Vector源码解析
Vector源码解析
1. Vector概述及继承体系
Vector 类可以实现可增长的对象数组。与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引进行访问的组件。与新 collection 实现不同,Vector 是同步的。
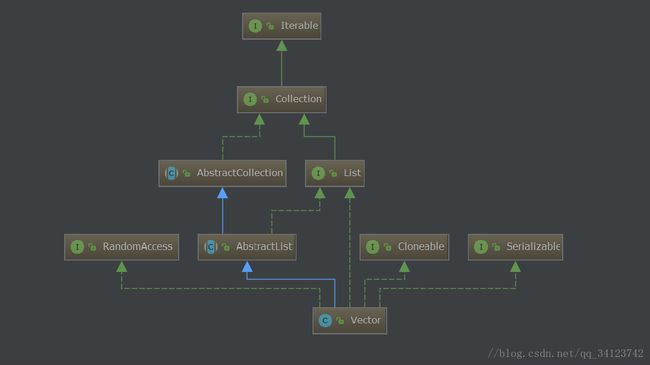
看一下Vector的继承体系:
public class Vector<E>extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, SerializableMarker interface used by List implementations to indicate that they
support fast (generally constant time) random access.
翻译下就是:这是一个标记性的接口,谁实现了这个接口就表明他具有快速随机访问的能力。
2. Vector属性
capacityIncrement:自动扩容的大小,即当数组满了之后,就添加capacityIncrement个空间装载元素,如果capacityIncrement<=0,则扩容时就扩容到目前Vector容量的两倍。
elementCount:记录数组中数据的个数。
elementData:数组,因为Vector底层也是数组存储的,所以用这个来存储数据。
protected int capacityIncrement; //扩容大小
protected int elementCount; //数组数据条数
protected Object[] elementData; //数组3. Vector构造方法
Vector构造方法有四个构造方法
3.1.Vector()
构造一个空向量,使其内部数据数组的大小为 10,其标准容量增量为零。
public Vector() {
this(10);//这里的this调用的是Vector(int initialCapacity) 方法
}3.2.Vector(Collection <\?extends E> c)
构造一个包含指定 collection 中的元素的向量,这些元素按其 collection 的迭代器返回元素的顺序排列。
public Vector(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
//c.toArray可能(不正确)不返回Object [](参见6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
//用Arrays.copyOf()方法转换类型。
}3.3.Vector(int initialCapacity)
使用指定的初始容量和等于零的容量增量构造一个空向量。
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);//这里的this其实调用的是Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)方法
}3.4.Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)
我们从前面知道,无参构造和单参构造本质上都调用的是这个方法。我们来具体了解一下。
使用指定的初始容量和容量增量构造一个空的向量。
//initialCapacity指的是初始容量。
//capacityIncrement指的是扩容容量。
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
//从这里可以看出Vector底层也是数组实现的。
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}4. Vector常用方法
4.1.Vector最初的方法
1.addElement(E obj)
将指定的组件添加到此向量的末尾,将其大小增加 1。如果向量的大小比容量大,则增大其容量。
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}从addElement方法中有ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
我们大致可以推测出这一步是用来扩容的。接着看这个方法:
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code检测是否大于数组长度
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
} private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
//注意:这是和ArrayList不同的地方,这个的自动扩容是直接增加一个oldCapacity,也就是扩大了一倍。
/*第一个判断是怕扩容的数组长度还是太小,就用minCapacity 来进行对数组的扩张。
第二个判断是如果扩张1倍太大或者是我们所需的空间大小minCapacity太大,则进行Integer.MAX_VALUE来进行扩张。
*/
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}2.elementAt(int index)
返回指定索引处的组件。 其实这个方法就是和我们之前使用的get方法很相似。源码很简单,就是说先进行一个index的有效位检验,如果正确在进入elementData(int index)方法,直接取数组的数据。
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
//---------------------------------------------
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}3. elements()
返回此向量的组件的枚举。返回的 Enumeration 对象将生成此向量中的所有项。生成的第一项为索引 0 处的项,然后是索引 1 处的项,依此类推。
其实我们仔细观察就可以发现,这个和我们之前遍历时候用的Iterator很相似。
public Enumeration elements() {
return new Enumeration() {
int count = 0;
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return elementData(count++);
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
} Enumeration是一个接口,直接在方法里面实现。从中我们可以看到hasMoreElements()和nextElement()方法。下来举个例子来体会一下。
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 对Vector的一个简单使用
* */
Vector v=new Vector ();
v.addElement ("hello"); //-------------->add()
v.addElement ("world");
v.addElement ("java");
System.out.println (v.elementAt (1));//下标从0开始 //-------------->get()
System.out.println ("-----------------");
Enumeration elements = v.elements (); //-------------->Iterator()
while (elements.hasMoreElements ()){ //-------------->hasNext()
Object o = elements.nextElement (); //-------------->next()
System.out.println (o);
}
}4.2.Vector JDK1.2之后的方法
JDK1.2之后出来的方法,为什么有之前的方法还要再加入新方法?
JDK1.2升级的原因无非有三个:1.安全问题2.效率问题3.简化书写
1.add
添加元素的方法实现比较简单:直接在数组的后一个位置添加即可,不过在添加元素之前需要检查数组中是否已满,如果已满,则扩容。
//添加一个元素到末尾,数组长度+1
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
//添加一个元素到指定位置。
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
/*insertElementAt()方法,先进行有效位检验,然后在使用ensureCapacityHelper更改数组长度+1,在使用
System.arraycopy()方法,这个方法的具体解析,可以去看ArrayList的源码,里面有分析。
*/
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
//
public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection c) {
modCount++;
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}2.get
返回向量中指定位置的元素。
先进行有效位检验,直接从数组取相应下标元素。类似于elementAt(int index)
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}3. set
用指定的元素替换此向量中指定位置处的元素。 Vector底层使用的是数组,所以这就相当于对数组的操作。先进行有效位检验,然后把指定下标的元素改成element。
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}4.remove
remove方法其实和ArrayList里面的方法区别不大。我们主要来看两个方法就可以了。
4.4.1.remove(int index)
先进行有效位检测,然后取出index下标的元素,在计算index元素之后的长度,最后使用 System.arraycopy()直接把index位置跳过,再把elementData[]最后一位元素置为null,让垃圾回收器将其回收。
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}4.4.2.remove(Object o)
删除指定元素。其实这个也特别简单,remove(Object o)底层调用了removeElement(o)方法。removeElement(o)的实现就是先把当前元素的位置下标取出来,然后有了下标就可以使用remove(int index)方法了。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
//--------------------------------
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}5. 总结
Vector里面是基于数组来实现的需要注意的是:Vector是线程安全的,因此,在多线程并发中是不需要使用额外同步的,而ArrayList实现基本与Vector一样,但是区别是:ArrayList是线程不安全的,在多线程并发时,需要我们进行额外的同步。