EF框架
只是为了归纳整理而已。
EF
什么事EF。全称EntityFramework,官方解释是ADO.NET(专门用于访问数据库的组件)中的一套支持面向数据的软件应用程序的技术,是微软的一个ORM框架。
那么什么是ORM呢。
全称Object Relational Mapping ,对象关系映射。
怎么说呢,为了与数据库进行更加简单深切的交流,我们引入这个框架。我们用实体类来对数据库进行操作。
我们操作的实体对应于数据库的关系表。实体中的属性对应于数据表中的字段。
比如我设一个类 db 它对应的就是我的一个数据库。
db.Students 就是数据库中Students的一个表。如果要查询,
var students = (from s in Students
where s.Name == “wax”
select s).ToList();
这就相当于查询了。
db.SaveChanges();
这个就是存储了,当把db当作一个数据库,我们改了它的表,现在保存一下。
LINQ
说起EF,就避不开LINQ。这里有几个词语,跟SQL语言差不多,但又不是,叫LINQ,语言集成查询,全称Language Integrated Query。它是一种查询技术,分别用三个组件来封装,分别是LINQ to ADO.NET 、ADO.NET、LINQ to XML 。他们与.NET语言的关系如下:
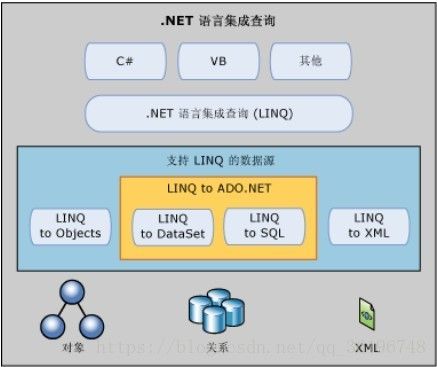 //转自网上
//转自网上
可以把它作为一种编程语言,具有“标准查询运算符”,如where、select、groupby、join.
代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LinkConsole
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//最基本的简单查询
//List numbers = new List() { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
//var numQuery = from num in numbers
// where num % 2 == 0
// select num;
//foreach (var num in numQuery)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("{0,1}", num);
//}
//读取List<>中的句子
// FormExpDemo2();
//-------------复合form子句----------------//
//FormExpDemo();
//-------------多个from句子---------------//
//FormExpDemo3();
//-------------where-------------------//
// WhereExpDemo();
//-------------select------------------//
//SelectDemo();
//-------------group--------------------//
//GroupDemo();
//-------------into------------------------//
//IntoDemo();
//--------------OrderBy--------------------//
//ThenByDemo();
//--------------let----------------------//
//LetDemo();
//--------------join--------------------//
JoinDemo();
Console.ReadLine();
}
public class CustomerInfo
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Tel { get; set; }
public List telTable { get; set; }
}
public static void FormExpDemo2()
{
//
List customers = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "欧阳晓晓",Age = 35,Tel = "123"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "上官飘飘",Age = 17,Tel = "456"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "诸葛菲菲",Age = 23,Tel = "789"}
};
var query = from ci in customers
where ci.Age > 20
select ci;
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}年龄:{1}电话:{2}", ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Tel);
}
}
//复合from子句 // 相当于两个for循环而已
private static void FormExpDemo()
{
List customers = new List
{
new CustomerInfo { Name = "欧阳小小",Age= 35,telTable = new List {"123","234"} },
new CustomerInfo { Name = "上官飘飘",Age= 35,telTable = new List {"456","567"} },
new CustomerInfo { Name = "诸葛菲菲",Age= 35,telTable = new List {"789","456"} },
};
//查询包含电话号码456的客户
var query = from ci in customers
from tel in ci.telTable
where tel.IndexOf("456") > -1
select ci;
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}年龄:{1}", ci.Name, ci.Age);
foreach (var tel in ci.telTable)
{
Console.WriteLine(" 电话:{0}", tel);
}
}
}
//多个from子句,和复合子句看起来是一样的,其实不一样,一个是单个数据源中的子元素的集合,一个是对多个数据源进行查询
private static void FormExpDemo3()
{
List customers = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "欧阳晓晓",Age = 35,Tel = "123"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "上官飘飘",Age = 77,Tel = "456"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "诸葛菲菲",Age = 23,Tel = "789"}
};
List customers2 = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "令狐冲",Age = 25,Tel = "123"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "东方不败",Age = 15,Tel = "456"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name = "任盈盈",Age = 13,Tel = "789"}
};
//在customers 中寻找年龄大于20的客户
//在customenrs中寻找年龄小于30岁的客户
var query = from custo in customers
where custo.Age > 20
from custo2 in customers2
where custo2.Age < 30
