《随笔二十二》——C#中的 “ where字句、扩展方法和泛型类、泛型委托、泛型接口、协变、逆变”
目录
泛型类的示例
where 字句 (317P)
有哪些类型可以被 where 子句所约束 (318P)
泛型方法 (319P)
扩展方法 (145P)
扩展方法和泛型类 (322P)
泛型结构体 (323P)
泛型委托 (323P)
泛型接口 ( 325P )
在普通类中实现泛型接口 (326P)
泛型接口的实现必须唯一 (327P)
泛型类的示例
c# 可以把以下类型编写为泛型:
- 类、结构、接口、委托和方法。注意前四个是类型,方法是成员。
下面是一个泛型栈的代码示例:
namespace HelloWorld_Console
{
class MyStack
{
const int MaxStack = 10;
T[] StackArray;
int StackPointer = 0;
public MyStack()
{
StackArray = new T[MaxStack];
}
public void Push(T x)
{
if (!IsStackFull)
StackArray[StackPointer++] = x;
}
public T Pop()
{
return (!IsStackEmpty) ? StackArray[--StackPointer] : StackArray[0];
}
public void Print()
{
for (int i=0;i= MaxStack;
}
}
bool IsStackEmpty
{
get
{
return StackPointer <= 0;
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyStack StackInt = new MyStack();
MyStack StackString = new MyStack();
var StackDouble = new MyStack(); //使用 var 关键字让编译器自己判断类型
StackInt.Push(3);
StackInt.Push(5);
StackInt.Push(7);
StackInt.Push(9);
StackInt.Print();
ReadKey();
}
}
}
where 字句 (317P)
要让泛型变得更有用, 我们需要提供额外的信息让编译器知道类型参数可以接受哪些类型。这些额外的信息叫做约束( constrain ),只有符合约束的类型才能替代给定的类型参数, 来产生构造类型。
那么约束 使用 where 字句。
- 每个具有约束的类型参数都有自己的where子句。
- 如果参数具有多个约束,则它们将在where子句中列出,以逗号分隔。
where 字句的语法如下:
例如, 如下泛型类有3个类型参数。
- T1是未绑定的, 对于T2只有 Customer类型 或从Customer继承的类型的类才能用作类型实参,
- 而对于T3只有实现IComparable接口的类才能用于类型实参。
有哪些类型可以被 where 子句所约束 (318P)
共有五种类型的约束,如图:
where子句可以以任何次序列出。然而, where子句中的约束列表中的约束必须有特定的顺序:
- 最多只能有一个主约束,如果有则必须放在第一位。
- 可以有任意多的接口名约束。
- 如果存在构造函数约束, 则必须放在最后。
泛型方法 (319P)
泛型方法可以在哪些地方声明:
- 可以在 泛型类 和非泛型类
- 以及在结构 和 接口中声明。
泛型方法具有类型参数列表 和 可选的约束。
那么声明 泛型方法的语法为:
记住: 类型参数列表在函数名之后,形参列表之前。
泛型方法的代码示例:
namespace HelloWorld_Console
{
class Simple
{
static public void ReverseAndPrint(T[]arr) // 泛型方法
{
Array.Reverse(arr);
foreach (T item in arr)
Write($"{item.ToString()}");
WriteLine("");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建各种类型的数组
var intArray = new int[] { 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 };
var stringArray = new string[] {"first","second","third",};
var doubleArray = new double[] { 3.597, 7.891, 2.345 };
Simple.ReverseAndPrint(intArray); // 调用方法
Simple.ReverseAndPrint(intArray); // 推断类型并调用
Simple.ReverseAndPrint(stringArray);
Simple.ReverseAndPrint(stringArray);
Simple.ReverseAndPrint(doubleArray);
Simple.ReverseAndPrint(doubleArray);
ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出结果为:
119753
357911
thirdsecondfirst
firstsecondthird
2.3457.8913.597
3.5977.8912.345
扩展方法 (145P)
到目前为止,在本文中,您看到的每个方法都与声明它的类相关联。扩展方法特性扩展了这个边界,允许您编写与声明类以外的类相关联的方法。
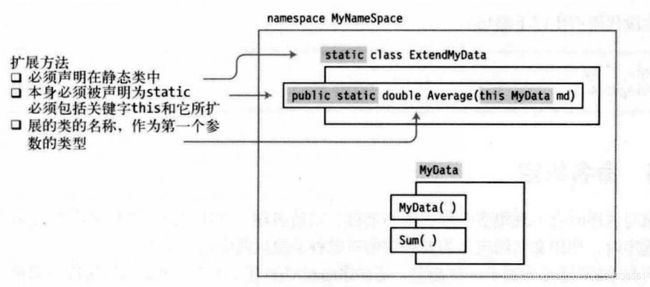
扩展方法的重点要求:
- 声明扩展方法的类必须声明为static。
- 扩展方法本身必须声明为static.
