编译原理实验一:词法分析
实验一:词法分析程序
一、实验目的
通过设计编制调试一个具体的词法分析程序,加深对词法分析原理的理解。并掌握在对程序设计语言源程序进行扫描过程中将其分解为各类单词的词法分析方法。
编制一个读单词过程,从输入的源程序中,识别出各个具有独立意义的单词,即基本保留字、标识符、常数、运算符、分隔符五大类。并依次输出各个单词的类型码及单词符号的自身值。(遇到错误时可显示“Error”,然后跳过错误部分继续显示)
二、实验要求
用C或C++写一个简单的词法分析程序,程序可以满足下列要求:
1、能分析如下几种简单的语言词法
(1) 标识符: ID=letter(letter|digit)*
(2) 关键字(全部小写)
main int float double char if then else switch case break continue while do for
(3)整型常量:NUM=digit digit*
(4)运算符
= + - * / < <= == != > >= ; ( )? :
(5)空格由空白、制表符和换行符组成,用以分隔ID、NUM、运算符等,字符分析时被忽略。
2、单词符号和相应的类别码
假定单词符号和相应的类别码如下:
单词符号 种别码
int 1
= 17
float 2
< 20
if 3
<= 21
switch 4
== 22
while 5
!= 23
Do 6
> 24
标识符 10
>= 25
整型常量 11
; 26
+ 13
( 27
- 14
) 28
* 15
? 29
/ 16
: 30
3、词法分析程序实现的功能
输入:单词序列(以文件形式提供),输出识别的单词的二元组序列到文件和屏幕
输出:二元组构成: (syn,token或sum)
其中: syn 为单词的种别码
token 为存放的单词自身符号串
sum 为整型常数
例:
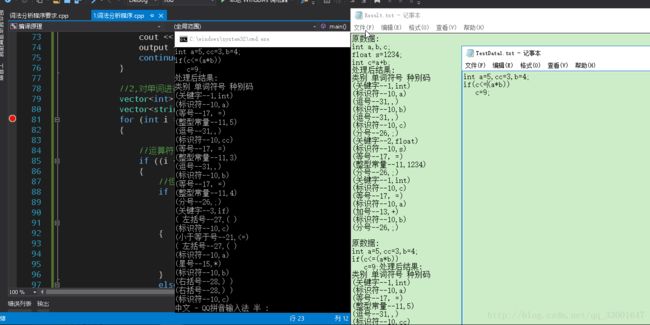
源程序: int ab; float ef=20;
ab=10+ef;
输出:
(保留字--1,int)
(标识符--10,ab)
(分号--26,;)
(保留字--2,float)
(标识符--10,ef)
(等号--17,=)
(整数--11,20)
(分号--26,;)
(标识符--10,ab)
(等号--17,=)
(整数--11,10)
(加号--13,+)
(标识符--10,ef)
(分号--26,;)
4、自己准备测试数据存放于TestData.txt文件中,测试数据中应覆盖有以上5种数据,测试结果要求以原数据与结果对照的形式输出并保存在Result.txt中,同时要把结果输出到屏幕。
5、提前准备
① 实验前,先编制好程序,上机时输入并调试程序。
② 准备好多组测试数据(存放于文件TestData.txt中)。
本以为很快就能做出来的,没想到前前后后共总共大概花了3个小时,惭愧,大体流程就是读取文件中的内容,先一行一行的读,读取一行后然后利用istringstream流读取单词,需要注意,比如一行输入是”int a=1,bcd=4;”,这里单词就是”int”和”a=1,bcd=4”,因为读取时遇到空格,制表符等就读入一个单词,所以还要对单词进行分割,将标识符,运算符(+,-,<=,>=,!=,==,逗号等等),整型数字(为了简单起见,只用整形数字)分开,难点就在于怎么分,分开后对每个分开的单词然后再根据是标识符还是运算符等等,对应输出就行了
代码:
# include//流对象
# include"pause");
return 0;
}
bool isIdentifier(string s)//标识符,试验要求:ID=letter(letter|digit)*
{
if (!isKeywords(s))//标识符不能是关键字
{
if ((s[0] >= 'a'&&s[0] <= 'z') || (s[0] >= 'A'&&s[0] <= 'Z'))//是字母
{
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++)
{
if ((s[i] >= 'a'&&s[i] <= 'z') || (s[i] >= 'A'&&s[i] <= 'Z')
|| (s[i] >= '0'&&s[i] <= '9'))
continue;
else return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
return false;
}
bool isKeywords(string s)//关键字
{
static vector<string> keyVec = { "main", "int", "float", "double", "char",
"if", "then","else", "switch", "case", "break", "continue", "while",
"do", "for" };
vector<string>::iterator result = find(keyVec.begin(), keyVec.end(),s);
if (result != keyVec.end())
return true;
else return false;
}
bool isDigit(string s)//整型数字,NUM=digit digit*
{
if (s[0] >= '0'&&s[0] <= '9')
{
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); ++i)
if (s[i] >= '0'&&s[i] <= '9')
continue;
else return false;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool isOperator(string s)//运算符
{
static vector<string> opeVec = { "=","+","-","*","/","<","<=","==","!=",
">",">=",";","(",")","?",":","," };
vector<string>::iterator result = find(opeVec.begin(), opeVec.end(), s);
if (result != opeVec.end())
return true;
else return false;
}
bool isOperator(char c)//运算符
{
static vector<char> opeVec = { '=','+','-','*','/','<',
//"<=","==","!=",
'>',
//">=",
';','(',')','?',':',',' };
vector<char>::iterator result = find(opeVec.begin(), opeVec.end(), c);
if (result != opeVec.end())
return true;
else return false;
}
string result(string s)//根据传入的参数s产生对应的输出
{
//种别码
//1.标识符
if (isIdentifier(s))
return "(标识符--10,"+s+")";
//2.关键字
static map<string, string> keyMap;
keyMap["int"] = "1";
keyMap["float"] = "2";
keyMap["if"] = "3";
keyMap["switch"] = "4";
keyMap["while"] = "5";//只写5个吧,没必要全写
if (isKeywords(s))
return "(关键字--"+keyMap[s]+"," +s+")";
//3.整型常量
if (isDigit(s))
return "(整型常量--11,"+s+")";
//4.运算符
static map<string, string> opeMap;
opeMap["="] = "(等号--17,=)";
opeMap["<"] = "(小于号--20,<)";
opeMap["<="] = "(小于等于号--21,<=)";
opeMap["=="] = "(赋值运算符--22,==)";
opeMap["!="] = "(不等于号--23,!=)";
opeMap[">"] = "(大于号--24,>)";
opeMap[">="] = "(大于等于号--25,>=)";
opeMap[";"] = "(分号--26,;)";
opeMap["+"] = "(加号--13,+)";
opeMap["("] = "( 左括号--27,( )";
opeMap["-"] = "(减号--14,-)";
opeMap[")"] = "(右括号--28,) )";
opeMap[">"] = "(大于号--24,>)";
opeMap["*"] = "(星号--15,*)";
opeMap["?"] = "(问号--29,?)";
opeMap["/"] = "(除号--16,/)";
opeMap[":"] = "(冒号--30,:)";
opeMap[","] = "(逗号--31,,)";
if (isOperator(s))
return opeMap[s];
return "Error";
}