select new { custo, custo2 };
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", ci.custo.Name, ci.custo2.Name);//这样得到的是一个交叉联结表,有点类似于SQL中的笛卡尔沉积
}
}
//where子句查询
//where就是用来筛选元素的,除了开始和结束位置,where可以在任意位置使用,
//一个LIKQ语句中可以有where子句,也可以没有,可以有一个,也可以有多个。
//多个where子句之间的关系相当于逻辑“与”,每个子句中又可以包含多个用“谓词”链接的逻辑表达式,&&,或者||
private static void WhereExpDemo()
{
List clist = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name="欧阳晓晓", Age=35, Tel ="1330708****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="上官飘飘", Age=17, Tel ="1592842****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="令狐冲", Age=23, Tel ="1380524****"}
};
//可以查询符合多个条件的人(名字是三个字或者姓令的,但年龄必须大于20)
var query = from custo in clist
where (custo.Name.Length == 3 || custo.Name.Substring(0, 1) == "令") && custo.Age > 20
select custo;//select 也可以改成,比如custo.Name。或者用一个函数,把变量传出去
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}年龄:{1}电话:{2}", ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Tel);
}
//where中使用自定义函数,查询三个字并且姓令的客户
var query2 = from custo in clist
where (custo.Name.Length == 3 && ChechName(custo.Name))
select custo;
foreach (var ci in query2)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}年龄:{1}电话:{2}", ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Tel);
}
}
private static bool ChechName(string name)
{
if (name.Substring(0, 1) == "令")
return true;
else
return false;
}
//select 用法举例
private static void SelectDemo()
{
List clist = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name="欧阳晓晓", Age=35, Tel ="1330708****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="上官飘飘", Age=17, Tel ="1592842****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="令狐冲", Age=23, Tel ="1380524****"}
};
string[] names = { "令狐冲", "任盈盈", "杨过", "小龙女", "欧阳小夏", "欧阳晓晓" };
//查询在给定谓词数组里存在的客户
var query = from custo in clist
where custo.Age < 30
select new MyCustomerInfo { Name = custo.Name, Tel = custo.Tel };
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}电话:{1}类型{2}", ci.Name, ci.Tel, ci.GetType().FullName);
}
}
public class MyCustomerInfo
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Tel { get; set; }
}
//-------------------Group----------------------//
static List clist = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name="欧阳晓晓", Age=35, Tel ="1330708"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="上官飘飘", Age=17, Tel ="1592842"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="欧阳锦鹏", Age=35, Tel ="1330708"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="上官无忌", Age=23, Tel ="1380524"}
};
private static void GroupDemo()
{
//按照名字的前两个字进行分组
var query = from custo in clist
group custo by custo.Name.Substring(0, 2);
foreach (IGrouping group in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("分组键:{0}", group.Key);
foreach (var ci in group)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}电话:{1}", ci.Name, ci.Tel);
}
Console.WriteLine("*********************");
}
//可以知道group子句返回的是一个IGrouping泛型接口的对象集合
//TKey是键的对象类型,在用于group子句的时候,编译器会识别数据类型,用于存储分组的键值,也就是根据什么分的组
//TElement是指的对象类型用于分配储存结果,变量基于这个接口的类型就是遍历这个值,也就是分组的对象
}
//----------------into子句---------------//
private static void IntoDemo()
{
//into提供了一个临时标识符,它储存了into子句前面的查询内容,使他后面的子句可以方便使用,再次查询投影
var query = from custo in clist
group custo by custo.Name.Substring(0, 2) into gpcustomer
orderby gpcustomer.Key descending //排序,
select gpcustomer;
Console.WriteLine("into用于group子句");
foreach (var group in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("分组见:{0}", group.Key);
foreach (var ci in group)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}电话:{1}", ci.Name, ci.Tel);
}
Console.WriteLine("***********************");
}
var query2 = from custo in clist