- 扩展方法必须包含关键字 this 作为它的第一个参数类型, 并在后面写它所扩展的类的类名。
namespace HelloWorld_Console { sealed class MyData // 密封类 { private double D1, D2, D3; public MyData(double d1, double d2, double d3) { D1 = d1; D2 = d2; D3 = d3; } public double Sum() { return D1 + D2 + D3; } } static class ExtendMyData { public static double Average(this MyData md) // 这里要写关键字this 和你想扩展的类的类名 { return md.Sum() / 3; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MyData md = new MyData(3,4,5); WriteLine(md.Sum()); WriteLine(md.Average()); // Average 方法可以当作 MyData 类的实例成员来调用 WriteLine(ExtendMyData.Average(md)); // 静态调用形式,等价调用 ReadKey(); } } } 输出结果为: 12 4 4
扩展方法和泛型类 (322P)
在上面我们介绍了扩展方法。 我们还可以吧它和泛型类结合使用。 它允许我们将类中的static 方法 关联到不同的 generic 类上。并调用该方法,就好像它是该类的构造实例上的实例方法一样。
和非泛型类一样, 泛型类的扩展方法:
- 声明扩展方法的类必须声明为static。
- 扩展方法本身必须声明为static.
- 扩展方法必须包含关键字this作为它的第一个参数类型, 并在后面写它所扩展的类的类名。
下面写一个代码示例演示了 一个 静态类 中写了两个扩展方法,然后关联到了不同的泛型类上:
namespace HelloWorld_Console { class Holder// 第一个 泛型类 { T[] Vals = new T[3]; public Holder(T v0, T v1, T v2) { Vals[0] = v0; Vals[1] = v1; Vals[2] = v2; } public T[] GetValuesHolder() { return Vals; } } class Holder2 // 第二个 泛型类 { T[] Vals = new T[4]; public Holder2(T v0, T v1, T v2,T v3) { Vals[0] = v0; Vals[1] = v1; Vals[2] = v2; Vals[3] = v3; } public T[] GetValuesHolder2() { return Vals; } } static class ExtendHolder // 扩展方法 { public static void PrintHolder (this Holder h) //这是第一个泛型类的扩展方法 { T[] vals = h.GetValuesHolder(); Console.WriteLine("{0},\t{1},\t{2}", vals[0], vals[1], vals[2]); } public static void PrintHolder2 (this Holder2 h) //这是第二个泛型类的扩展方法 { T[] vals = h.GetValuesHolder2(); Console.WriteLine("{0},\t{1},\t{2},\t{3}", vals[0], vals[1], vals[2], vals[3]); } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 创建第一个泛型类的实例 var intHolder = new Holder (3, 5, 7); var stringHolder = new Holder ("a1", "b2", "c3"); intHolder.PrintHolder(); stringHolder.PrintHolder(); WriteLine(); var intHolder2 = new Holder2 (500, 200, 300,600); var stringHolder2 = new Holder2 ("a1", "b2", "c3","d4"); intHolder2.PrintHolder2(); stringHolder2.PrintHolder2(); ReadKey(); } } } 输出结果为: 3, 5, 7 a1, b2, c3 500, 200, 300, 600 a1, b2, c3, d4
泛型结构体 (323P)
与泛型类相似, 泛型结构可以有类型参数和约束。泛型结构的规则和条件与泛型类是一样的。
namespace HelloWorld_Console { struct PieceOfData// Generic struct { private T _data; public PieceOfData(T value) { _data = value; } public T Data { get { return _data; } set { _data = value; } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var intData = new PieceOfData (10); var stringData = new PieceOfData ("Hi there."); Console.WriteLine("intData = {0}", intData.Data); Console.WriteLine("stringData = {0}", stringData.Data); ReadKey(); } } } 输出结果为: intData = 10 stringData = Hi there.
