背景
Read the fucking source code!--By 鲁迅A picture is worth a thousand words.--By 高尔基
说明:
- Kernel版本:4.14
- ARM64处理器,Contex-A53,双核
- 使用工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio
1. 概述
本文将描述memory compaction,内存碎片整理技术。
内存碎片分为内碎片和外碎片:
- 内碎片:内存页里边的碎片;
- 外碎片:内存页之间的碎片,可能会造成连续物理页面分配失败。
memory compaction就是通过将正在使用的可移动页面迁移到另一个地方以获得连续的空闲页面的方法。针对内存碎片,内核中定义了migrate_type用于描述迁移类型:
MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE:不可移动,对应于内核分配的页面;MIGRATE_MOVABLE:可移动,对应于从用户空间分配的内存或文件;MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE:不可移动,可以进行回收处理;
上图对应的是struct page的操作,而针对物理内存的操作如下图所示:
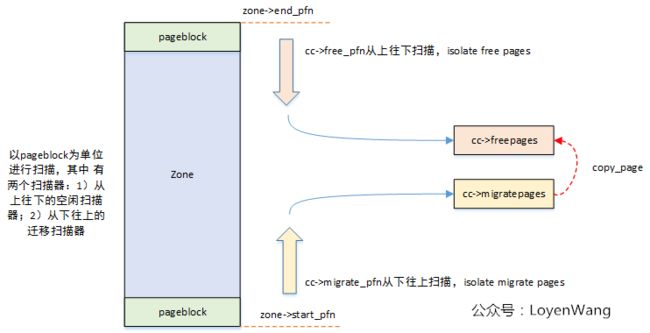
在之前的文章中提到过pageblock,我们看到图中zone区域是以pageblock为单位上下扫描的,pageblock的大小定义如下(未使用huge table情况下),与Buddy System管理中的最大块大小一致:
/* If huge pages are not used, group by MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES */
#define pageblock_order (MAX_ORDER-1)
#define pageblock_nr_pages (1UL << pageblock_order)好了,已经有一个初步印象了,那就进一步的分析吧。
1. 数据结构
1.1 compact_priority
/*
* Determines how hard direct compaction should try to succeed.
* Lower value means higher priority, analogically to reclaim priority.
*/
enum compact_priority {
COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_FULL,
MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_FULL,
COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT,
MIN_COMPACT_COSTLY_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT,
DEF_COMPACT_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT,
COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC,
INIT_COMPACT_PRIORITY = COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC
};本结构用于描述memory compact的几种不同方式:
COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_FULL/MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY:最高优先级,压缩和迁移以同步的方式完成;COMPACT_PRIO_SYNC_LIGHT/MIN_COMPACT_COSTLY_PRIORITY/DEF_COMPACT_PRIORITY:中优先级,压缩以同步方式处理,迁移以异步方式处理;COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC/INIT_COMPACT_PRIORITY:最低优先级,压缩和迁移以异步方式处理。
1.2 compact_result
本结构用于描述压缩处理函数的返回值:
/* Return values for compact_zone() and try_to_compact_pages() */
/* When adding new states, please adjust include/trace/events/compaction.h */
enum compact_result {
/* For more detailed tracepoint output - internal to compaction */
COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE,
/*
* compaction didn't start as it was not possible or direct reclaim
* was more suitable
*/
COMPACT_SKIPPED,
/* compaction didn't start as it was deferred due to past failures */
COMPACT_DEFERRED,
/* compaction not active last round */
COMPACT_INACTIVE = COMPACT_DEFERRED,
/* For more detailed tracepoint output - internal to compaction */
COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE,
/* compaction should continue to another pageblock */
COMPACT_CONTINUE,
/*
* The full zone was compacted scanned but wasn't successfull to compact
* suitable pages.
*/
COMPACT_COMPLETE,
/*
* direct compaction has scanned part of the zone but wasn't successfull
* to compact suitable pages.