select new { NewName = custo.Name, NewAge = custo.Age } into newCustomer
orderby newCustomer.NewAge
select newCustomer;
Console.WriteLine("into用于select子句");
foreach (var ci in query2)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}年龄:{1}", ci.NewName, ci.NewAge);
}
}
//---------------排序子句--------------------//
//LINQ可以按元素的一个或者多个属性对元素进行排序,表达式的排序方式分为OrderBy、OrderByDescending、ThenBy、ThenByDescending
//加了Descending的就是降序,没有加的就是升序
private static void ThenByDemo()
{
List clist = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name="欧阳晓晓 ", Age=35, Tel ="1330708****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="上官飘飘 ", Age=17, Tel ="1592842****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="郭靖 ", Age=17, Tel ="1330708****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="黄蓉 ", Age=17, Tel ="1300524****"}
};
//按照年龄升序,再按照名字的字数次要排序
var query = from customer in clist
orderby customer.Age, customer.Name.Length
select customer;
Console.WriteLine("按年龄排列,按名字字数进行次要排序");
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0} 年龄:{1} 电话:{2}",ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Tel);
}
//按年龄降序,再按名字的字数降序次要排列
var query2 = from customer in clist
orderby customer.Age descending , customer.Name.Length descending
select customer;
Console.WriteLine("\n按年龄排列,按名字字数进行降序次要排列");
foreach (var ci in query2)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0} 年龄:{1} 电话:{2}", ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Tel);
}
}
//--------------let子句---------------------//
private static void LetDemo()
{
var query = from custo in clist
let g = custo.Name.Substring(0, 1)//let建立一个范围变量,在where中使用
where g == "欧" || g == "上"//也可以不写,写成customer.Name.Substring(0, 1) == "郭" || customer.Name.Substring(0, 1) == "黄"
select custo;
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0} 年龄:{1} 电话:{2}", ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Tel);
}
}
//-------------join子句-------------------//
private static void JoinDemo()
{
//如果两个数据源中的属性可以进行相等比较,那么两个句子可以用join进行关联,比较的符号为equal,而不是==
List clist = new List
{
new CustomerInfo{ Name="欧阳晓晓", Age=35, Tel ="1330708****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="上官飘飘", Age=17, Tel ="1592842****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="郭靖", Age=17, Tel ="1330708****"},
new CustomerInfo{ Name="黄蓉", Age=17, Tel ="1300524****"}
};
List titleList = new List
{
new CustomerTitle{ Name="欧阳晓晓", Title="歌手"},
new CustomerTitle{ Name="郭靖", Title="大侠"},
new CustomerTitle{ Name="郭靖", Title="洪七公徒弟"},
new CustomerTitle{ Name="黄蓉", Title="才女"},
new CustomerTitle{ Name="黄蓉", Title="丐帮帮主"}
};
//根据姓名进行内部联结
var query = from customer in clist
join title in titleList
on customer.Name equals title.Name
select new { Name = customer.Name, Age = customer.Age, Title = title.Title };
foreach (var ci in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0} 年龄:{1}{2}", ci.Name, ci.Age, ci.Title);
}
//根据姓名进行分组联结
Console.WriteLine("\n根据姓名进行分组联结");
var query2 = from customer in clist
join title in titleList
on customer.Name equals title.Name into tgroup
select new { Name = customer.Name, Titles = tgroup };
foreach (var g in query2)
{
Console.WriteLine(g.Name);
foreach (var g2 in g.Titles)
{
Console.WriteLine(" {0}", g2.Title);
}
}
//根据姓名进行 左外部联结
Console.WriteLine("\n左外部联结");
var query3 = from customer in clist
join title in titleList
on customer.Name equals title.Name into tgroup
from subTitle in tgroup.DefaultIfEmpty()
select new { Name = customer.Name, Title = (subTitle == null ? "空缺" : subTitle.Title) };
foreach (var ci in query3)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0} ", ci.Name, ci.Title);
}
}
public class CustomerTitle
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
}
}
}
参考