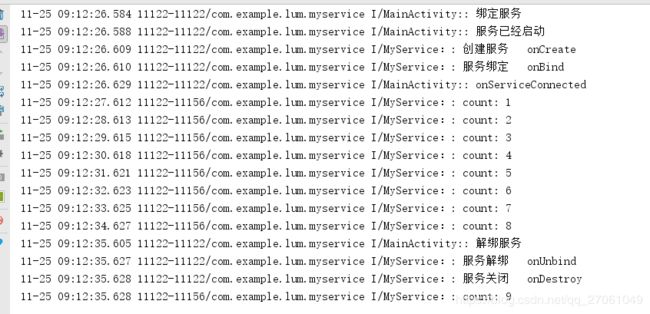
4、log 打印
(1)这里是采用 bindService(myService,serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 来启动服务的,标记为自动建立。虽然是自动建立,但是仍然是,没有调用了startService
开启服务,所以不会出现 onStart()方法。
(2)绑定服务时,需要定义内部类ServiceConnect,用于链接Service 和 Activity ,并实现里面的方法。当绑定成功后会调用ServiceConnection中的回调函数,onServiceConnected(ComponentName name,IBinder service);
文章参考:
《Android 典型技术模块开发详解》
本人郑重声明,本博客所编文章、图片版权归权利人持有,本博只做学习交流分享所用,不做任何商业用途。访问者可將本博提供的內容或服务用于个人学习、研究或欣赏,不得用于商业使用。同時,访问者应遵守著作权法及其他相关法律的规定,不得侵犯相关权利人的合法权利;如果用于商业用途,须征得相关权利人的书面授权。若文章、图片的原作者不愿意在此展示內容,请及时通知在下,將及时予以刪除。