*/
COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED,
/* compaction terminated prematurely due to lock contentions */
COMPACT_CONTENDED,
/*
* direct compaction terminated after concluding that the allocation
* should now succeed
*/
COMPACT_SUCCESS,
};1.3 migrate_mode
本结构用于描述migrate过程中的不同模式,主要针对同步和异步的处理。
/*
* MIGRATE_ASYNC means never block
* MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT in the current implementation means to allow blocking
* on most operations but not ->writepage as the potential stall time
* is too significant
* MIGRATE_SYNC will block when migrating pages
* MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY will block when migrating pages but will not copy pages
* with the CPU. Instead, page copy happens outside the migratepage()
* callback and is likely using a DMA engine. See migrate_vma() and HMM
* (mm/hmm.c) for users of this mode.
*/
enum migrate_mode {
MIGRATE_ASYNC,
MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT,
MIGRATE_SYNC,
MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY,
};1.4 compact_control
compact_control结构体用于在执行compact的时候,维护两个扫描器,对应freepages和migratepages,最终将migratepages中的页拷贝到freepages中去。具体的字段注释足够详尽,不细说了。
/*
* compact_control is used to track pages being migrated and the free pages
* they are being migrated to during memory compaction. The free_pfn starts
* at the end of a zone and migrate_pfn begins at the start. Movable pages
* are moved to the end of a zone during a compaction run and the run
* completes when free_pfn <= migrate_pfn
*/
struct compact_control {
struct list_head freepages; /* List of free pages to migrate to */
struct list_head migratepages; /* List of pages being migrated */
struct zone *zone;
unsigned long nr_freepages; /* Number of isolated free pages */
unsigned long nr_migratepages; /* Number of pages to migrate */
unsigned long total_migrate_scanned;
unsigned long total_free_scanned;
unsigned long free_pfn; /* isolate_freepages search base */
unsigned long migrate_pfn; /* isolate_migratepages search base */
unsigned long last_migrated_pfn;/* Not yet flushed page being freed */
const gfp_t gfp_mask; /* gfp mask of a direct compactor */
