一个列子让你弄懂SpringBoot实现后台框架的搭建
- 首先项目搭建
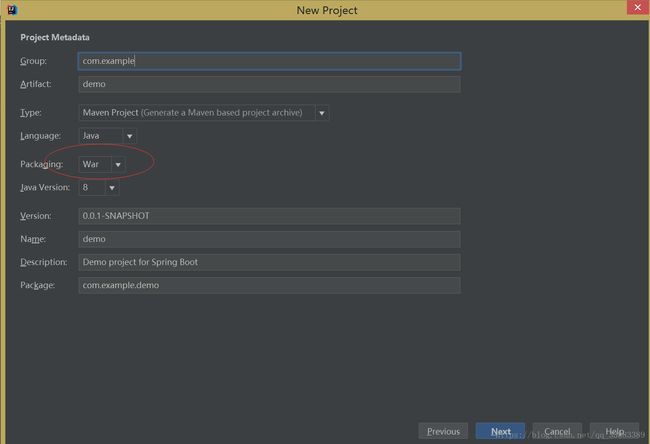
首先项目基于idea来写的,下面演示项目搭建d
记住Application文件一定要在根目录底下不然程序会运行不起来的
-
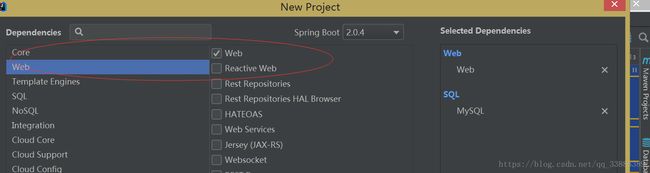
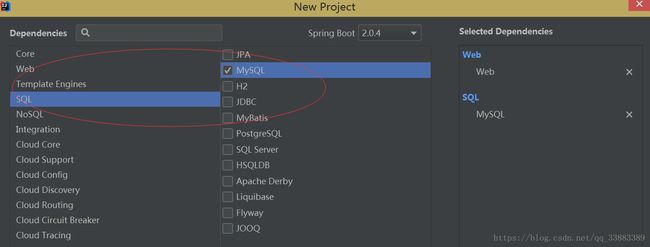
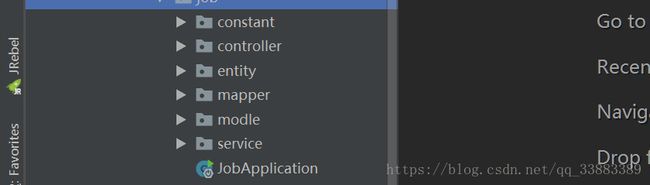
然后开始新建包。
- constant :常量包,存放一些常量数据,如定义服务器响应状态码。
- controller: 控制器,存放各种控制器,来提供数据或者返回界面
- entity:实体类包,存放各种与数据库对应的实体类
- mapper:存放各种与数据库映射的类
- modle:封装返回数据json的格式样式
- service:返回数据给控制调用
Application:程序的入口:
package com.wust.job;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@MapperScan("com.wust.job.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class JobApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(JobApplication.class, args);
}
}
解释:@MapperScan("com.wust.job.mapper") 这个用来扫描当前项目的实体类的映射。
- pom文件
4.0.0
com.wust
job
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
war
job
Demo project for Spring Boot
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.0.3.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
javax.servlet
jstl
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.apache.commons
commons-lang3
3.4
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-core
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype
jackson-datatype-joda
com.fasterxml.jackson.module
jackson-module-parameter-names
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper-spring-boot-starter
1.2.5
com.alibaba
druid-spring-boot-starter
1.1.9
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
- 配置我们的yml文件
spring:
mvc:
view:
prefix: /WEB-INF/view/
suffix: .jsp
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: zhengmeng001
解释: 这里用yml来写,格式要严谨点,但是看的清楚点。
下面介绍怎样封装一个(通用)json数据格式。
{
"code":0,
"msg":"essays success",
"count":100,
"data":[
Object{...},
{
"id":54,
"title":"测试文章",
"username":"admin",
"viewCount":148321,
"remarkCount":897897,
"collectCount":574804,
"titleid":243557,
"date":"2018-07-22T16:00:00.000+0000"
},
{
"id":55,
"title":"fsdfds",
"username":"admin",
"viewCount":194468,
"remarkCount":576879,
"collectCount":328477,
"titleid":737659,
"date":"2018-07-23T16:00:00.000+0000"
}
]
}解释 :
- code 为响应码,这里0 表示成功,1表示失败
- msg 返回信息,成功者返回成功的信息,错误者返回为什么错了
- count 返回数据的长度
- data 里存放我们的真实数据的集合 ,所以我们只需动态的改变他就可以了,当是文章这里填的是文章的集合,当时个人信息是则填个人信息的集合。
- 上面code,msg count为公用字段,我们可以提取出来作为公共字段,其他的json模板继承他就可以了。
package com.wust.job.modle;
/**
* 〈json封装的基类
*
* 其他json的实体类必须继承该类
* 〉
* 〈〉
*
* @author meng
* @create 2018/7/17
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public class BaseModle {
public int code;
public String msg;
public int count;
public BaseModle() {
}
public BaseModle(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public BaseModle(int code, String msg, int count) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.count = count;
}
}
譬如:
package com.wust.job.modle.users;
import com.wust.job.entity.Users;
import com.wust.job.entity.UsersInformation;
import com.wust.job.modle.BaseModle;
import java.util.List;
//返回个人信息的json
public class UsersModle extends BaseModle {
public List data;
}
于是我们可以写出如下的东西:
封装好了我们的(在此之前应该封装好了我们实体类层)json数据层之后,开始写我们的Mapper层(操作数据库层)
- Mapper层(基于注解形式完成)
package com.wust.job.mapper;
import com.wust.job.entity.Essay;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public interface IEssayMapper {
@Select("select *from essay")
public List getAllEssay();
@Select("Select *from essay where username=#{username}")
public List getUsersEssay(@Param("username") String username);