泛型委托 (323P)
泛型 委托 非常类似于 非泛型委托,只是类型参数决定了能接受什么样的方法。
创建泛型委托的语法为:
类型参数的范围包括:
- 返回值;
- 形参列表;
- 约束子句。
namespace HelloWorld_Console { delegate void MyDelegate(T value); // Generic delegate class Simple { static public void PrintString(string s) // Method matches delegate { Console.WriteLine(s); } static public void PrintUpperString(string s) // Method matches delegate { Console.WriteLine("{0}", s.ToUpper()); // 把string 变为大写字母 } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var myDel = new MyDelegate (Simple.PrintString); // Create inst of delegate. myDel += Simple.PrintUpperString; // Add a method. myDel("Hi There."); // Call delegate. ReadKey(); } } } 输出结果为: Hi There. HI THERE.
泛型接口 ( 325P )
泛型接口指的是其中接口成员的形式参数和返回类型是泛型类型参数。泛型接口声明类似于非泛型接口声明,但在接口名称后面有尖括号中的类型参数列表。
namespace HelloWorld_Console { interface IMyIfc// Generic interface { T ReturnIt(T inValue); } class Simple : IMyIfc// Generic class { public S ReturnIt(S inValue) // Implement generic interface. { return inValue; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var trivInt = new Simple(); var trivString = new Simple (); Console.WriteLine("{0}", trivInt.ReturnIt(5)); Console.WriteLine("{0}", trivString.ReturnIt("Hi there.")); ReadKey(); } } } 输出结果为: 5 Hi there.
在普通类中实现泛型接口 (326P)
如下示例演示了泛型接口的两个额外的能力:
- 像其他泛型一样,用不同类型实参实例化的泛型接口,它们是不同的接口。
- 我们可以在非泛型类型中实现泛型接口。
namespace HelloWorld_Console { interface IMyIfc// Generic interface { T ReturnIt(T inValue); } // 源于同一泛型接口的两个不同接口 class Simple : IMyIfc , IMyIfc // Nongeneric class { public int ReturnIt(int inValue) // Implement interface using int. { return inValue; } public string ReturnIt(string inValue) // Implement interface using string. { return inValue; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Simple trivial = new Simple(); Console.WriteLine("{0}", trivial.ReturnIt(5)); Console.WriteLine("{0}", trivial.ReturnIt("Hi there.")); ReadKey(); } } } 输出结果为: 5 Hi there.
泛型接口的实现必须唯一 (327P)
实现泛型类型接口时, 必须保证类型实参组合不会在类型中产生两个重复的接口。
在下面的代码中, Simple类使用了两个IMyIfc接口的实例化。
- 第一个是构造类型,使用类型int进行实例化。
- 第二个有一个类型参数但不是实参。
对于泛型接口, 使用两个相同接口本身并没有错, 问题在于这么做会产生一个潜在的冲突, 因为如果把int作为类型参数来替代第二个接口中的S的话, Simple可能会有两个相同类型的接口, 这是不允许的。
interface IMyIfc
{
T ReturnIt(T inValue);
}
// 这里有两个接口
class Simple : IMyIfc, IMyIfc // Error!
{
public int ReturnIt(int inValue) // Implement first interface.
{
return inValue;
}
public S ReturnIt(S inValue) // Implement second interface,
{ //如果它不是int 类型的, 将和第一个接口一样
return inValue;
}
}
注意: 泛型接口的名字不会和非泛型冲突。例如, 在前面的代码中我们还可以声明一个名称为 IMyIfc 的非泛型接口。