Leetcode学习之栈、队列、堆(3)
开宗明义:本系列基于小象学院林沐老师课程《面试算法 LeetCode 刷题班》,刷题小白,旨在理解和交流,重在记录,望各位大牛指点!
Leetcode学习之栈、队列、堆(3)
文章目录
- 1、STL优先级队列(二叉堆)
- 2、求数组中第K大的数(Top K) Leetcode 215.
- 3、寻找中位数 Leetcode 295.
1、STL优先级队列(二叉堆)
堆:通常可以被看做一棵树,它满足下列性质:
- 堆中任意节点的值总是不大于(不小于)其子节点的值;
- 堆总是一棵完全树。
二叉堆:二叉堆是完全二元树或者是近似完全二元树,它分为两种:最大堆和最小堆。
最大堆:父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值;
最小堆:父结点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值。
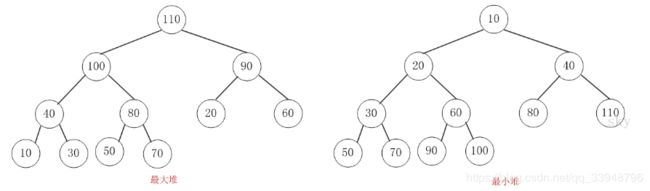
二叉堆,也叫优先级队列,STL包含到 # i n c l u d e < q u e u e > \#include <queue> #include<queue>中。
测试代码:
#include , isgreater> small_heap;//最小堆构造方法
priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::less<int>> big_heap2;//最大堆构造方法
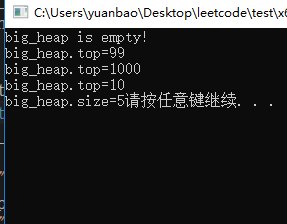
if (big_heap.empty()) {
printf("big_heap is empty!\n");
}
int test[] = { 6,10,1,7,99,4,33 };
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
big_heap.push(test[i]);//把元素push进入最大堆
}
printf("big_heap.top=%d\n", big_heap.top());//打印这个优先级队列的第一个元素,普通的queue是33,但是最大堆应为99
big_heap.push(1000);
printf("big_heap.top=%d\n", big_heap.top());//这时候应该1000
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
big_heap.pop();
}
printf("big_heap.top=%d\n", big_heap.top());//这时候应该10
printf("big_heap.size=%d", big_heap.size());
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、求数组中第K大的数(Top K) Leetcode 215.
题目来源: L e e t c o d e 215. K t h L a r g e s t E l e m e n t i n a n A r r a y Leetcode \ 215.\ Kth \ Largest \ Element \ in \ an \ Array Leetcode 215. Kth Largest Element in an Array
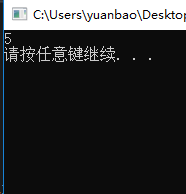
题目描述:已知一个未排序的数组,求这个数组中第K大的数字,如,array=[3,2,1,5,6,4],k=2,return 5。
思路:维护一个K大小的最小堆,堆中元素个数小于K时,新元素直接进入堆中;否则,当堆顶的元素小于新元素时,弹出堆顶,将新元素加入堆,注意啊:加入堆的话,会调整堆,因为这个堆只有k大小,进来一个就会出去一个。这样做的理由:使用的堆为最小堆,堆顶是堆中最小的元素,新元素都会保证比堆顶小,因为新元素比堆顶大的话,会进入堆,调整堆。所以堆中K个元素是已扫描的元素里最大的K个。堆顶即第K大的数。
设数组长度为 N N N,求第 K K K大的数,时间复杂度为: N ∗ l o g K N*logK N∗logK。

测试代码:
#include 3、寻找中位数 Leetcode 295.
题目来源: L e e t c o d e 295. F i n d M e d i a n f r o m D a t a S t r e a m Leetcode \ 295. \ Find \ Median \ from \ Data \ Stream Leetcode 295. Find Median from Data Stream
题目描述:设计一个数据结构,该数据结构动态维护一组数据,且支持如下操作:
1、添加元素:void addNum(int num),将整型num添加至数据结构中。
2、返回数据的中位数:double findMedian(),返回其维护的数据的中位数。
其中,中位数的定义:
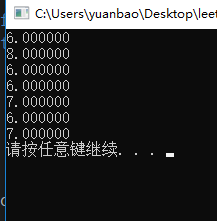
1.若数据个数为奇数,中位数是该组数排序后中间的数。如[1,2,3]->2。
2. 若数据个数为偶数,中位数是该组数排序后中间两个数字的平均值。如[1,2,3,4]->2.5。
要求描述:

思路:
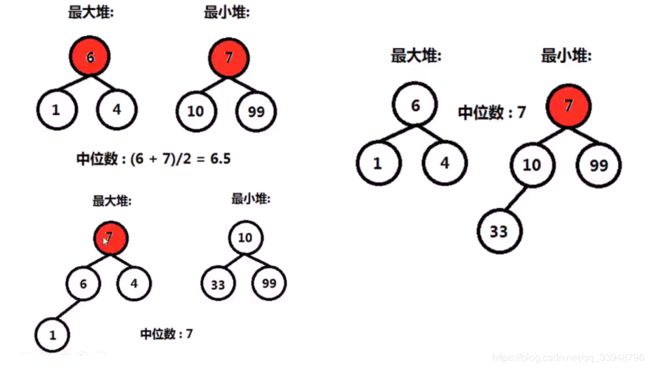
复杂度太高->巧用堆的性质:动态维护一个最大堆与最小堆,最大堆存储一半数据,最小堆存储一半的数据,维持的状态是:最大堆的堆顶比最小堆的堆顶小。
有三种情形:①偶数,最大堆与最小堆各一半;
②奇数,最大堆比最小堆多一个元素;
③奇数,最大堆比最小堆少一个元素;
测试代码:
#include