@Select("select *from essay where title=#{title}")
public List getUsersEssayByTitle(@Param("title") String title);
@Delete("delete from essay where username=#{username}")
public int deleteMyEssay(String username);
@Delete("delete from essay where titleid=#{titleid}")
public int deleteMyEssayByTitleId(int titleid);
@Insert("insert into essay value (null,#{title},#{username},#{viewCount},#{remarkCount},#{collectCount},#{titleid},#{date})")
int addEssay(Essay essay);
}
- 再写我们的Service层(调用Mapper层来完成相应操作)
-
/** * Copyright (C), 2015-2018, XXX有限公司 * FileName: EssayService * Author: meng * Date: 2018/7/17 15:36 * Description: * History: *
- 再写Controller层
package com.wust.job.controller;
import com.wust.job.constant.Constant;
import com.wust.job.entity.Essay;
import com.wust.job.modle.BaseModle;
import com.wust.job.modle.EssayModle.EssayModle;
import com.wust.job.service.EssayService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 〈一句话功能简述〉
* 〈〉
*
* @author meng
* @create 2018/7/19
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@CrossOrigin
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/essay")
public class EssayController {
@Autowired
private EssayService essayService;
@Autowired
HttpServletRequest request;
@Autowired
HttpSession httpSession;
/**
* 返回文章的列表信息
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getAllEssay")
@ResponseBody
public EssayModle getAllEssay() {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String title = request.getParameter("title");
if(username == null){
return returnEssays(essayService.getAllEssay());
}else{//如果输入框为空
System.out.println("username = "+username);
System.out.println("title = "+title);
if(username.length() == 0){
return returnEssays(essayService.getAllEssay());
}else{//输入框不为空,可能是按照用户名,或者是文章标题来搜索
List essays = essayService.getUsersEssayByTitle(title);//按照用户名搜索
if(essays == null ||essays.size() ==0){//为空的时候说明不是用户名搜索,或者是不存在
essays = essayService.getUserEssay(username);
if(essays !=null){
return returnEssays(essays);
}else{
return null;
}
}else {//不为空说明是为标题
return returnEssays(essays);
}
}//end else
}//end if
}
/**
* 返回该用户的文章
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getUserEssay")
@ResponseBody
public EssayModle getUserEssay( ) {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("getUserEssay"+username);
return returnEssays(essayService.getUserEssay(username));
}
public EssayModle returnEssays(List essays) {
if (essays != null) {
return new EssayModle(0, "essays success",100, essays);
}
return new EssayModle(1, "essays error",0, null);
}
/**
* 添加图书界面
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/addEssayPage")
public String essayPage(){
return "account/addEssay";
}
//只能超级用户添加即 admin
@RequestMapping("/addEssay")
@ResponseBody
public BaseModle addEssay(){
String title = request.getParameter("title");
System.out.println("title = "+title);
Random random = new Random();
int viewCount = random.nextInt(1000000);
int remarkCount = random.nextInt(1000000);
int collectCount = random.nextInt(1000000);
int titleId = random.nextInt(1000000);
if(essayService.addEssay(new Essay(
0,
title,
"admin",
viewCount,
remarkCount,
collectCount,
titleId,
new Date()
))){
return new BaseModle(Constant.SUCESS,"添加文章成功",10);
}
return new BaseModle(Constant.ERROR,"添加文章失败",0);
}
}
解释:
- @Autowired 实际上等于new
- @ResponseBody 标志这个方法返回我们的数据的 这里我们只需返回我们上层封装好的Modle 及json模板 将其返回springboot会自动的将其转化为json格式的数据
- @CrossOrigin 开启跨域访问
这样我就一层层的搭建好了。
这样我们可以实现如下功能了