int order; /* order a direct compactor needs */
int migratetype; /* migratetype of direct compactor */
const unsigned int alloc_flags; /* alloc flags of a direct compactor */
const int classzone_idx; /* zone index of a direct compactor */
enum migrate_mode mode; /* Async or sync migration mode */
bool ignore_skip_hint; /* Scan blocks even if marked skip */
bool ignore_block_suitable; /* Scan blocks considered unsuitable */
bool direct_compaction; /* False from kcompactd or /proc/... */
bool whole_zone; /* Whole zone should/has been scanned */
bool contended; /* Signal lock or sched contention */
bool finishing_block; /* Finishing current pageblock */
};2. 调用流程
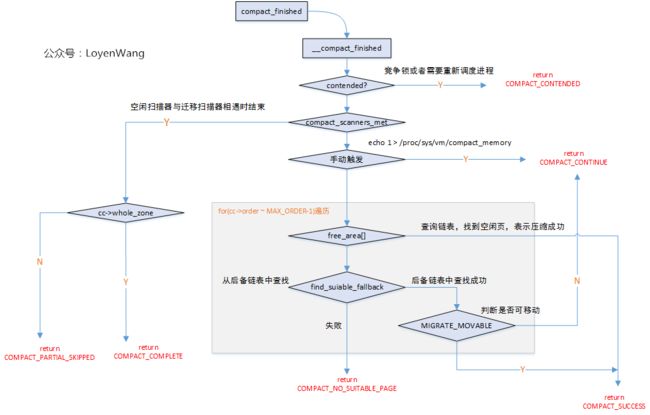
光看上文的数据结构,会比较零散,看看整体的流程吧。
在内核中,有三种方式来操作memory compact:
- 在内存分配过程中,由于分配请求不能满足,直接触发内存
compact处理; - 在没有足够内存的情况下,
kcompactd守护线程在后台唤醒,执行compact处理; - 手动触发,通过
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/compact_memory来触发;
实际操作一把:
cat /proc/pagetypeinfo如下图:
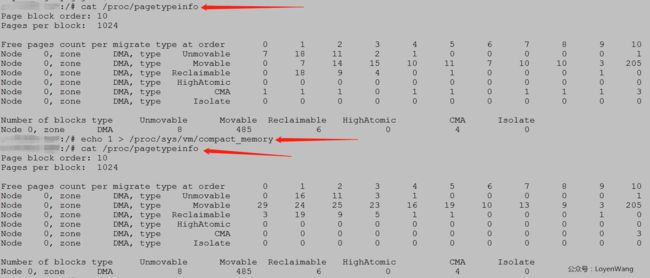
3. compact处理
下边将针对各个子模块更深入点分析。
判断是否执行内存的碎片整理,需要满足以下三个条件:
- 除去申请的页面,空闲页面数将低于水印值,或者虽然大于等于水印值,但是没有一个足够大的空闲页块;
- 空闲页面减去两倍的申请页面(两倍表明有足够多的的空闲页面作为迁移目标),高于水印值;
- 申请的
order大于PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER时,计算碎片指数fragindex,根据值来判断;
isolate_migratepages
isolate_migratepages函数中,迁移扫描器以pageblock为单位,扫描可移动页,最终把可移动的页添加到struct compact_control结构中的migratepages链表中。如下图所示:
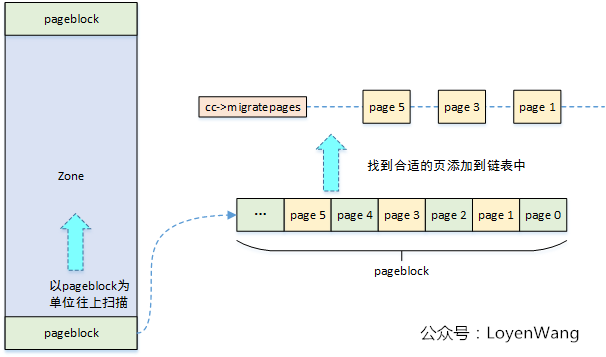
isolate_freepages的逻辑与isolate_migratepages类似,也是对页进行隔离处理,最终添加cc->freepages链表中。
当空闲扫描器和迁移扫描器完成扫描之后,那就是时候将两个链表中的页做一下migrate操作了。
migrate_pages
- 调用
compact_alloc函数,从cc->freepages链表中取出一个空闲页; - 调用
__unmap_and_move来把可移动页移动到空闲页处;
_unmap_and_move函数涉及到反向映射,以及页缓存等,留在以后再深入看。这个函数两个关键作用:1)调用try_to_unmap删除进程页表中旧的映射关系,在需要访问的时候再重新映射到新的物理地址上;2)调用move_to_new_page函数将旧页移动到新的物理页上,其中在汇编文件arch/arm64/lib/copy_page.S中copy_page函数完成拷贝。
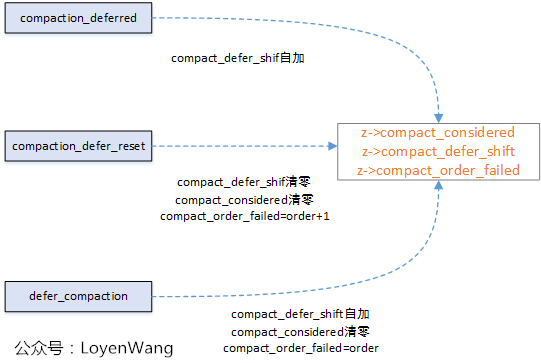
compaction_deferred/compaction_defer_reset/defer_compaction
上述这三个函数与内存碎片推迟compact有关,这三个函数是在try_to_compact_pages中调用。当free pages除去申请页面数高于水位值,且申请或备用的迁移类型至少有一个足够大的空闲页面时,可以认为compact成功。在没有成功时,可能需要推迟几次来处理。
struct zone结构中与之有关的字段如下:
struct zone {
...
/*
* On compaction failure, 1<